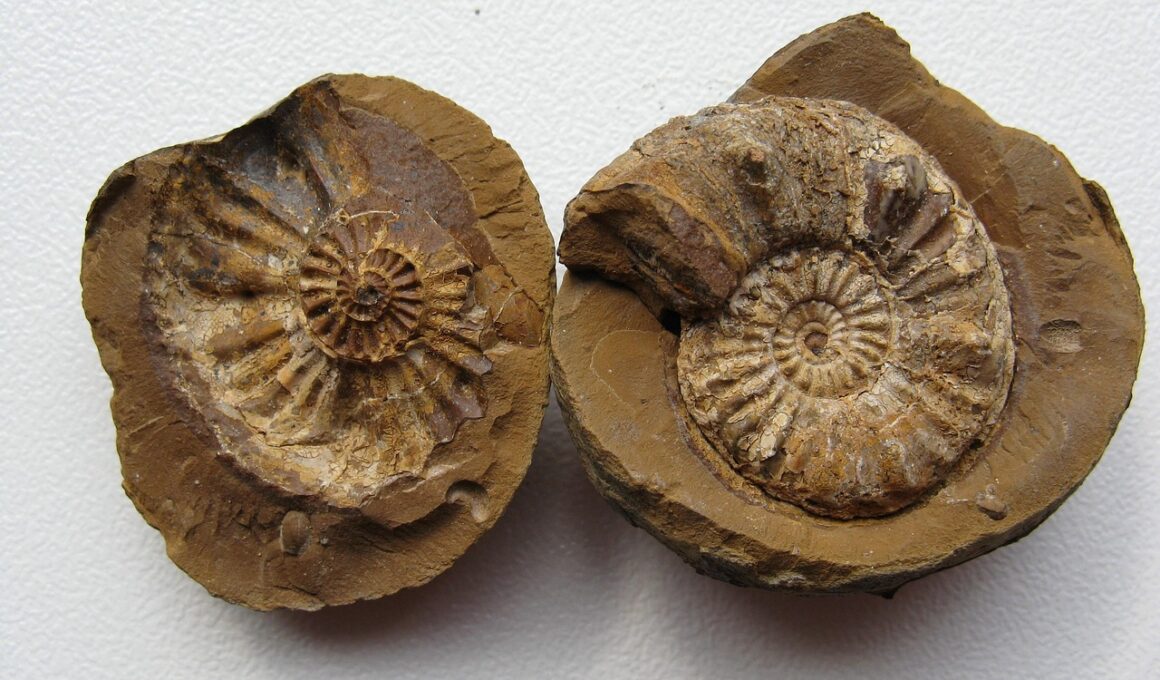
The Importance of Jungle Animal Fossils in Climate Reconstruction
Jungle animal fossils play a crucial role in understanding past climate patterns and ecosystem changes. By studying these fossils, researchers can gain insights into the biodiversity and environmental conditions that existed millions of years ago. Fossils indicate which species thrived in certain climates, helping scientists to map the historical distribution of flora and fauna. The analysis of these remains also reveals adaptations that animals developed over time in response to changing climates. This data is invaluable, as it provides context for current climate shifts and can help predict future ecological responses. Fossils are found embedded in different sedimentary rocks, often recovered from ancient riverbeds, caves, and sediment layers. Each fossil tells a unique story that contributes to the broader understanding of environmental history. Moreover, studying these ancient remains aids in reconstructing the climatic conditions under which species existed. Thus, examining jungle fossils not only sheds light on specific animal habits but also on the overall health of jungles. This insight is vital as we face increasing temperature fluctuations and deforestation globally, threatening the survival of many species.
One fascinating aspect of studying jungle animal fossils is the potential to understand migration patterns. These patterns shed light on how species responded to climatic shifts. For instance, when temperatures dropped, certain animals migrated to more hospitable regions. Fossil records reveal these movements, illustrating links between climate changes and animal distribution over geological time scales. Additionally, the preservation of these fossils allows scientists to analyze various species’ physical characteristics, providing insights into their adaptability. For example, large herbivores from the past showcase adaptations like prolonged necks for feeding on treetops. The findings derived from fossil examinations contribute significantly to reconstructing the ecological tapestry of ancient jungles. In discovering how different species coexisted, scientists can infer interactions between species and their environments. This information aids in understanding current ecological dynamics, as similar interactions can be observed today. Moreover, fossils inform conservation efforts by highlighting species that previously thrived and may offer clues about current vulnerabilities. In this way, understanding ancient ecosystems through fossil study is not just an academic pursuit—it serves practical purposes in biodiversity preservation today.
Fossil Analysis Techniques
Technological advancements have dramatically improved our ability to analyze jungle animal fossils. Paleontologists employ various methods to extract information without damaging specimens, including CT scanning and isotope analysis. CT scanning allows for a three-dimensional visualization of fossils, revealing their intricate details and structures. This technique provides insights into growth patterns and health conditions of ancient species that lived in jungles. Isotope analysis, on the other hand, helps to reconstruct ancient diets and environmental conditions. By measuring the ratios of stable isotopes in fossils, researchers can ascertain the types of vegetation consumed by herbivores and, in turn, infer the climate that supported such vegetation. Additionally, molecular methods like ancient DNA extraction provide further layers of understanding about extinct species. These techniques have revolutionized paleobiology, enabling detailed mapping of species interactions and ecosystem functions that existed long ago. During studies, researchers place jungle fossils within broader geological timelines, allowing a clearer perspective on the pace and form of climate change through time. Collectively, these methodologies empower scientists in their quest to unravel the complexities embedded within ancient ecosystems.
One pressing issue associated with the study of jungle animal fossils is the impact of modern climate change. Today, those same jungles that provide insights into past climates face unprecedented threats. Increased temperatures and deforestation dramatically affect biodiversity and can lead to irreversible losses. Understanding historical climate responses through these fossils is essential for effective conservation strategies in contemporary settings. By learning how animals adapted in response to past climate variations, conservationists can devise effective plans to mitigate current species vulnerabilities. Furthermore, utilizing data from fossil analyses can influence policy decisions regarding habitat preservation. By adopting a forward-thinking approach, incorporating lessons from the past into current practices creates a sustainable framework. This is particularly crucial in tropical regions where ecosystems are delicately balanced. The impacts of climate change on these layers of flora and fauna provide urgent evidence for immediate action. Fossil studies remind us that ecosystems are ever-changing, but the current rate of change is alarming. Thus, it becomes imperative to leverage insights from these ancient remains not only to honor history but to secure the future of existing species within their habitats.
Collaboration Across Disciplines
Collaboration between various scientific disciplines enhances the understanding of jungle animal fossils. Paleontologists work closely with climatologists, ecologists, and geochemists to build a comprehensive view of historical climatic conditions. This multidisciplinary approach yields a synergy that deepens insights into how ancient ecosystems operated. The intersection of these fields allows for a richer narrative of how jungle animals and their environments changed over time. For example, climatologists can analyze fossil data and correlate it with historical climate patterns derived from ice cores and sediment records. Consequently, the integration of paleobiology with climate science creates a multilayered understanding of how global climate fluctuations affected local ecosystems. These connections not only present a more complete picture of past environments but also inform predictions about future ecological responses to ongoing changes. Expanding the dialog among disciplines raises awareness about the complex interplay between climate and ecosystems. This collaboration can lead to innovative solutions for conservation and restoration efforts. In today’s world, such interdisciplinary efforts are essential to addressing environmental challenges efficiently and sustainably.
Moreover, engaging local communities in fossil research is vital for both preserving knowledge and enhancing conservation efforts. Many indigenous populations have traditional ecological knowledge that can complement scientific findings. By involving local communities, paleontologists can gain insights into animal behaviors and understand the significance of certain species within local ecosystems. This collaboration not only helps in research but also empowers communities by recognizing their contributions and beliefs related to their environments. In many cases, these individuals are stewards of the land who possess a profound connection to their surroundings. Their experiences can illuminate the cultural relevance of species and habitats. Education programs developed in partnership with local rights-holding communities can bridge gaps in knowledge. This partnership can facilitate successful conservation initiatives by marrying traditional and scientific methods. When communities are engaged, they often become invested in protecting their ecosystems. Such collaborative efforts cultivate a sense of shared responsibility towards conserving jungles and their unique biodiversity. Therefore, when inclusive approaches to fossil research are adopted, they enhance both scientific knowledge and community empowerment.
Conclusion: Preserving Our Past for the Future
In conclusion, jungle animal fossils are far more than mere relics of the past; they are essential keys to understanding our planet’s climatic history and ecology. The insights gleaned from these fossils are invaluable in reconstructing environmental changes and adaptations over millennia. Connecting our present ecological concerns with ancient data provides a context for urgent action in biodiversity conservation. The methods employed to study these fossils continue evolving, benefiting both science and society at large. By embracing collaboration across different scientific disciplines and integrating community knowledge, it is possible to foster a deeper connection between humanity and the natural world. The importance of these ancient remains will only grow as we continue to confront pressing environmental challenges. Indeed, the lessons of the past hold immense potential for shaping proactive solutions today. Therefore, conserving jungle ecosystems must be prioritized for the health of our planet. By learning from the history of these fossilized remains, we can craft informed strategies for the protection of wildlife and habitats in the future. Emphasizing this connection ensures we safeguard not only the environment but also our shared legacy.