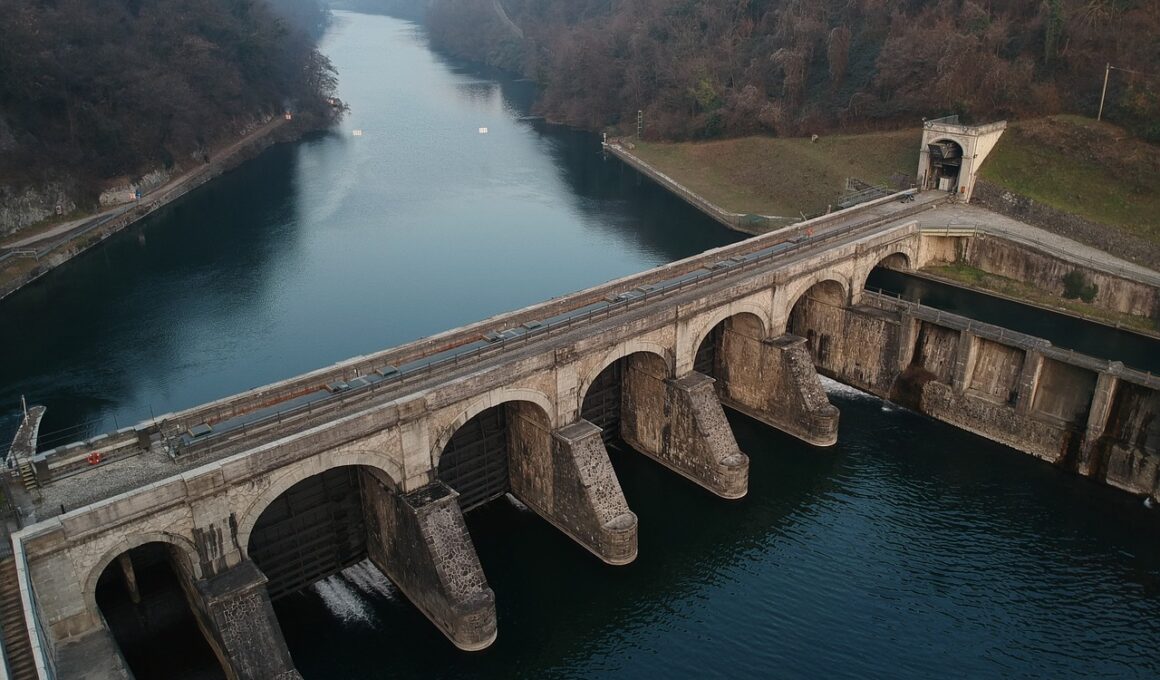
The Effects of Dams on Freshwater Animal Migration
Dams are crucial infrastructures that provide various benefits, including hydroelectric power and water storage. However, their construction significantly impacts freshwater ecosystems. One major concern is how dams obstruct natural migration routes for various aquatic species. Freshwater animals, such as fish, rely on migration to spawn or find food. When a dam is constructed, these migratory paths can be blocked, contributing to population declines. For instance, salmon populations experience significant drop-offs due to barriers. The obstruction also alters habitats, making it challenging for species to survive and adapt. Aquatic organisms may become isolated in different environments, impeding gene flow and leading to inbreeding. Adaptations may be limited as well, with evolutionary changes stunted by decreased genetic diversity. Conservation efforts are necessary to address these problems. Restoration projects focus on creating fish ladders or bypasses to facilitate movement. These constructed features help small fish and other organisms navigate through or around dams. To sustain biodiversity and ecosystems, the effects of dams on freshwater animal migration need special attention from both conservationists and policymakers.
Human intervention in aquatic habitats also raises concerns. The ecological balance maintained naturally can be disrupted by dams, leading to unforeseen consequences. The area adjacent to the dam, known as the reservoir, can experience ecological shifts. Altered water temperatures and fluctuations in water levels can affect the growth and reproduction of species. Furthermore, many dam projects involve clearing land that disrupts existing habitats, putting pressure on native wildlife. Consequently, the introduction of non-native species can further complicate the fight for survival among freshwater animals. These changes create an unstable environment where native species struggle to thrive. Implementing adequate site-specific conservation measures is pivotal to mitigating these effects. Enforcement of stricter regulations, alongside community awareness programs, can help limit damages caused by dam construction and operation. Additionally, investing in habitat restoration can support the recovery of affected species and maintain existing fish populations. Research can further guide the conservation objectives, ensuring that freshwater ecosystems are preserved. The intricate relationships among species highlight the necessity for harmonious coexistence between humans and aquatic wildlife.
Biological Implications of Dams
When dams obstruct waterways, the biological implications are both immediate and long-term. Fish, amphibians, and invertebrates rely on specific migratory patterns for spawning and feeding. Dams interfere with these patterns, severely affecting life cycles. Species like eels, which travel incredible distances to reproduce, face tremendous challenges when barriers emerge. Enhanced pressure on freshwater populations can disrupt food chains, further impacting ecosystems. Additionally, stagnant waters created by dams can promote the growth of harmful algal blooms, leading to toxic conditions. These conditions can be fatal for many aquatic species and pose risks for animals relying on water sources. Such ecological changes can drive some species to extinction, which leads to a loss of biodiversity. The importance of freshwater habitats cannot be understated. They are home to countless species that maintain ecological balance and health. Sustainable management of dam projects must consider the wider effects on biological diversity. Public awareness and sound management practices are crucial for preserving life in freshwater ecosystems. Implementing safeguards against contamination and habitat destruction remains essential for safeguarding affected populations.
Climate change, alongside dam construction, amplifies the challenges freshwater animals face. Increased temperatures can alter the timing of seasonal migrations, leading to mismatches in the timing of food availability and reproductive needs. Altering water flow characteristics due to drought can drastically change habitats and the conditions necessary for native species to thrive. Freshwater habitats are generally delicate environments, and even minor alterations can lead to significant ramifications for local wildlife. Hence, climate considerations should inform the planning and design of new dams. Adaptive management strategies must also be put in place, allowing for a more flexible approach in how dam operations can adjust in response to changing environmental conditions. Engaging communities and stakeholders in conservation dialogues can foster collaborative action plans to manage freshwater habitats better. This approach involves local input to create a comprehensive understanding of which species need the most protection and how best to implement these plans. Conservation organizations are actively working to restore migrations for affected species and develop robust policies to protect priceless aquatic biodiversity, bridging cultural and scientific insights to achieve holistic solutions.
Restoration Efforts and Innovations
Active restoration efforts are paramount in mitigating the adverse effects dams have on freshwater animal migration. Many organizations are creating successful fish ladders and bypass systems designed specifically to enhance migration pathways for various aquatic species. These innovative structures allow fish and other animals to navigate barriers, regain access to traditional spawning grounds, and maintain healthy populations. Engineers and ecologists collaborate to design more effective solutions tailored to the unique challenges presented in specific locations. Using natural materials and mimicking natural streambed structures can encourage successful passage and maintain ecosystem health. Engaging local communities in restoration projects often supports conservation efforts and raises awareness of aquatic issues. Educational programs promote understanding and stewardship of local waterways, resulting in increased public support for conservation initiatives. Monitoring projects carefully ensures ongoing evaluation of fish migration success and ecosystem health, providing valuable data for future projects. Engaging in scientifically informed actions continually helps enhance and protect freshwater ecosystems. By investing time and resources into developing robust restoration practices, the negative effects of dams on wildlife can be reduced significantly.
Incorporating the latest technology into monitoring freshwater ecosystems yields promising results for conservation success. Tracking devices can provide valuable information on the migration patterns of various species. Data collected helps identify migration routes, spawning sites, and potential dangers faced by different populations. Such insights are invaluable for understanding species’ behaviors and adapting conservation efforts effectively. Additionally, using real-time monitoring, environmental scientists can assess the immediate impacts of dam operations on local habitats. These assessments inform management decisions, ensuring that both human interests and ecological needs are balanced. More integrated approaches also involve utilizing artificial intelligence to predict potential outcomes of new dam projects before they begin. This foresight allows for thoughtful design and construction mitigating negative impacts on local biodiversity. Increased public awareness and stakeholder involvement become crucial in supporting these efforts and garnering support for conservation initiatives. Balancing infrastructural needs with ecological integrity remains a major challenge, further emphasizing the need for cooperation between various factions. Therefore, innovative technology and community engagement must align in forging a sustainable path forward for freshwater habitats.
The Future of Freshwater Habitats
Looking ahead, maintaining healthy freshwater habitats requires a collaborative and multidisciplinary approach. Future dam projects must integrate ecological assessments at the planning stage. Such flexibility allows regulators, engineers, and conservationists to work jointly towards less destructive solutions. Developing policies that prioritize the preservation of aquatic habitats while accommodating human needs is essential for long-term sustainability. Conducting comprehensive environmental impact assessments will help decision-makers understand potential consequences before the construction of any dam. Equally vital is continuous research into the impact of existing dams on local ecosystems and wildlife behavior, informing future regulatory updates for improved conservation. Building ecological networks and restoring connectivity between isolated habitats can bolster species resilience, fostering robust populations capable of adapting to ongoing changes. Strengthening partnerships between governmental organizations, non-profits, and local communities can further enhance conservation efforts. Engaging the public through education and restoration initiatives ensures that the significance of freshwater ecosystems resonates within society. Balancing economic needs while fostering ecological preservation may be challenging, but it is necessary for sustaining freshwater animal populations and their habitats.
Ultimately, the impact of dams on freshwater migrations serves as an urgent warning about the balance between human progress and sustainability. The intricate relationships between aquatic organisms are vital to preserving ecological stability. Both immediate and long-term consequences of dam construction should inform our actions, stressing the necessity of approaching environmental issues holistically. The collective efforts toward improving dam infrastructures, restoring migratory paths, incorporating technology, and engaging local communities ensure future generations inherit vibrant freshwater ecosystems. Conserving aquatic biodiversity must remain a worldwide priority. By acknowledging the significance of freshwater habitats and prioritizing sustainable development, the potential for harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife becomes tangible. It is imperative to act decisively and thoughtfully toward preserving these environments. Doing so ensures not only the survival of various freshwater species but also the ecological prosperity that supports human life. As we face continued environmental challenges, innovative and adaptive management practices will be essential. Addressing the needs of freshwater animal populations, alongside human development, will contribute to restoring our planet’s crucial ecosystems for a resilient future.