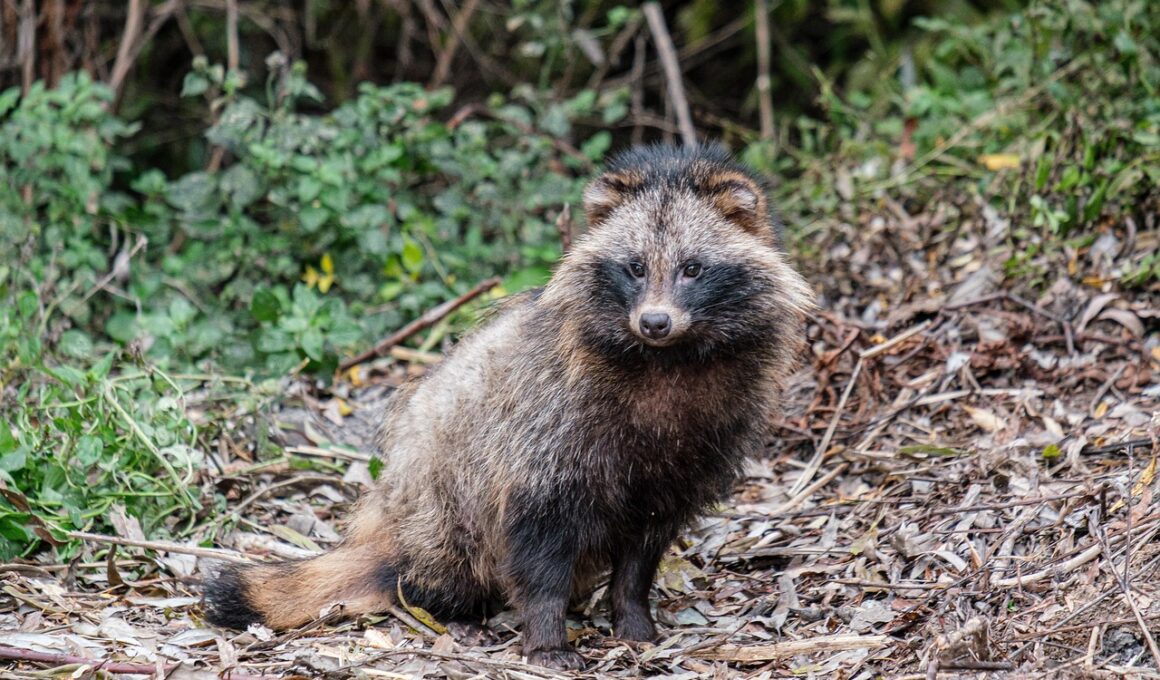
Ecotourism and Its Influence on Carnivore Behavior and Human Safety
Ecotourism has emerged as a significant factor in the relationship between carnivores and humans. As more individuals engage in eco-friendly travel, the need to understand how these activities affect wildlife becomes essential. Carnivores, inherently territorial and often elusive, are influenced by the increased presence of humans in their habitats. In many instances, human interaction can lead to behavioral changes in these animals, which may create unforeseen consequences. For instance, the attraction of tourists may encourage certain carnivore species to venture closer to populated areas, in search of food scraps or easy sustenance. Therefore, it becomes crucial for ecotourism operators to educate visitors about the consequences of their actions and the importance of maintaining a respectful distance from wildlife. This helps mitigate adverse effects, ensuring that both visitors and carnivores can coexist harmoniously. Additionally, managing these interactions can alleviate potential conflicts, enhancing not only human safety but also the long-term survival of carnivore populations. Understanding this dynamic maximizes the positive impacts of ecotourism while preserving the natural behaviors of these majestic animals.
Human Awareness and Safety
As the popularity of ecotourism grows, so does the responsibility of tourists to understand the risks involved when encountering carnivores in their natural surroundings. Many visitors are often unaware of the behaviors exhibited by these animals and how to react appropriately in different situations. For example, some may mistakenly believe that carnivores are harmless or approachable, leading to dangerous encounters. Proper awareness and education about the wildlife behaviors can significantly enhance human safety. Tourists should be informed about the signs of distress in carnivores and the best practices for staying safe in their presence. Implementing guidelines and educational materials can help travelers become more responsible in their interactions, reducing the likelihood of aggressiveness from these animals. Additionally, trained guides can play a crucial role in leading safe excursions, as they can provide necessary information and ensure that the guidelines are respected. Overall, as ecotourism develops, promoting human awareness about interactions with carnivores will be pivotal in minimizing risks and ensuring memorable, safe experiences that respect wildlife.
The human-carnivore interaction doesn’t merely hinge on direct encounters; it also extends to the environmental impact of increased tourism. The influx of visitors to ecotourism sites often leads to habitat degradation, which can adversely affect carnivores and their prey. For instance, trampling of vegetation or littering can disrupt ecosystems, reducing the availability of food resources for these considerable predators. Moreover, roads created for easy access to viewing venues facilitate human encroachment into carnivore territories, ultimately leading to habitat fragmentation. Such disturbances can have cascading effects on carnivore behavior, reducing their hunting success and potentially increasing human-wildlife conflicts. Protecting natural habitats is vital not only for the health of carnivore populations but also for preserving the overall environment visitors come to enjoy. Strategies like establishing well-defined trails and educating tourists about minimizing their footprint can help mitigate adverse impacts. It is essential for ecotourism enterprises to implement sustainable practices, ensuring the safety of both carnivores and humans while fostering a path towards conservation and responsible wildlife tourism.
The Role of Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts in ecotourism play an instrumental role in shaping the dynamics between carnivores and humans. Committed organizations often partner with local communities, boosting sustainable practices that protect both wildlife and visitors. Engaging local stakeholders provides insights into traditional knowledge and ecological perspectives, creating a comprehensive conservation strategy. Such initiatives can promote coexistence through the implementation of wildlife corridors that allow carnivores to traverse their territories without conflict. Besides creating a safe space for carnivore movements, these efforts also enhance wildlife viewing experiences for tourists. Moreover, many of these programs include anti-poaching initiatives that can further protect vulnerable carnivore populations from immediate threats. As successful conservation models emerge, they can inspire similar efforts in other regions, raising awareness about the importance of wildlife preservation. For example, educational programs for tourists can highlight successful conservation stories, cultivating an appreciation for both the ecosystem and responsible ecotourism practices. By prioritizing conservation alongside ecotourism, there can be a healthier balance that fosters both human safety and the sustainability of carnivore populations.
Moreover, the ethical considerations surrounding ecotourism necessitate careful evaluation of its impact on carnivore behavior and safety. As the demand for wildlife encounters escalates, differentiating between responsible tourism and exploitative practices becomes increasingly essential. Activities such as baiting carnivores to entice tourists for better wildlife sighting can lead to detrimental behavioral changes among these animals. In such cases, the wildlife may associate humans with food, thus increasing the likelihood of aggressive interactions. Promoting ethical guidelines can assist tour operators in ensuring that wildlife remains undisturbed and free to exhibit natural behaviors. The development of certification programs for eco-friendly operators can incentivize best practices while discouraging potentially harmful activities. Additionally, transparency with tourists about the implications of their choices can empower consumers to make informed decisions. By prioritizing ethical considerations in ecotourism, all stakeholders can contribute positively towards fostering a healthy environment for both carnivores and humans. Ultimately, understanding the intersection between sustainability, ethics, and wildlife experiences will ensure a responsible approach to ecotourism.
Community Involvement and Education
An integral part of successful ecotourism lies in involving local communities in the decision-making process regarding carnivore interactions. When community members contribute to policies and practices surrounding wildlife tourism, they feel a heightened sense of ownership and responsibility. This involvement ensures that local values and knowledge are respected, leading to a more harmonious relationship with the surrounding wildlife. Education programs aimed at local residents can equip them with wildlife management skills, enabling them to safeguard both their communities and the carnivores that inhabit their area. Promoting community-led initiatives fosters a cooperative dynamic; local people become advocates for conservation while sharing their experiences with visitors. Furthermore, community outreach can extend to educating tourists about local ecosystems and the necessity of protecting carnivores, enhancing their understanding and appreciation for wildlife. As interactions thrive in a respectful and informed environment, attitudes towards carnivores are likely to shift positively. Ultimately, community involvement enhances the sustainability of ecotourism, forging pathways for mutual respect and cooperation between humans and carnivores.
Finally, successful integration of ecotourism into the carnivore-human interface relies on continuous monitoring and evaluation of conservation efforts. This ongoing assessment is critical to adapting strategies that ensure both environmental protections and the safety of tourists. Data collection and analysis can provide insights into emerging trends in carnivore behavior, human interactions, and environmental impact. By employing technologies such as GPS tracking and remote camera monitoring, ecotourism operators can gain a better understanding of carnivores’ movements and potential hotspot areas for human contact. Moreover, feedback mechanisms for tourists can help gauge their perceptions and experiences, informing future improvements in operational practices. Ensuring that sufficient resources are allocated for research and monitoring will help to maintain a proactive approach. In conclusion, the intersection of ecotourism with carnivore interactions necessitates a holistic approach grounded in education, community involvement, and continuous adaptation. This framework not only preserves the safety of human visitors but also fosters a healthier dynamic between carnivores and their ecosystems. Through effective management, ecotourism can emerge as a valuable tool for both conservation and sustainable travel.
Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Practices
To conclude, the relationship between carnivores and humans through ecotourism is intricate and multifaceted. By recognizing the potential influences of tourism on wildlife behavior and human safety, stakeholders can pave the way for more sustainable practices. This requires a commitment to education, ethical tourism, and a deeper understanding of ecological dynamics. In essence, preserving the integrity of carnivore populations while providing meaningful wildlife experiences for visitors is not only possible but essential. Future strategies must focus on community engagement, ethical practices, and continuous research to ensure harmony between environment and tourism. Ultimately, as the global ecotourism industry continues to evolve, these efforts will hold the key to fostering coexistence and ensuring the protection of both endangered species and human safety.