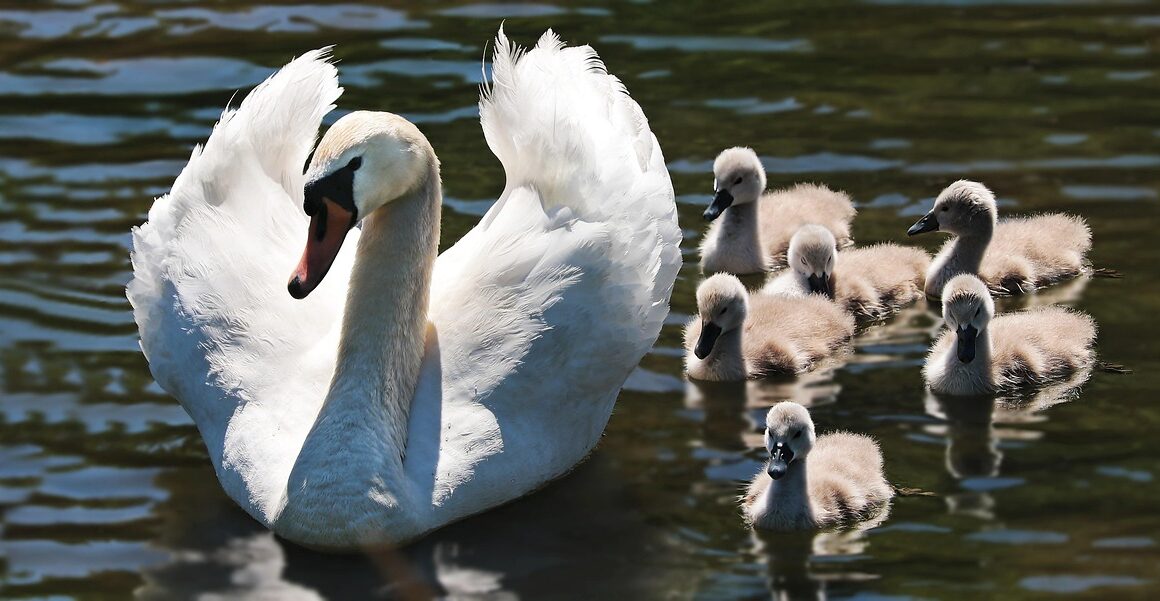
How Feed Quality Affects Waterfowl Reproduction
The quality of waterfowl feed plays a crucial role in their reproduction rates and overall health. Proper nutrition directly impacts the reproductive success, influencing everything from egg production to chick survival. Waterfowl require a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Factors such as feed composition and availability must be considered to enhance breeding outcomes. Energetically dense feed is vital to meet the metabolic demands during the breeding season. Lower-quality feed can lead to nutritional deficiencies, resulting in poor egg quality and decreased hatchability. In addition to nutritional composition, the timing of feed availability also affects the reproductive cycle. Access to high-quality feed during critical times, such as pre-laying and laying phases, can ensure that females have the necessary resources for healthy egg production. Furthermore, nourishing feed not only benefits females but also impacts male waterfowl by enhancing their physical condition, which is essential for successful mating. As such, understanding the correlation between feed quality and reproductive success is vital for any waterfowl management strategy.
One significant aspect of feed quality is the protein source used in formulations. Waterfowl diets that are higher in protein contribute to improved reproductive performance. Protein is essential for growth, tissue repair, and the production of eggs. Therefore, formulating diets that include high-quality protein sources such as soybean meal, fish meal, or certain insects can positively influence reproductive success. Additionally, the incorporation of carbohydrates helps provide the energy required during the breeding season. The type and amount of carbohydrates should be carefully considered, ensuring they do not overshadow the necessary nutrient balance. An optimal mix of these nutrients should cater to the specific needs of various waterfowl species, including ducks and geese. Notably, the nutritional requirements may differ between wild and domesticated waterfowl. Research in nutritional science continues to evolve, leading to more efficient feeding strategies. Moreover, ensuring that feed is free from contaminants is vital, as toxins can have detrimental effects on reproduction. Regular assessments and quality control measures should be implemented for all provided feed sources.
Impact of Feeding Practices
Feeding practices are also an essential consideration when examining waterfowl reproduction. The method in which feed is presented can significantly influence feeding behavior and overall consumption rates. For instance, using scattered feeding can encourage natural foraging behavior, which has been shown to contribute to better health outcomes. Alternatively, providing concentrated feed in certain locations might ensure that all individuals receive adequate nutrition. Moreover, the frequency of feeding is paramount. Regular feeding schedules can help maintain a consistent nutrient intake, thus supporting healthy reproduction. Monitoring and adjusting feeding practices based on the waterfowl’s responsiveness can optimize results. In addition, environmental factors, such as habitat type and seasonal changes, dictate the most effective feeding strategies. Managing habitat to provide natural food sources in tandem with supplemented feed can create a balanced ecosystem. By maintaining a diverse feeding environment, it is possible to not only support waterfowl reproduction but also enhance population stability. This multifaceted approach to feeding aligns with sustainable waterfowl management practices.
A key factor influencing reproduction is the presence of appropriate micronutrients. Micronutrients, particularly vitamins and minerals, are essential for optimal reproductive performance, egg quality, and chick health. For example, vitamins A, E, and D, along with calcium and phosphorus, are particularly crucial during the laying phase. While macronutrients provide energy and structural components, micronutrients support physiological functions necessary for reproduction. Ensuring waterfowl have access to these nutrients through quality feed formulations can lead to enhanced reproductive outcomes. It is equally important to note that nutrient deficiencies can manifest in various ways in reproductive health. Symptoms may include reduced egg production, poor egg quality, and weakened immune responses, impacting both adults and chicks. Therefore, regular nutritional assessments are vital to determine if feed is meeting the reproductive needs of waterfowl populations. This practice involves analyzing feed samples for nutrient content to ensure they match the established dietary guidelines for waterfowl. Through optimizing micronutrient levels in feed, we can significantly improve reproductive success rates in waterfowl.
Environmental Effects on Nutrition
The environment plays a critical role in determining the availability and quality of natural waterfowl feed, which subsequently impacts their reproductive success. Factors such as habitat degradation, climate change, and pollution can greatly influence the abundance of natural food resources. In many cases, reduced access to high-quality foraging areas leads to reliance on supplement feeds that may not fully meet the nutritional needs of waterfowl. Furthermore, pollution can result in the contamination of natural foraging sites, posing health risks. It is essential to protect and restore natural habitats to provide a sustainable food source for breeding waterfowl. Sustainable agricultural practices can also mitigate environmental impacts, promoting healthier ecosystems. By investing in habitat conservation and restoration efforts, we can enhance food availability and quality, supporting waterfowl reproduction. Conservation initiatives focusing on wetland protection can help maintain critical feeding areas. Collaborating with local wildlife agencies and communities can foster a sense of stewardship over these environments, contributing to the long-term success of waterfowl populations.
In conclusion, waterfowl feed quality is a complicated interplay of nutritional elements, environmental factors, and management practices that directly affect reproduction. For waterfowl to thrive during the breeding season, they must receive comprehensive, balanced diets that fulfill their nutritional requirements. Consequently, wildlife managers must prioritize feed formulations that incorporate high-protein sources and essential micronutrients. Simultaneously, attention must be given to the timing, method, and frequency of feeding practices, maximizing reproductive success. Effective waterfowl management will also seek cooperation with conservation efforts aimed at preserving habitats. A focus on sustainability will ensure accessibility to natural feed sources, allowing waterfowl populations to flourish. Effective programs can also help monitor changes in breeding habits and adjust feeding strategies accordingly. By understanding the interplay between feed quality and reproduction, wildlife managers can implement informed strategies that contribute to healthy waterfowl populations. This proactive approach can ensure that waterfowl will continue to thrive in the ecosystems they inhabit, thus supporting biodiversity and the natural function of wetlands.
Future Considerations
Looking ahead, ongoing research into waterfowl feed and nutrition will be vital to enhancing reproductive success. Advances in nutritional science can lead to more effective feed formulations tailored to the needs of different waterfowl species based on their specific dietary requirements. Moreover, further studies will provide insight into the long-term effects of various feeding practices on waterfowl populations. Innovations in feed technology could also improve the bioavailability of nutrients, making them easier for waterfowl to absorb. Integrating genetic research with nutritional strategies may allow for the development of feed that meets both health and reproductive needs. Every factor, including environmental, socioeconomic, and ecological, will need to be taken into account as we continue to evolve the approach to waterfowl nutrition. This holistic perspective will enable conservationists and wildlife managers to make more informed decisions, ensuring that their efforts yield sustainable results. Ultimately, meeting the nutritional needs of waterfowl will remain essential not just for their reproduction but also for the ecosystems they inhabit and the biodiversity they represent.
As we move toward a future focused on sustainable wildlife management, collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and local communities will be critical in implementing effective waterfowl feed strategies. Increasing public awareness of the importance of waterfowl nutrition can lead to support for initiatives aimed at improving habitats and food resources. Engaging local stakeholders in conservation efforts strengthens community ties and fosters a shared responsibility for wildlife. This collaboration may include citizen science projects that monitor waterfowl populations and their health. The data collected can provide valuable insights and inform adaptive management practices. Keeping informed of advancements in agricultural practices and potential environmental threats will also aid in maintaining the health of waterfowl populations. It is crucial for the future that we stay proactive in addressing the challenges waterfowl may face concerning food availability due to the pressures of a changing environment. Protecting the habitats where waterfowl thrive, coupled with continuously optimizing feed quality, will ensure sustained reproduction and the overall resilience of these species in their natural habitats. Together, our concerted efforts can contribute to the successful management and conservation of waterfowl for generations to come.