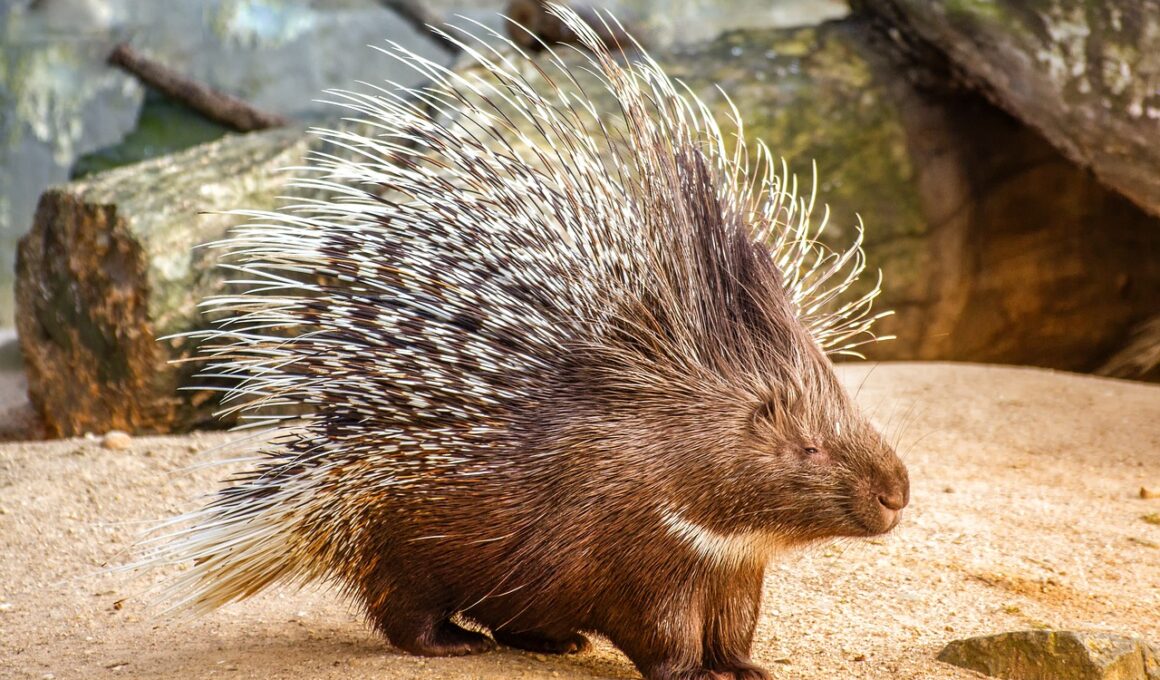
Porcupine Herbivores: Nocturnal Habits and Lifestyle
Porcupines are fascinating creatures primarily recognized for their distinctive quills and unique herbivorous diet. Found predominantly in wooded and forested regions, these nocturnal mammals display a variety of habits suited for survival. As a member of the rodent family, they are primarily herbivores, feeding on a range of plant materials including leaves, fruits, and bark. Porcupines have adapted their diet according to seasonal changes, showcasing a remarkable ability to thrive in different environments. During the night, they forage for food, which often includes large quantities of vegetation, allowing them to maintain healthy bodily functions. Their teeth continuously grow, meaning they must regularly gnaw on materials like tree bark to wear them down. This unique habit not only addresses their dental needs but also plays a critical role in their habitat’s ecology. The consumption of specific trees can influence forest dynamics, as porcupines help in shaping the growth patterns of various plants. Furthermore, porcupines sometimes engage in playful activities and social behaviors, especially during mating seasons, showcasing their complex lifestyle.
When examining the nocturnal behavior of porcupines, several interesting traits come to light. Unlike many daytime mammals, porcupines exhibit heightened senses during the night, particularly when it comes to foraging and avoiding predators. Their keen sense of smell is instrumental in locating food from a considerable distance, ensuring they can find nutritious plants even in thick underbrush. Additionally, they are equipped with strong limbs and claws, which assist in climbing trees to access both food sources and safe resting spots. When threatened, porcupines can utilize their quill-covered backs for self-defense, making them less appealing targets for many predators. However, they generally prefer to retreat from confrontations rather than engage directly. Their social dynamics are fascinating as they often communicate through vocalizations, scents, and body language to express emotions or territorial claims. Observing porcupines during their active hours can provide insights into their interactions and ecological roles within their habitats. The balance they maintain in their ecosystems highlights the importance of herbivores like porcupines, showcasing how they contribute to biodiversity.
Nutritional Needs of Porcupines
The nutritional requirements of porcupines are highly specialized, necessitating a diet rich in fibrous materials and essential nutrients. Their primary diet consists of various plant species, including leaves, twigs, bark, and roots, especially during winter months when other food sources are scarce. Porcupines are particularly fond of certain hardwoods, as the inner bark offers a significant source of carbohydrates and energy. This selection of food is crucial for their survival, as it provides the calories needed to endure cold environments. Moreover, they have been known to consume fruits and nuts, enhancing their diet with vitamins and minerals necessary for overall health. The foraging strategy of porcupines often involves selecting specific species of trees, impacting their habitats by promoting new growth. Their nutrient absorption is optimized through a slow digestive process that allows for maximum extraction of necessary components from plant materials. In addition to their foraging behaviors, porcupines occasionally eat clay and soil to obtain minerals that may be missing from their diets, highlighting their ability to adapt to nutritional deficiencies.
Porcupines also engage in grooming behaviors, which play a crucial role in their health and wellbeing. Grooming not only keeps their quills clean but also helps maintain skin health by removing parasites and promoting proper circulation. Their unique quill structure, composed of keratin, requires periodic maintenance as well to preserve their functionality. When porcupines groom themselves, they can apply natural oils to their quills, enhancing their protective features against predators. Furthermore, these behaviors serve as a form of social interaction among porcupines, particularly in mating pairs. Observing these grooming rituals during twilight hours offers a glimpse into their intimate relationships and daily routines. In terms of habitat preference, porcupines tend to remain close to their preferred food sources while also seeking out places that provide shelter from severe weather. Their choices showcase a balance between foraging efficiency and safety, ensuring they can thrive in various environments. Additionally, porcupines demonstrate a surprising level of intelligence, able to navigate complex terrains while evading potential threats.
Porcupine Social Dynamics
The social structure of porcupines is primarily solitary, though they engage in specific social interactions during certain periods such as mating seasons. Male and female porcupines exhibit distinct behaviors when attracting mates, often involving vocalizations and scent-marking to communicate their readiness to breed. This social aspect becomes particularly interesting during the mating season when males may compete for female attention through displays of strength and agility. These courtship rituals can include physical displays, such as climbing or wrestling, which help determine the strongest and most viable suitor. Female porcupines typically exhibit a high degree of selectiveness in choosing mates, ensuring the survival of strong genetic traits. After mating, the female will carry her young for approximately 7 months, resulting in the birth of one or two offspring, known as porcupettes. These young ones are born with soft quills that harden over time, allowing them to adapt to their environment effectively. Maternal care plays a significant role in their early development, with mothers providing protection and nutrition until the young are mature enough to fend for themselves.
As porcupines live primarily in tree environments, their arboreal skills enhance their survival and social behaviors. They spend considerable time climbing trees, not only for food but also to establish territories and evade predators. This climbing ability is a significant part of their lifestyle, allowing them to fulfill foraging habits effectively. In terms of social interactions, porcupine young often stay with their mothers for up to a year before dispersing to find their own territories. This period allows them to learn essential survival skills, resting, and foraging techniques that are crucial. During this formative year, young porcupines also observe social behaviors and interactions among adults, which aids in their overall development. Their nocturnal habits and specialized foraging techniques reflect their adaptation to ecological niches. As herbivores, porcupines play an essential role within their ecosystems by managing plant populations and contributing to soil health. Thus, understanding their social dynamics provides valuable insights into their ecological roles and the importance of conserving their habitats.
Conservation Challenges for Porcupines
Like many species, porcupines face various conservation challenges that threaten their populations and habitats. Habitat destruction due to urbanization, agricultural expansion, and deforestation poses the most significant risk, as these activities lead to loss of essential foraging areas and shelter. As they lose their natural habitats, porcupines flock to suburban and urban regions in search of food, often leading to conflicts with humans. Additionally, climate change disrupts their food sources and migratory patterns, further complicating their survival. The impact of hunting and poaching exacerbates these issues, as porcupines are sometimes targeted for their quills and meat. Efforts are underway to raise awareness about porcupine conservation and promote sustainable practices that protect their habitats. Educational initiatives and wildlife corridors are critical elements in helping porcupines thrive in areas affected by human activities. Collaboration among conservationists is essential in developing effective strategies to mitigate challenges and ensure these herbivores continue to play a vital role in their ecosystems. Advocating for porcupines helps protect biodiversity and promote ecological balance in their environments.
In conclusion, porcupines are unique herbivores with a complex lifestyle centered around their nocturnal habits and dietary requirements. Their foraging strategies not only ensure their survival but also impact their ecosystems positively by managing plant populations. As they navigate their environments with impressive arboreal skills, their social structures and interactions further enhance their intriguing nature as wildlife. However, the conservation challenges they face highlight the importance of proactive measures in maintaining their populations and habitats. Educating the public about porcupines and their ecological significance is crucial for fostering an appreciation of wildlife conservation. By understanding the role of porcupines in their ecosystems, we can appreciate the intricate connections between species and their environments. We should advocate for responsible land-use practices to ensure the continuity of porcupine populations. As a vital part of the herbivore community, porcupines contribute to maintaining biodiversity. In this way, protecting these remarkable creatures not only benefits them but also enhances the ecological balance within their habitats. The future of porcupines and their nocturnal lifestyle hinges on our commitment to preserving natural habitats.