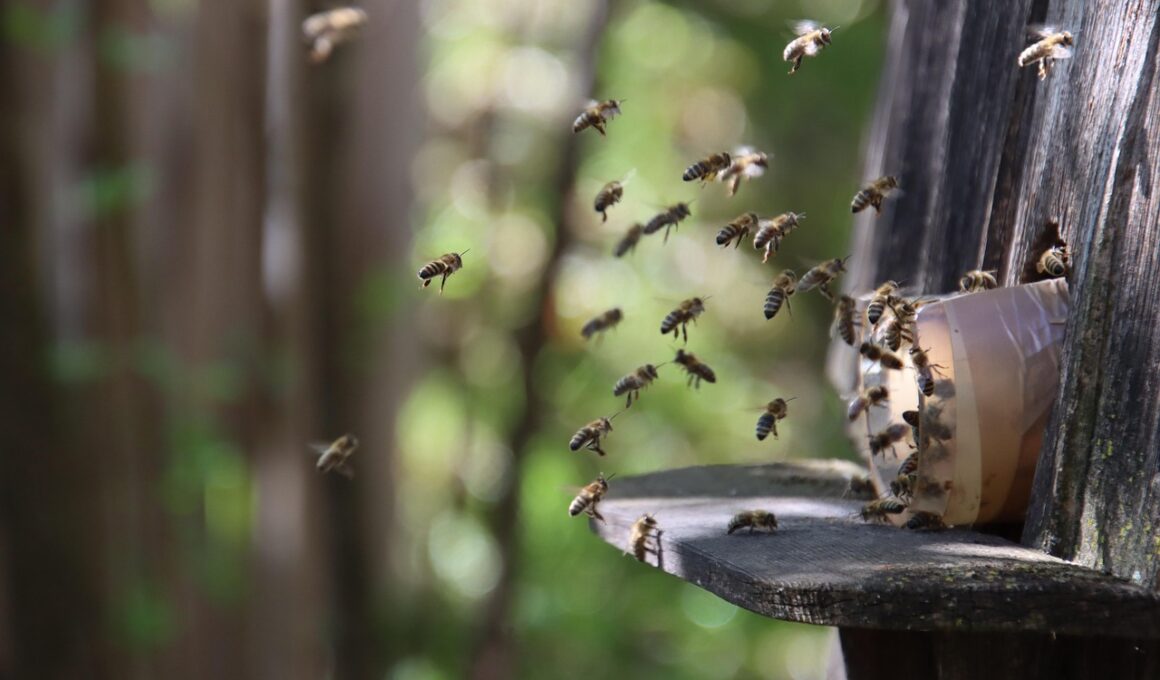
The Role of Bees in Sustainable Agriculture
Bees play an essential role in our ecosystem, particularly in sustainable agriculture. These industrious insects are responsible for pollinating a vast array of plants, including many crops that form the backbone of global food supply. In fact, it is estimated that one-third of the food we consume relies on bee pollination. This vital process not only ensures fruits and vegetables can grow but also helps preserve plant diversity which is crucial for a resilient food system. Farmers rely heavily on bees to increase yields and ensure the quality of their produce. Without bees, many of the foods we take for granted would become scarce, and farming as we know it could be severely impacted. Sustainable agricultural practices that protect and promote bee populations are therefore essential. Moreover, by supporting habitats for these pollinators, we facilitate improved crop production, which contributes to a healthier ecosystem overall. By maintaining floral diversity and reducing chemical use, farmers can create a more hospitable environment for bees, thus fostering the longevity of both pollinators and agriculture itself. The health of bees directly impacts agricultural sustainability and food security worldwide.
The relationship between bees and agriculture goes beyond mere pollination. Bees enhance biodiversity in farming systems by promoting cross-pollination. This process leads to a wider variety of crops, which can contribute tremendously to a balanced diet among communities. When farmers grow an array of plants, they not only attract bees but also create habitats for numerous other beneficial insects and wildlife. This cultivation of monocultures has become problematic in modern agriculture, decreasing biodiversity and making crops more susceptible to pests and diseases. Implementing agroecological practices can increase bee habitat and at the same time provide food for the surrounding ecosystem. These sustainable approaches can include integrating more flowering plants into and around crop fields, reducing pesticide use, and practicing organic farming. Farmers can actively engage in fostering a healthy environment for bees by adopting these practices, which ultimately leads to healthier soil and ecosystems. Investment in bee-friendly practices not only benefits farmers but also bolsters community health through increased access to nutritious foods and enhanced environmental resilience and stability.
Challenges Facing Bee Populations
Despite their critical role, bee populations are facing unprecedented challenges due to various factors. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural expansion is one of the primary reasons for the decline of bee populations. As cities grow and agricultural lands intensify, natural habitats where bees thrive are erased. Furthermore, the widespread use of pesticides poses significant risks to bee health. These chemicals can directly harm bees by affecting their ability to navigate and communicate, and may ultimately lead to colony collapse. Additionally, climate change exacerbates these challenges, altering the flowering schedules of plants and disrupting the synchrony between bees and their food sources. Diseases and parasites, such as the Varroa mite, have also contributed significantly to the decline in bee populations. To combat these threats, conservation efforts must be ramped up. Initiatives aimed at restoring habitats, promoting organic farming, and enhancing public awareness about the importance of bees are crucial for their survival. Each individual can contribute by supporting local beekeepers and advocating for policies that protect pollinators and their habitats.
Another significant aspect of maintaining healthy bee populations is community engagement in sustainability initiatives. Local communities can promote beekeeping as a practice and encourage urban agriculture. This can facilitate the creation of small bee-friendly spaces through backyard gardens and green roofs. Examples of community-based conservation can be seen in various urban areas where gardens are planted with pollen-rich flowers specifically for bees. Such collective efforts can create green corridors that connect isolated habitats, enabling bees to forage more effectively. Education also plays a critical role in addressing the challenges bees face. Schools can engage children through educational programs about the importance of bees in food production and gardening, fostering the next generation’s appreciation for pollinators. Workshops and community events centered around beekeeping can help demystify the practice while encouraging local economies. Additionally, promoting pollinator-friendly practices can provide sweet rewards for both nature and the farmers involved. By investing in local biodiversity and beekeeping endeavors, communities can cultivate an environment that supports both human and bee populations sustainably.
Economic Benefits of Bees
Bees provide significant economic value to agriculture and humanity. The economic impact of bee pollination includes billions of dollars in increased crop yields. It is estimated that bees contribute over $15 billion annually to the U.S. economy alone, reflected by enhanced production of fruits, nuts, and vegetables. Many crops like almonds, apples, and blueberries are highly dependent on bee pollination for optimal yields. Farmers can substantially reduce input costs and maximize profits through sustainable agricultural practices that protect and boost bee populations. Investing in beekeeping not only supports farmers financially but also unemployed individuals can find new opportunities. As the demand for local and organic produce continues to rise, the importance of bees aligns with market trends. Furthermore, honey production serves as another income stream for beekeepers. By diversifying their offerings, beekeepers can also offer related goods such as beeswax, propolis, and royal jelly—all contributing positively to local economies. Sustainable practices ensure this long-term economic viability, while a healthy bee population leads to a robust agricultural framework that can produce food for a growing global population.
The increased awareness of the benefits of bees extends beyond agricultural sustainability. The public is becoming more conscious of organic and local food sources, demanding that agricultural practices align with sustainability principles. This growing demand drives positive change in the agricultural sector, with more farmers transitioning to organic farming to protect pollinators. Entities such as non-profit organizations, governmental bodies, and environmental groups play an essential role in advocating for bee conservation. Programs aimed at reducing pesticide use and promoting ecological practices have gained traction and encouraged farmers to adopt environmentally responsible approaches. More consumers are also willing to engage with local producers who prioritize bee health in their farming practices. Moreover, initiatives aimed at providing financial support to farmers implementing bee-friendly practices have begun to emerge. Grants and incentives from conservation organizations encourage the adoption of sustainable farming methods that benefit bees and promote ecological agro-systems. As the dialogue around sustainability continues, the convergence of social awareness and agricultural practices is vital to ensuring a harmonious coexistence of ecology and food production that responsibly serves future generations.
Future Directions in Bee Conservation
Looking ahead, the future of bee conservation appears promising with ongoing research and innovations intended to protect these species. Advances in agriculture technology allow farmers to utilize precision farming techniques, minimizing chemical usage and maximizing productivity. Drones and sensors are increasingly being deployed in agriculture to monitor bee activities and their health in real time, thus enabling farmers to create better conditions for foraging and reproduction. While challenges remain, collaborative efforts among farmers, scientists, and policymakers are showing results. Governments worldwide are beginning to implement regulations that protect bee habitats, limit pesticide use, and promote best practices for sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, educational campaigns are crucial to raising public awareness about bees and the actions individuals can take to support their survival. By planting native flowers, creating bee gardens, and advocating for policy changes, we can foster environments conducive to bee habitats positively. Engaging the community in conservation efforts leads to more innovative solutions for protecting bees, ensuring a resilient food system that supports agricultural dependability.
In conclusion, bees are indispensable not only for agricultural sustainability but also for the intricate web of life that supports ecosystems globally. The challenges they face are significant, yet with sustained efforts, we can foster environments that promote their health and increase agricultural productivity. By emphasizing biodiversity, collaboration, and community involvement, we can create a future where bees thrive alongside human agriculture. Encouraging sustainable practices such as organic farming and habitat restoration contributes immensely to this goal. As advocates for change, we must educate ourselves and others about the importance of supporting bees and their ecosystems. Active participation in conservation initiatives can yield tangible benefits that last for generations. Understanding the economic, ecological, and social dimensions of bee health creates a multi-faceted approach to conservation. Anticipating future challenges requires innovation and adaptability, influenced by ongoing research and technological advancements in agriculture. Together, we can secure the future of these vital pollinators in a sustainable agricultural landscape. The role of bees in our food system is undeniable, and promoting their well-being is crucial to sustainability and ecological balance. Therefore, unity, education, and proactive measures are essential for fostering a vibrant future for bees and their contributions to our planet.