Adaptations of Marine Mammals: An Evolutionary Perspective
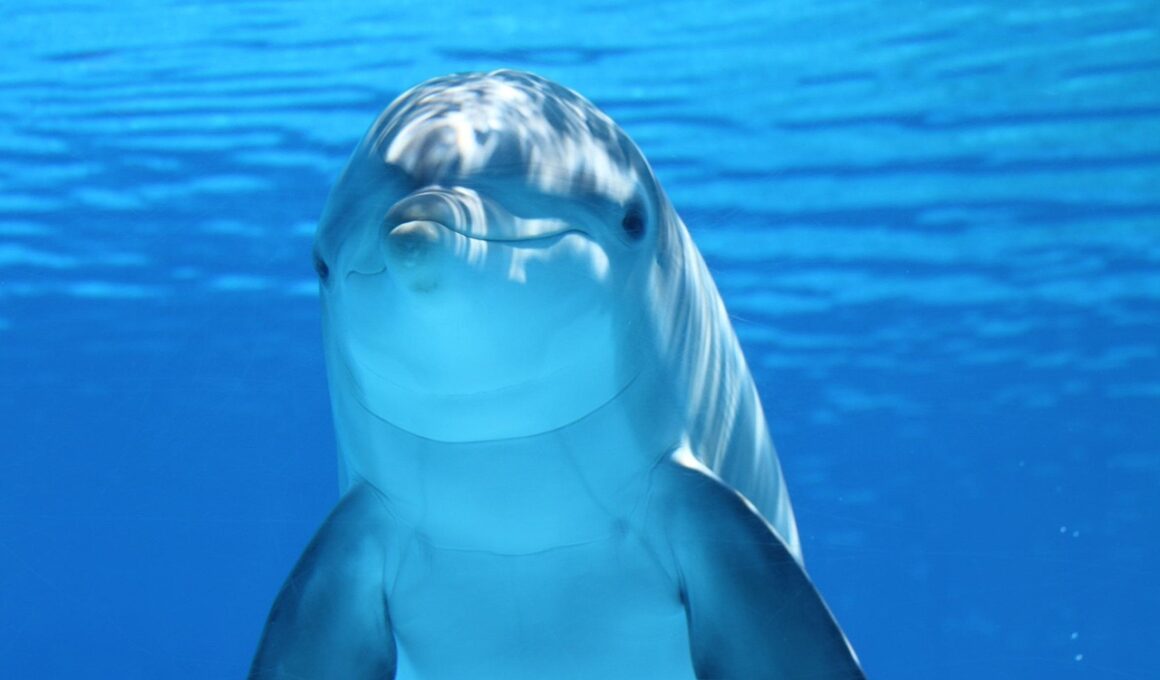
Marine mammals, including dolphins, whales, and seals, exhibit fascinating adaptations that showcase their evolutionary journey. Adaptations are essential for survival in diverse aquatic habitats, highlighting the complex relationship between environment and physiology. One of the most striking adaptations is in the shape of their bodies; streamlined forms reduce resistance while swimming, allowing for efficient travel over long distances. Their limbs have transformed into flippers, which provide stability and maneuverability in water. Additionally, marine mammals have evolved specialized respiratory systems, enabling them to hold their breath for extended periods while diving for food or escaping predators.
Another critical adaptation is the development of blubber, which serves as insulation against cold ocean waters, maintaining body temperature. This fat layer is crucial for species in polar regions, such as seals and whales, where cold exposure is frequent. Moreover, blubber aids buoyancy, making it easier for marine mammals to float and navigate underwater. The ability to communicate through sophisticated vocalizations is another evolutionary trait, enabling social bonding and coordination during hunting or migration. Echolocation, used by some dolphins and whales, allows them to navigate and locate prey in dark or murky water, highlighting their cognitive capabilities.
Feeding Strategies and Diet Adaptations
The dietary habits of marine mammals vary significantly across species, leading to specialized feeding strategies. Baleen whales, for instance, possess baleen plates that filter small organisms like krill from the water, providing an abundance of food with minimal effort. In contrast, toothed whales, such as orcas, rely on sophisticated hunting techniques, preying on larger fish and even other marine mammals. Seals, particularly those that dive deep, often exhibit adaptations in hunting skills, allowing them to pursue fish effectively. These diverse feeding strategies reflect the evolutionary pressures faced by each species in its respective environment.
Reproductive adaptations also play a crucial role in the survival of marine mammals. Many species exhibit extended parental care, ensuring the young receive sufficient nourishment from mothers, which is vital in a challenging aquatic environment. For instance, dolphins are known for their complex social structures, where communal care enhances the survival of the young. Additionally, mating rituals and seasonal migrations form part of their reproductive adaptations, allowing species to optimize breeding conditions. Such strategies enhance genetic diversity as animals seek the best available mates within their social groups.
Impact of Environmental Changes on Marine Mammals
Marine mammals are increasingly impacted by climate change, leading to shifts in their habitats and food sources. Warming ocean temperatures and rising sea levels threaten pink habitats such as polar ice caps, which are critical for seals and polar bears. As prey species migrate in response to environmental shifts, marine mammals must adapt their hunting behaviors and migratory routes. This adaptability is vital for their survival, yet not all species respond successfully to rapid changes, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts in protecting these vulnerable populations.
In addition to climate change, human activities pose significant threats to marine mammal populations. Overfishing depletes fish stocks, impacting the food web and ultimately affecting marine mammals that rely on these resources. Pollution, particularly plastic waste and toxic substances, poses additional risks by contaminating their habitats and food sources. Growth in shipping and maritime traffic has led to increased noise pollution, which can disrupt communication among marine mammals. These factors underline the urgent need for policy changes aimed at protecting marine ecosystems and ensuring the survival of these remarkable species.
The Future of Marine Mammals and Conservation Efforts
Efforts to conserve marine mammals include establishing marine protected areas to safeguard habitats critical for feeding, breeding, and migration. These initiatives not only help preserve biodiversity but also allow researchers to monitor populations and implement effective management strategies. Education and community engagement are essential components of successful conservation efforts, raising awareness about the importance of marine ecosystems. Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and local communities is crucial for creating resilient strategies in the face of ongoing environmental challenges. Such collaborative efforts may significantly influence the future of marine mammals.
Research is pivotal in understanding the evolutionary adaptations of marine mammals and their responses to a changing world. Ongoing studies provide insights into their behaviors and habitats, informing conservation strategies. Technological advancements, such as satellite tracking and underwater drones, facilitate better monitoring and understanding of marine mammals in their natural habitats. Public interest and support for marine conservation can lead to substantial policy changes. As awareness of marine mammal conservation grows, there is hope for ensuring their continuation and flourishing in the ocean’s vast, dynamic ecosystems.