Vocalizations as Expressions of Emotion in Animals
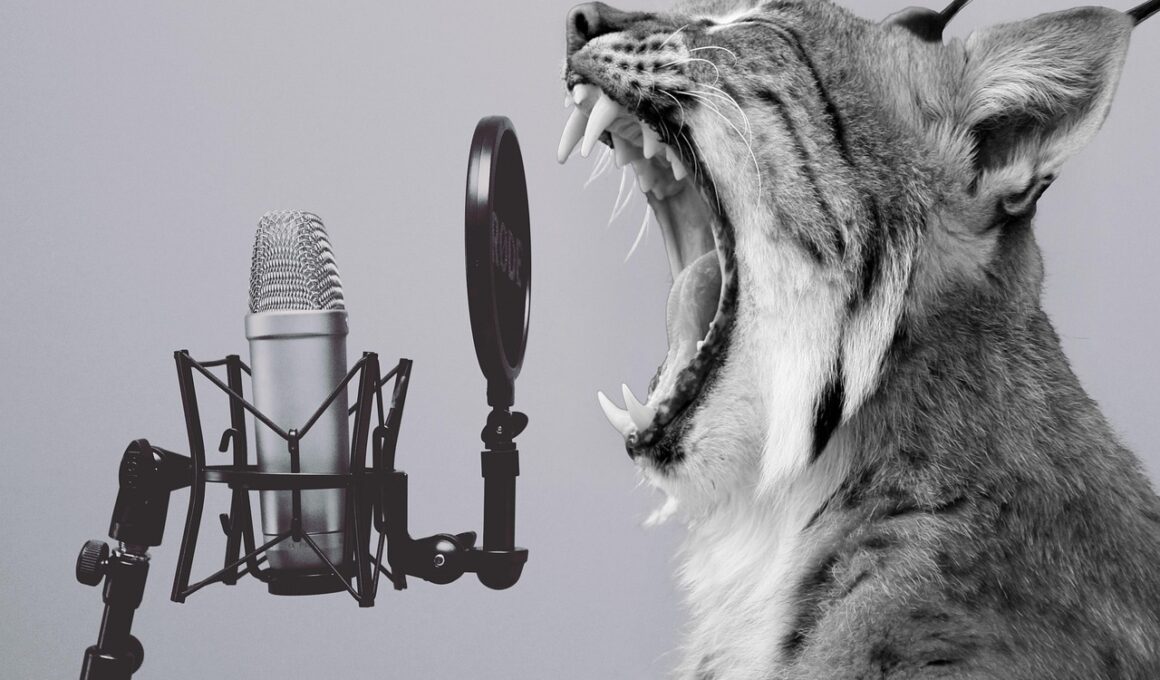
Animals, like humans, communicate their emotions through various vocalizations. These sounds play a critical role in social interactions, serving as non-verbal cues that reflect the emotional states of animals. Research in animal behavior has revealed diverse vocalizations, from the melancholic howls of wolves to the playful chirps of parrots. Each type of vocalization can convey different emotions ranging from fear and aggression to happiness and contentment. For example, the growling of a dog may serve as a warning signal to potential intruders, indicating fear or aggression. In contrast, purring in felines often signifies relaxation and pleasure. These vocalizations help establish social bonds and facilitate communication within species. Furthermore, some vocalizations might even extend beyond species, allowing for interspecies communication. Observing the dynamics of these vocalizations can help deepen our understanding of animal emotions and their responses to external stimuli. Scientists continually strive to decode the meanings behind various sounds, thus enriching our comprehension of animal psychology. This exploration into vocal expressions enhances our appreciation for the emotional complexities present in the animal kingdom, guiding conservation efforts and fostering empathy toward various species in their habitats.
Interpreting animal vocalizations necessitates comprehensive study and observation. Different species exhibit unique vocalization patterns that correspond to their ecological niches and social structures. For instance, birds often employ intricate songs to attract mates or establish territory, while elephants produce low-frequency rumblings that convey information over long distances. Such vocalizations often evolve to suit the specific needs and environments of each species. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for recognizing the emotional undertones in animal sounds, as the context greatly influences interpretation. Recent advancements in technology, including machine learning and sound analysis, have provided new tools to facilitate this research. These tools can analyze large datasets of animal sounds, identifying patterns that may not be discernible to the human ear. By collaborating interdisciplinary methods of ethology, acoustics, and bioinformatics, researchers are uncovering the complex relationships between vocalizations and emotional states. This collaborative approach accelerates the process of decoding these vocal cues, contributing to the broader field of animal cognition and emotion. As our understanding of these vocal expressions deepens, it fundamentally alters our relationship with animals, promoting greater awareness and sensitivity towards their emotional needs and well-being.
Case Studies in Vocalizations
Numerous case studies illustrate the remarkable ways animals utilize vocalizations to express their feelings. For example, the acclaimed research on bottlenose dolphins showcases their ability to use signature whistles to identify themselves and express a range of emotions. Each dolphin has its unique whistle, functioning similarly to a name, fostering social bonds within pods. Similarly, studies on vervet monkeys have revealed their use of different alarm calls that signify specific predators, triggering various behavioral responses in the troop. These alarm calls reflect fear and urgency, demonstrating an emotional response to threats in their environment. Conversely, studies on songbirds have provided insights into mating rituals, where intricate songs not only attract females but also convey the singer’s health and vitality. Such diverse case studies across species reinforce the idea that vocalizations are not merely instinctual but are deeply rooted in the emotional lives of animals. They serve critical functions in navigating intricate social landscapes, establishing hierarchies, and maintaining cohesion within groups. Furthermore, these findings emphasize the value of acoustic communication, shedding light on animal emotions in specific contexts and enhancing empathy towards non-human species in their ecosystems.
The implications of understanding vocalizations extend into areas such as animal welfare and conservation. Insights gained from studying animal emotions through vocal expressions influence how we manage and interact with wildlife in captivity and in the wild. For instance, zoos and aquariums increasingly rely on behavioral enrichment strategies that align with natural vocalization patterns to enhance the well-being of animals. Creating environments that mimic their natural habitats supports their emotional health and encourages natural behaviors. In conservation settings, knowledge of vocalizations helps assess population health and dynamics. Furthermore, community engagement in protecting habitats illuminates the emotional aspects of wildlife that are often overlooked. This understanding cultivates a deeper sense of responsibility towards conservation efforts, drives public support, and ultimately aids in the protection of endangered species. Fostering empathy towards animals based on their emotional needs is essential for successful conservation strategies. When societies recognize that animals have rich emotional lives illuminated by their vocal expressions, it fuels the urgency to safeguard their existence and promote harmonious coexistence with nature. Thus, the study of animal vocalizations resonates beyond academia, impacting practical conservation measures and ethical considerations in human-animal relationships.
Impact of Human Activity
Human activities have significant consequences for animal vocalizations and their emotional expressions. Urbanization, deforestation, and climate change alter habitats and disrupt communication channels among species. Noise pollution, in particular, is a pervasive issue that can obscure vocal signals essential for social interactions and breeding. Animals such as frogs and birds struggle to communicate amidst the cacophony of human-generated sounds. Consequently, this disruption can lead to stress, altered behaviors, and hindered reproductive success. For example, studies on urban songbirds indicate that increased noise levels may cause changes in their song patterns, leading to less effective communication. Religiously conveyed sounds that once thrived in natural settings are drowned out, impacting their ability to establish territories and attract mates. This environmental degradation threatens the emotional lives of many animals, compounding existing stressors affecting their populations. Moreover, human encroachment often leads to habitat loss, further challenging the survival of various species. Recognizing the profound implications of human impact on animal vocalizations emphasizes the need for conscientious conservation practices. It calls for a collective effort to minimize noise pollution and promote habitat preservation, thereby enhancing the emotional and social well-being of wildlife.
The future of research into animal vocalizations appears promising as technology continues to advance, enabling deeper insights into their emotional landscapes. Innovations in bioacoustics allow for more precise recording and analysis of animal sounds, paving the way for a fuller understanding of their communicative intents. Emerging studies focus on how context influences vocalizations, examining the interplay between emotional states and environmental conditions. For instance, understanding how stress affects vocal patterns can inform animal husbandry practices, leading to improved welfare standards. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches increasingly involve collaboration between conservationists and technologists to leverage machine learning algorithms in identifying and cataloging vocalizations across various species. As datasets grow, creating comprehensive databases will enhance our understanding of vocalization patterns globally. This vast pool of knowledge not only improves our recognition of animal emotions but also informs conservation strategies tailored to specific species’ needs. Harnessing these findings enhances our efforts to foster more empathetic relationships with wildlife. By prioritizing the understanding of animal emotions through vocalizations, society can promote better environments for coexistence, highlighting the intrinsic value of animal life and the need for proactive measures to ensure their emotional well-being and survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of vocalizations in animals reveals a complex interplay of emotions that enriches our understanding of their behavior. Each sound generated can represent various feelings, serving as a window into their emotional lives. The studies conducted across many species emphasize the importance of vocalizations, highlighting how these expressions are vital for communication, social bonding, and survival. Whether it is the joyful song of a bird, the soothing purr of a cat, or the communicative growl of a dog, these vocal signals profoundly impact the dynamics within animal communities. Thus, researchers must continue to investigate these vocalizations to foster greater empathy and awareness towards different species. The ongoing work in this field plays an essential role in promoting animal welfare, conservation efforts, and the understanding of species’ emotional needs. As we learn more about these vocal expressions, we become guardians of animal emotions, advocating for respectful interactions with the natural world. Valuing their emotional well-being enhances our lives and ensures a healthy ecosystem for future generations. The challenge lies in applying this knowledge responsibly, shaping a world where both humans and animals coexist harmoniously.
Future studies will likely focus on refining techniques for monitoring and interpreting these vocalizations. Engaging in cross-disciplinary exchanges will fuel innovation, leading to novel insights that benefit both humans and animals. Efforts must also extend to educating the public about the significance of animal emotions, cultivating compassionate attitudes towards wildlife. By integrating knowledge garnered from vocalization studies into education and policy-making, we can inspire conscious efforts in protecting both animal welfare and ecosystems. This knowledge is paramount, as it not only enhances our understanding of the animals around us but also drives meaningful action toward conservation. Collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and communities will be vital in addressing the challenges faced by wildlife. Our collective responsibility extends to preserving the emotional lives of animals while ensuring their habitats remain intact. Each vocalization cast into the atmosphere carries meaning and significance, reminding us of the interconnectedness of life. Embracing this perspective allows humanity to take meaningful strides towards coexistence with the animal kingdom, enriching our lives and ensuring their survival. The more we comprehend animal emotions through their vocalizations, the better equipped we become to act as responsible stewards of the natural world.