Freshwater Birds and Their Diet
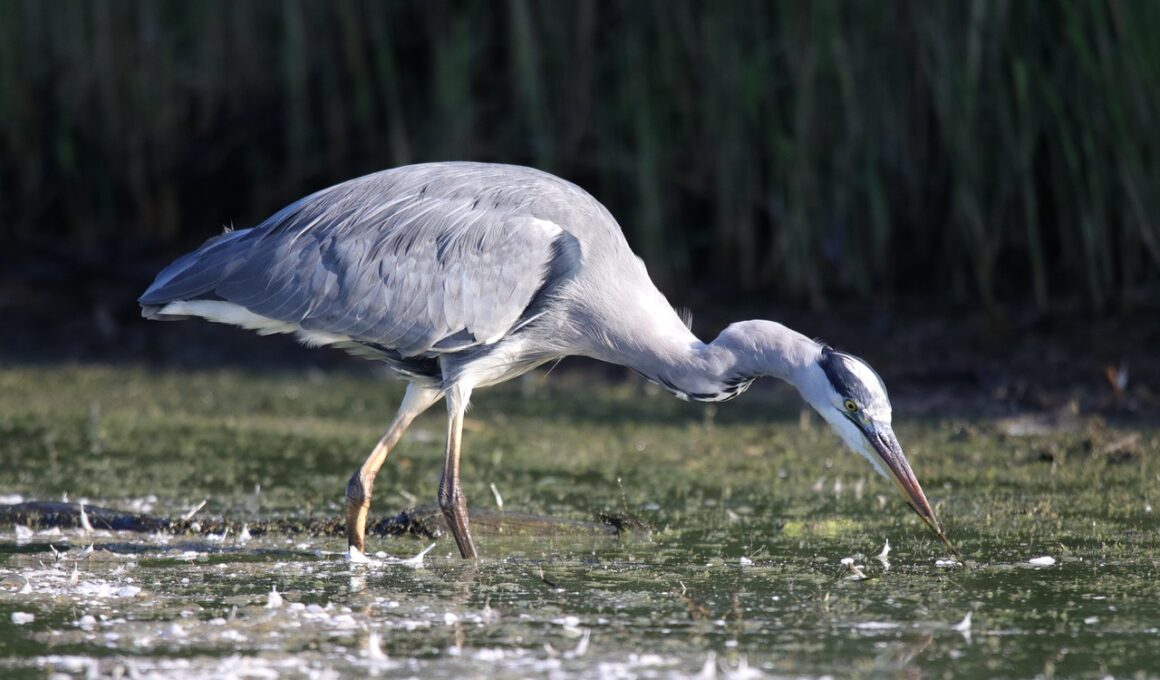
Freshwater birds occupy a vital niche in aquatic ecosystems, often preying on various species to sustain themselves. These birds include species such as herons, ducks, and kingfishers, which primarily rely on fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates. Their predation influences the population dynamics of these prey species, highlighting their role as both consumers and contributors to ecological balance. Birds like the great blue heron excel at wading in shallow waters, utilizing their keen eyesight to spot unsuspecting fish and crustaceans. Additionally, ducks often employ a foraging technique known as dabbling, which allows them to feed on small fish and aquatic plant matter. Furthermore, higher trophic levels in these food chains often depend on the healthier presence of freshwater birds. By maintaining fish populations and supporting ecological diversity, these birds ensure the stability of their environments. Conservation efforts focused on freshwater habitats are essential to protect these birds, as they rely on healthy ecosystems rich in biodiversity. Their diets directly impact the ecological balance, making it crucial to study their feeding habits and prey preferences in freshwater ecosystems.
Understanding the dietary habits of freshwater birds reveals much about their adaptations and behaviors. For instance, species like the osprey are known for their remarkable fishing skills. These birds have specialized talons and an adept diving technique that enable them to capture fish. On the other hand, some ducks, such as the mallard, exhibit omnivorous behaviors, consuming both plant material and animal matter, including invertebrates and small fish. The seasonality of prey availability greatly influences the diets of these birds, leading to variations in food sources throughout the year. During summer months, when warmer waters support diverse fish populations, birds like kingfishers experience an abundance of food. Conversely, in winter, many species must adapt their foraging methods to the changing availability of prey. The presence of various prey species shapes the behavioral adaptations of freshwater birds, ensuring that they can optimize their hunting efficiency. By focusing on a variety of feeding strategies, freshwater birds exemplify how dietary habits shape ecological relationships within their habitats.
The Role of Prey Species
Prey species play a critical role in the survival of freshwater birds, providing essential sources of nutrition and energy. Often, specific bird species specialize in targeting certain types of prey, which can include fish, amphibians, or invertebrates. For example, certain heron species primarily hunt fish, while others may focus on catching frogs or insects found in the water. Their specific dietary preferences influence their hunting strategies, including hunting locations and timing. Many herons will remain motionless for extended periods, waiting for the perfect moment to strike, which helps them optimize energy use. Similarly, ducks are equipped with various feeding adaptations such as their broad bills, enabling them to filter small prey from the water. Additionally, seasonal shifts can affect the availability of prey, requiring birds to adapt and switch their diets accordingly. By monitoring the changes in prey availability, researchers can gain valuable insights into the health of freshwater ecosystems. Understanding the relationship between freshwater birds and their prey helps in crafting effective conservation strategies to protect these vulnerable species.
The impact of competition cannot be overlooked when discussing freshwater birds’ diets. In habitats where multiple bird species coexist, competition for limited food resources can be intense. Birds like cormorants may compete with ospreys for similar fish species, highlighting how the presence of one species can directly affect the feeding success of another. This interspecific competition can lead to spatial and temporal avoidance of certain feeding grounds, where one species may limit its foraging efforts in areas heavily frequented by its rivals. Furthermore, local environmental conditions, like water temperatures and pollution levels, can also influence the prey availability and the respective dietary patterns of these birds. Understanding these competitive interactions is crucial for habitat management and species conservation efforts. Ensuring that habitats support sufficient prey populations and reduce anthropogenic pressures enables a balanced and diverse bird community. Moreover, such knowledge can influence ecological restoration strategies aimed at recovering compromised freshwater environments, further supporting the diverse avifauna dependent on these ecosystems for survival.
Seasonal Variability and Adaptation
Seasonal changes significantly affect the diets of freshwater birds, urging them to adapt their feeding practices. In most regions, summer offers an abundance of food due to increased productivity in aquatic ecosystems. Fish spawn, insects flourish, and vegetation grows, providing diverse feeding options. This period typically sees a surge in bird populations, drawn by rich feeding grounds. However, as temperatures drop, many freshwater birds face food scarcity, compelling them to adapt and innovate in their search for nutrition. Some species migrate to warmer climates, where food remains plentiful year-round. Others may alter their diets to include a broader range of available prey or forage more extensively during daylight hours. Additionally, during winter months, ice cover can limit access to their usual feeding areas. By diversifying their prey options, these birds enhance their chances of survival during adverse conditions. The capacity of freshwater birds to adjust their feeding behavior highlights their resilience and adaptability in the face of ecological changes.
Monitoring the dietary habits of freshwater birds provides crucial insights into the health of aquatic ecosystems. Various studies have explored the interdependencies between bird populations and their prey dynamics, revealing how shifts in prey health and abundance often signal larger ecosystem changes. Birds serve as bioindicators, meaning their behaviors reflect the overall state of their environment. For instance, significant declines in fish populations directly influence the feeding success of piscivorous birds. This relationship emphasizes the importance of maintaining balanced aquatic environments to support diverse bird species. Conservation efforts can be enhanced by understanding these dynamics, allowing for targeted actions such as restoring habitats or regulating fishing activities. Additionally, research into the varying prey preferences of different freshwater bird species helps in recognizing critical dietary needs. Such comprehensive studies can guide policymakers in creating effective environmental regulations and management practices to sustain healthy bird populations alongside their prey. The interplay between freshwater birds and their prey is a fundamental aspect of ecosystem management that warrants ongoing attention and action.
Conservation Strategies
Effective conservation strategies are essential for protecting freshwater birds and ensuring the survival of vital prey species. Sustainable management practices play a key role in preserving diverse aquatic ecosystems by addressing threats such as habitat destruction and pollution. Implementing regulations that protect breeding grounds, restricting pesticide use, and promoting habitat restoration can often result in improved prey availability for these birds. Educating local communities about the importance of freshwater habitats fosters support for conservation initiatives. Engaging citizen science projects allows individuals to contribute to research efforts that monitor bird populations and their prey dynamics. Additionally, fostering collaboration between governmental and non-governmental organizations can enhance the scope and reach of conservation activities. By having a unified approach, conservation strategies can address the multifaceted challenges facing freshwater ecosystems efficiently. Protecting the delicate balance between freshwater birds and their prey is crucial for ecological stability. By focusing on both avian and aquatic organisms, conservation efforts can ensure a healthier environment that allows diverse species to thrive.
The intricate relationships and dependencies between freshwater birds and their prey encapsulate the complexities of aquatic ecosystems. As integral components of these environments, their interconnectedness reflects the overall health of the ecosystem. Recognizing the importance of these relationships is essential for nurturing biodiversity and implementing effective conservation strategies. Understanding factors such as diet variations, prey availability, competition, and seasonal adaptations helps clarify the ecological mechanisms at work. By studying these interactions, researchers can better predict the impacts of environmental changes on bird populations and their prey. Consequently, proactive measures can be taken to address potential declines in biodiversity. Looking forward, a comprehensive approach centering around integrated conservation efforts, alongside continuous research into the dynamics of freshwater ecosystems, holds the key to safeguarding these remarkable birds and their prey. The future of freshwater ecosystems depends not only on protecting bird populations but also on ensuring a thriving, diverse array of prey species that sustains them.