Conservation Strategies Addressing Rodent Migration Corridors
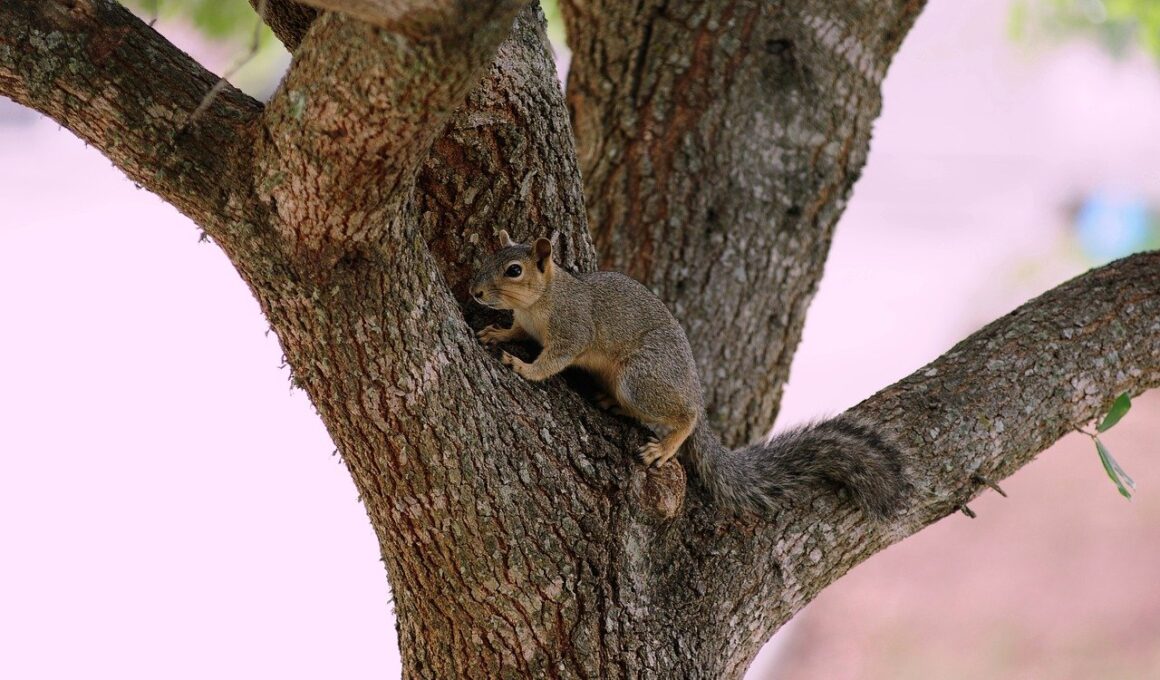
Rodents play a significant role in ecosystems, showcasing remarkable migration patterns influenced by environmental changes. Understanding these migration corridors is essential for conservation strategies aimed at protecting rodent populations and their habitats. Human activities, such as urban development and agriculture, often disrupt natural migration routes, leading to population declines and negative ecological impacts. Conservation efforts must prioritize the identification of these routes, ensuring safe passage for rodent species. Effective strategies include habitat restoration, creating wildlife corridors, and using land management techniques that accommodate rodent migration. Educating communities about the importance of preserving these corridors is also vital for fostering supportive conservation practices. Local governments can implement policies to restrict development in essential rodent habitats, encouraging landowners to maintain natural landscapes. Collaboration between ecologists, urban planners, and local communities enhances the effectiveness of these initiatives, ensuring a holistic approach to conservation. As urban areas expand, understanding and mitigating the impacts of human activity on rodent migration patterns remains crucial, allowing for sustained populations and healthy ecosystems.
One effective approach to conserving rodent migration corridors involves habitat restoration efforts that encourage the natural environment. Restoring native vegetation, wetlands, and other critical habitats can improve the quality of the ecosystems supporting rodents and their migration patterns. These actions not only provide food and shelter for rodents but also enhance biodiversity in the area. An increase in plant diversity leads to a healthier ecosystem, benefiting various animal species. Implementing restoration projects requires collaboration between local governments, non-profit organizations, and community members. Conducting comprehensive ecological assessments helps determine the best practices for restoration and conservation. Partnerships with universities and research institutions can provide valuable scientific insights into rodent behavior and habitat preferences. Engaging local communities through volunteer opportunities fosters a sense of stewardship, encouraging people to participate in reforestation, invasive species removal, and other conservation activities. Additionally, promoting awareness of the ecological significance of rodents and their migration corridors can lead to increased support for ongoing conservation projects. Sustainable practices help maintain healthy ecosystems and promote the rich biodiversity essential for resilient habitats.
Creating Wildlife Corridors
Establishing wildlife corridors is a key strategy for supporting rodent migration and maintaining ecological balance. These designated areas allow rodents to move safely between habitats, reducing the risks posed by habitat fragmentation. Effective wildlife corridors improve gene flow by connecting isolated populations, enhancing genetic diversity and resilience against environmental changes. To create successful corridors, conservationists must consider the unique needs of different rodent species. Mapping migration routes using GPS collars provides valuable data for refining corridor designs. High-quality corridors should provide adequate food resources, shelter, and suitable habitats for rodents. Local governments can implement land-use policies that prioritize wildlife passageways in urban planning. Raising public awareness about the importance of wildlife corridors can further support these initiatives, encouraging communities to advocate for their protection. Public engagement can result in grassroots efforts aimed at preserving vital migration habitats. Wildlife crossings, such as bridges or tunnels, can facilitate safe passage for rodents and reduce vehicle collisions. Integrating corridors into existing green spaces can maximize their effectiveness while promoting urban biodiversity. Overall, well-planned wildlife corridors contribute significantly to the conservation of rodent populations.
In addition to creating wildlife corridors, careful land management practices can support rodent migration patterns and overall biodiversity. Sustainable agriculture, for example, promotes practices that reduce the negative impact on wildlife populations and habitats. By incorporating techniques such as crop rotation, reduced pesticide usage, and maintaining hedgerows, farmers can create favorable conditions for rodents and other wildlife. Integrating agroecological principles allows for better coexistence between agricultural practices and natural ecosystems. Encouraging organic farming methods can further enhance rodent habitats while promoting healthier food systems for the community. Collaborative efforts between agricultural practitioners, conservationists, and researchers are essential to develop comprehensive land management strategies. Workshops and training sessions that educate farmers about the importance of biodiversity conservation can foster long-term collaborative relationships. Implementing buffer zones around agricultural fields can help protect nearby habitats from agricultural runoff and other pollutants. As awareness grows concerning the interdependence of wildlife, including rodents, and sustainable agriculture, more stakeholders are likely to support innovative land management approaches. Striking a balance between agricultural productivity and ecological sustainability benefits both the environment and local communities.
Community Engagement and Education
Community engagement is crucial for successful conservation strategies addressing rodent migration corridors. By fostering public awareness, encouraging participation, and promoting volunteerism, communities can play an active role in conservation efforts. Educational programs focusing on the ecological importance of rodents can inspire individuals to protect local wildlife. Schools, nature centers, and community organizations can collaborate to develop informative workshops, presentations, and hands-on activities related to rodent ecology. Involving local residents in habitat restoration projects enhances their connection to the landscape and promotes stewardship of their environment. Initiating citizen science programs allows community members to contribute valuable data on rodent populations and migrations. This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards conserving local ecosystems. Local media can also play a part in spreading awareness by highlighting conservation initiatives, success stories, and opportunities for involvement. Encouraging citizens to take action, such as creating wildlife-friendly gardens or reporting rodent sightings, contributes to maintaining healthy habitats. Ultimately, empowering communities through education fosters a culture of conservation that leads to sustained efforts in protecting rodent migration corridors and the ecosystems they support.
Collaborative partnerships between various sectors are vital for implementing effective conservation strategies for rodent migration corridors. Engaging diverse stakeholders—including government agencies, non-profits, and private landowners—helps streamline efforts toward common conservation goals. By sharing resources, knowledge, and expertise, these partnerships enhance the effectiveness of conservation programs aimed at preserving rodent habitats. Joint initiatives can include habitat mapping, monitoring rodent populations, and developing policies that support wildlife-friendly practices. Additionally, forming coalitions that unite individuals, organizations, and government entities promotes co-management and shared responsibility for conservation outcomes. Collaborative funding opportunities, such as grants and donations, can support ongoing conservation projects, ensuring their sustainability. Cross-sector collaborations can also lead to innovative solutions for mitigating the impacts of urbanization and land use changes on rodent migration corridors. By breaking down barriers and fostering open dialogue, stakeholders can address shared challenges, resulting in more effective and comprehensive conservation strategies. Ultimately, building cooperative networks strengthens the collective capacity to preserve rodent populations and their migration routes, contributing to thriving ecosystems.
Conclusion: The Future of Rodent Conservation
Looking ahead, the future of rodent conservation hinges on the successful implementation of strategies to protect migration corridors. As challenges such as climate change and urban development continue to threaten rodent populations, proactive measures are essential. Conservationists must remain adaptable, continuously refining approaches based on emerging research and environmental conditions. Continued investment in habitat restoration, wildlife corridors, and community engagement will enhance the effectiveness of conservation efforts. An adaptive management approach allows for ongoing evaluation and modification of strategies based on monitoring results. Engaging stakeholders at every stage ensures that efforts remain relevant and effective in supporting rodent populations. As awareness of the ecological importance of rodents grows, so does the potential for broader support for conservation initiatives. Promoting education and community involvement amplifies the impact of conservation actions, fostering a culture of stewardship. Conservation strategies that prioritize rodent migration corridors will contribute to healthier ecosystems, benefiting not only rodents but also other biodiversity elements. Ultimately, a collaborative and informed approach is essential to securing the future of rodent populations and ensuring the resilience of ecosystems in the face of ongoing environmental challenges.
To sum up, effective conservation strategies for rodent migration corridors must address the challenges posed by habitat loss, human activities, and environmental changes. Understanding rodent migration patterns is crucial for developing targeted interventions that support their movement and survival. Implementing wildlife corridors, habitat restoration, and community engagement fosters healthy ecosystems while promoting biodiversity. Continued research into the ecological roles of rodents and their interactions with habitats will inform ongoing conservation actions. Collaborative partnerships among stakeholders enhance the effectiveness of efforts to protect these vital migration routes. Engaging local communities in education and volunteer initiatives ensures widespread support for conservation practices. Embracing sustainable land management and agricultural techniques will further nurture rodent habitats. By prioritizing rodent migration corridors, we can protect these key species while contributing to overall ecosystem health. Future conservation initiatives must remain flexible and responsive to emerging challenges, ensuring lasting impacts. Together, these comprehensive approaches create a solid foundation for securing rodent populations and, by extension, the resilience of broader ecological networks.