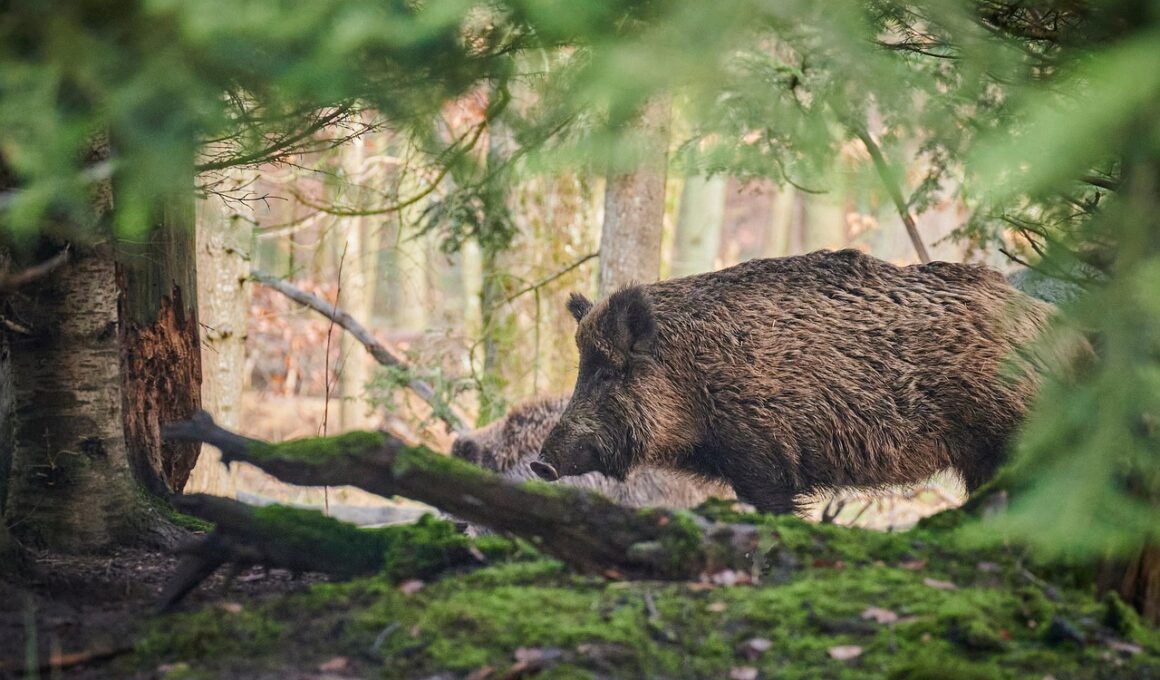
How Wild Boars Influence Soil Composition and Forest Regeneration
Wild boars, known scientifically as Sus scrofa, play a significant role in shaping forest ecosystems. Their foraging habits significantly contribute to the soil composition by aerating it through their rooting activities. When wild boars dig into the ground searching for tubers, roots, and insects, they disturb the soil layers. This disturbance enhances nutrient availability, promoting a richer habitat for various plants and microorganisms. As wild boars uproot plants, they often leave behind gaps in the vegetation, which encourages new growth. This interaction creates more diverse plant communities, essential for a healthy ecosystem. Their consumption of fruits and nuts assists in seed dispersal, allowing different plant species to repopulate successfully. Moreover, this behavior helps maintain biodiversity, crucial for forest resilience. Wild boars also contribute to the soil’s organic matter, significantly improving its fertility over time. Their activities lead to the breakdown of plant material, enriching the soil with essential nutrients. Effective management and monitoring of wild boar populations are vital to ensure their positive effects on forest ecosystems. Understanding their ecological contributions can enhance forest regeneration efforts, promoting sustainable forest management practices.
The Role of Wild Boars in Soil Structure
Soil structure significantly affects ecosystem health, and wild boars contribute to its enhancement. By burrowing into the earth, they break compacted layers, thereby improving water infiltration and reducing erosion. This process is critical, especially in areas prone to drought or heavy rainfall. The displacement of soil particles creates spaces that allow for better air circulation and healthier root development for plants. The humus they leave behind after foraging further enriches the upper soil layers, increasing microbial activity that aids in nutrient cycling. Additionally, the diversity of organic matter resulting from their feeding habits leads to better vegetation cover, which contributes positively to the forest ecosystem’s resilience. Their activities also facilitate the regeneration of native plant species, taking part in the succession process following disturbances. This further ensures a balanced habitat for various fauna. In regions with overpopulation, however, these benefits may be overshadowed by adverse effects, including excessive rooting that can damage young plants. It is essential to find a balance to maintain the positive impacts of wild boars on soil structure while managing their populations effectively.
Wild boars influence forest regeneration through their unique feeding behaviors that encourage a dynamic ecological balance. As these animals move through the forest in search of food, they inadvertently help to create conditions favorable for new plant growth. Their selective feeding often targets specific plant species, which can increase light availability for understory plants by reducing competition. Furthermore, the analysis of their feces reveals diverse seed dispersal patterns, allowing for widespread propagation of various plant species. This process is essential for maintaining genetic diversity within forest ecosystems. By consuming fruits and nuts, wild boars contribute to the cycle of life by enabling plants to spread over larger areas, especially following seasonal changes. Additionally, the nutrients contained in their droppings enrich the soil, providing further support for growing plants. This nutrient cycling is vital for ensuring healthy forest regeneration. In turn, the recovery of vegetation provides habitat and food sources for other wildlife species. Over time, these interactions contribute significantly to the overall health of the ecosystem, underscoring the importance of managing wild boar populations sustainably while recognizing their positive ecological roles.
The Impact of Wild Boars on Biodiversity
Biodiversity within an ecosystem is crucial for resilience, and wild boars play a pivotal role in enhancing it through their ecological behaviors. Their foraging activities can create microhabitats that supports various organisms. By impacting plant composition through selective feeding, wild boars contribute to a diverse array of plant species, which in turn supports a variety of animals, insects, and microorganisms. These interactions encourage trophic dynamics, where different species thrive in the ecosystem’s varied environmental niches. In addition, wild boars serve as a vital food source for predators such as wolves, bears, and large birds of prey. This predatory relationship further emphasizes their importance within the food web. When wild boars are absent or their populations decline, these cascading effects can lead to reduced species diversity and ecosystem quality, highlighting the ongoing need for effective management. Control measures that promote healthy populations of wild boars ensure biodiversity remains intact. Recognizing their role as ecosystem engineers can lead to more sustainable wildlife management policies focused on preserving the intricate balance of biodiversity within forested environments.
Wild boar populations have been known to impact the vegetative community structure significantly through their behaviors. By uprooting grasses and shrubs, they may promote the growth of certain desirable tree species in forests. This selective rooting allows light to reach the ground level, resulting in a better germination rate for seeds of various tree species, which may otherwise struggle in denser undergrowth. This gap creation aids in maintaining the natural processes of forest succession, thereby fostering a diverse and thriving ecosystem. One crucial aspect of this interaction is the importance of maintaining a natural balance within these ecosystems. Where wild boar populations are unmanaged, their foraging behavior can degrade forest habitats instead of enhancing them, causing destruction of young saplings and obstructing natural regeneration processes. Such destructive behavior often results in biodiversity loss and shifts in community dynamics toward less desirable plant species, which threaten the entire ecosystem. This underscores the necessity for careful monitoring and management of wild boar numbers to ensure their impact remains positive, thus enabling the sustained health of forest ecosystems and continued forest regeneration.
Challenges and Management Strategies
Managing wild boar populations presents unique challenges, particularly due to their adaptability and reproductive capacity. As they thrive in varied environments, their population sizes can escalate rapidly, leading to negative impacts on both forestry and agricultural sectors. To mitigate these challenges, various management strategies are implemented, including regulated hunting, habitat modification, and public education initiatives. Effective hunting strategies can help control their populations while providing necessary data on their ecological impacts. Additionally, modifications to habitats to reduce food availability, such as removal of certain plant species, can discourage excessive rooting behaviors. Public awareness campaigns are essential to educate communities about the ecological significance of wild boars and the need for sustainable management. These strategies encourage respect for wildlife while safeguarding local economies and natural resources. Collaboration between wildlife agencies, local communities, and conservation organizations can lead to innovative solutions that balance human activities with wildlife needs. By utilizing integrated approaches towards wild boar management, the forest ecosystems can thrive sustainably, ensuring wild boars continue to contribute positively to soil composition and forest regeneration.
In conclusion, wild boars have a complex and significant influence on soil composition and forest regeneration through their natural behaviors. Their rooting habits enhance soil structure and fertility, facilitating the growth of diverse plant species essential for maintaining ecosystem health. By contributing to nutrient cycling and promoting biodiversity, wild boars play a critical role in the dynamic processes of forest ecosystems. However, effective management is vital to ensure that their populations remain at levels where their benefits can be maximized without adverse effects on forest structure. Understanding the balance between the ecological roles of wild boars and their potential negative impacts is essential for sustainable forestry practices. Engaging in adaptive management strategies that incorporate scientific research, community involvement, and innovative solutions will promote long-term ecological health. Conservation and management efforts can ensure that the crucial contributions of wild boars to soil composition and forest regeneration are recognized and integrated into broader conservation strategies. Through continued research and adaptive practices, we can appreciate and support the complexities of ecosystems where wild boars thrive, benefiting forest health for generations to come.
Final Thoughts on Boar Ecosystem Services
Wild boars are vital contributors to ecosystem services essential for sustaining forest environments. They actively shape the physical features of their habitats through foraging, which impacts the overall health and diversity of vegetation. Their actions foster an environment where various plant species can thrive, encouraging wildlife interactions crucial for maintaining ecological balance. While acknowledging their impacts, it is important to find a sustainable way to coexist with boar populations. Stakeholders, including ecologists, forest managers, and local communities, must collaborate on integrating wild boar management into ongoing conservation efforts. Seeking innovative methods that prioritize ecological integrity while addressing challenges associated with their population growth will be critical. In many cases, promoting natural predators can be an effective method in controlling wild boar numbers sustainably. As we work to balance agricultural interests with ecological health, we can foster a deeper understanding of these magnificent creatures’ roles. Continued research into the ecological impacts of wild boars will help to enhance conservation strategies, ensuring that wild boar populations can thrive while contributing positively to the forest ecosystems where they reside.