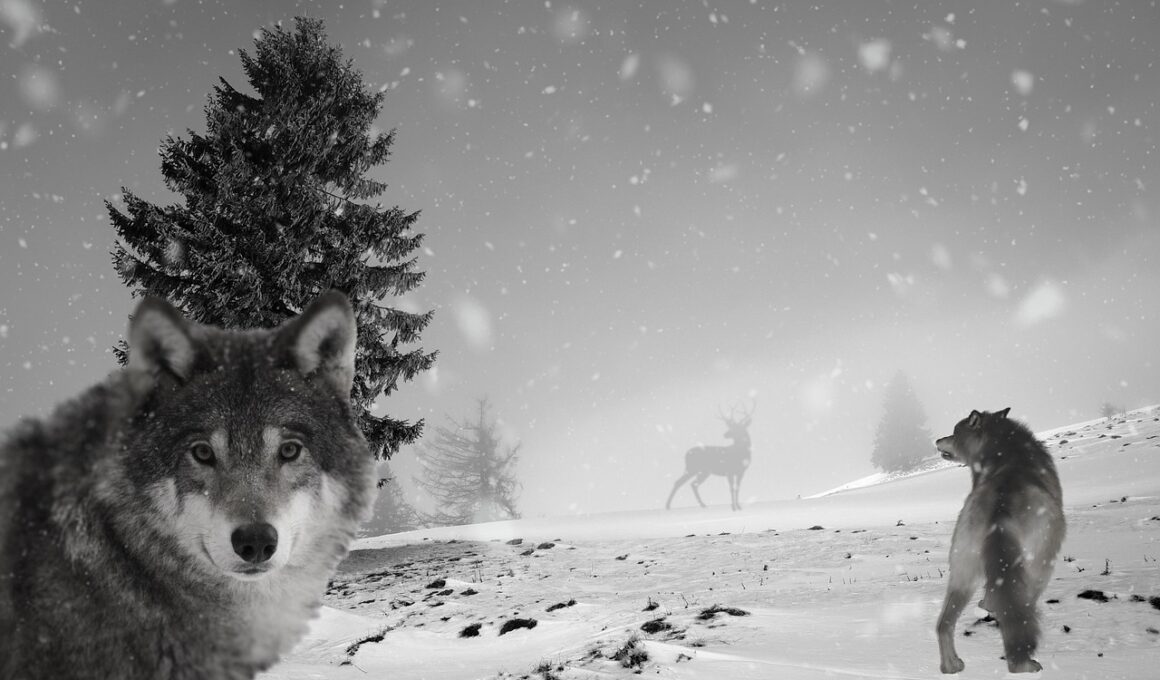
Wolves and Their Prey: Predator-Prey Dynamics
Wolves are fascinating predators that inhabit diverse ecosystems around the globe. Their role in the predator-prey dynamic is critical as they help maintain the balance within their habitats. By preying on certain species, wolves indirectly support flora and fauna diversity. The relationship between wolves and their prey is both intricate and essential, playing a significant role in promoting ecological stability. It is during the hunting process that these magnificent creatures exhibit their social structures and cooperative strategies. Most commonly, they target ungulates such as deer and moose as their primary food source. This type of behavior is vital for the health of prey populations, preventing overpopulation and depletion of vegetation. Furthermore, their predation influences the behavior of prey species, leading to safer habitats for other wildlife. Understanding wolves and their hunting patterns gives insight into how ecosystems function. Observations suggest that when wolves are absent, prey populations can explode, leading to significant ecological degradation. Thus, wolves are considered a keystone species, meaning their presence or absence dramatically impacts their environment. Therefore, the study of wolves’ predation methods is crucial in wildlife conservation efforts.
Wolves have evolved over thousands of years to become skilled hunters. They utilize various hunting techniques that adapt to the characteristics of their target prey. For instance, they often utilize pack strategies, enabling them to take down larger animals effectively. When hunting in groups, wolves exhibit remarkable coordination and communication, relying on vocalizations and body language. This social aspect not only highlights their intelligence but also their adaptability in different environments. Wolves often pursue their prey over long distances, showcasing their endurance and stamina. Various adaptations enhance their hunting efficiency, including keen senses of hearing and smell. Wolves can detect prey from miles away and can determine the health and vulnerability of their targets. This intelligence significantly impacts their hunting success rate. Additionally, wolves can modify their chase tactics according to the prey species, whether they are pursuing fast-moving animals like caribou or slower ones like elk. Understanding these tactics is essential for wildlife management strategies and conservation. By recognizing the predation patterns of wolves, biologists can make better-informed decisions when designing protective measures for both wolves and their prey.
The Impact of Wolves on Ecosystems
The presence of wolves has a profound impact on the functioning of ecosystems. Through their predatory behavior, wolves regulate the populations of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and subsequent habitat destruction. Healthy populations of plants and trees thrive when the prey species are adequately controlled. This process is known as trophic cascading, where changes at one trophic level influence several others, promoting greater biodiversity. When wolves are removed from an ecosystem, herbivore populations can expand unchecked, leading to overconsumption of vegetation. Consequently, this can result in soil erosion and declining plant diversity, thereby affecting the overall health of the ecosystem. Reintroduction of wolves in areas where they have been eradicated illustrates this dynamic clearly. In Yellowstone National Park, for instance, the reintroduction of wolves significantly impacted the local ecology. The stabilization of elk populations led to a resurgence of willow and aspen trees, benefiting a variety of other species. This phenomenon emphasizes the critical role that wolves play in maintaining not only their ecosystems but also the interconnectedness of various species within those communities. Thus, protecting wolves is crucial for preserving ecological balance.
Understanding the behavior of wolves when hunting is crucial for conservation and further research. They typically hunt during dawn or dusk, taking advantage of lower light conditions. This feeding behavior allows them to remain hidden from potential prey. Wolves communicate through howls, allowing pack members to coordinate in their hunts and establish territories. Their vocalizations also play a role in ensuring cohesive hunting strategies. Besides vocal.communication, wolves also utilize visual cues and scents to convey information among the pack. For example, they can inform other members about the presence of prey, territory boundaries, or even dangers nearby. Following successful hunts, wolves exhibit ritualistic behaviors, including caching food for later. This behavior ensures survival during scarce times, showcasing their intelligence and foresight. Additionally, their food storage practices can have a positive impact on the ecosystem by providing resources for scavengers and other wildlife. Studying these patterns helps give insight into their lifestyle and adaptations. Researching how wolves interact with prey further highlights their role within the ecosystem, ultimately contributing valuable information necessary for effective wildlife conservation policies.
Prey Adaptations and Responses
Over time, prey species have also evolved adaptations to escape from wolves. Many naTurally developed heightened senses, such as acute hearing and keen eyesight, help them detect predators from afar. In addition, their social structures, such as herding behavior in certain ungulate species, allow them to defend themselves against predation effectively. These survival strategies are crucial in the constant struggle between predator and prey. When wolves become too successful in hunting, prey may adapt behaviors or migrate to evade predators. Behavioral changes, such as increased movement patterns or altered feeding times, are common responses to the presence of wolves. These adaptive behaviors help maintain the balance in predator-prey dynamics. Furthermore, the changing patterns of prey influence other species within the ecosystem, as they often follow the dwindling resources. Therefore, studying prey dynamics is essential to understanding broader ecological interactions. Conservation efforts not only focus on protecting wolves but also ensure adequate habitats for prey species. This dual approach is vital for the sustainable coexistence of all wildlife, creating a more resilient ecosystem. Protecting such dynamics is essential for maintaining healthy natural habitats and preserving biodiversity.
The intricate dynamics between wolves and their prey continue to be subjects of extensive research. Scientists study these relationships to glean insights into ecosystem balance and conservation strategies. Modern tracking technology plays a vital role in observing wolf behavior in real-time. GPS collars provide data on wolves’ travel routes, hunting patterns, and social interactions. This technological advancement enables researchers to gather more accurate, comprehensive data about their predation habits. Moreover, a growing interest in ecological education has led to increased awareness around the importance of wolves in our ecosystems. Public workshops and educational programs discuss their role and highlight initiatives for preserving their populations. Such efforts ensure that future generations understand the delicate interconnections of nature. Understanding wolves’ behavior fosters a comprehensive approach to wildlife management. By engaging local communities in conservation initiatives, cooperation is established, which benefits both wolves and prey alike. Eco-tourism centered around observing wolves can also create economic incentives for communities. These collaborations promote wildlife conservation while fostering a deeper appreciation for the natural world, ensuring that wolves and their prey thrive in a balanced ecosystem.
Conclusion: The Importance of Predator-Prey Relationships
The predator-prey relationship, specifically between wolves and their prey, underscores the significance of maintaining ecological balance. The intricate interplay of predator and prey helps ensure biodiversity thrives in natural habitats. When both populations are healthy, ecosystems flourish. Wolves serve as indicators of environmental health; their presence signals a balanced ecosystem. Protecting such key predator species becomes essential for sustaining the health of various habitats. The study of these dynamics provides insights integral to evolving conservation strategies and policy-making. Furthermore, understanding this complex interaction fosters a connection to the environment and encourages collective responsibility for wildlife protection. It is vital for upcoming generations to comprehend the importance of all species, including apex predators like wolves. As global conservation efforts continue to evolve, ensuring wolves and their prey coexist harmoniously must remain a funding priority for wildlife management programs. Engaging the public in these discussions will promote a culture of biodiversity appreciation. As we secure the future of wolves and their prey, we safeguard the elaborate ecological balances that sustain our planet, promoting a healthy, vibrant natural world for all species.
While wolves have faced significant threats from habitat loss and hunting, conservation efforts are increasingly focused on their protection. Organizations dedicated to wildlife conservation actively engage in advocacy and awareness campaigns to promote coexistence between wolves and human communities. Education about the ecological benefits that wolves provide can help alleviate fears and misconceptions surrounding these majestic animals. Encouraging responsible land use while implementing strategies to reduce human-wolf conflict is critical to their survival. Initiatives like creating wildlife corridors and communal grazing areas can help to lessen adverse interactions. Research also plays a substantial role in informing these strategies by providing insights into wolf behavior, ecology, and prey dynamics. Ongoing studies continue to reveal the depth of wolves’ social structures and their vital roles within ecosystems throughout their range. Community involvement and support are essential components of successful conservation programs, fostering a shared sense of responsibility. By championing wolves as critical components of their ecosystems, we can contribute to a more balanced natural world. Preservation efforts focusing on safeguarding habitats for both wolves and their prey will be meaningful in promoting biodiversity and ecological health.