The Chinese Pangolin: Conservation Status and Threats in Asia
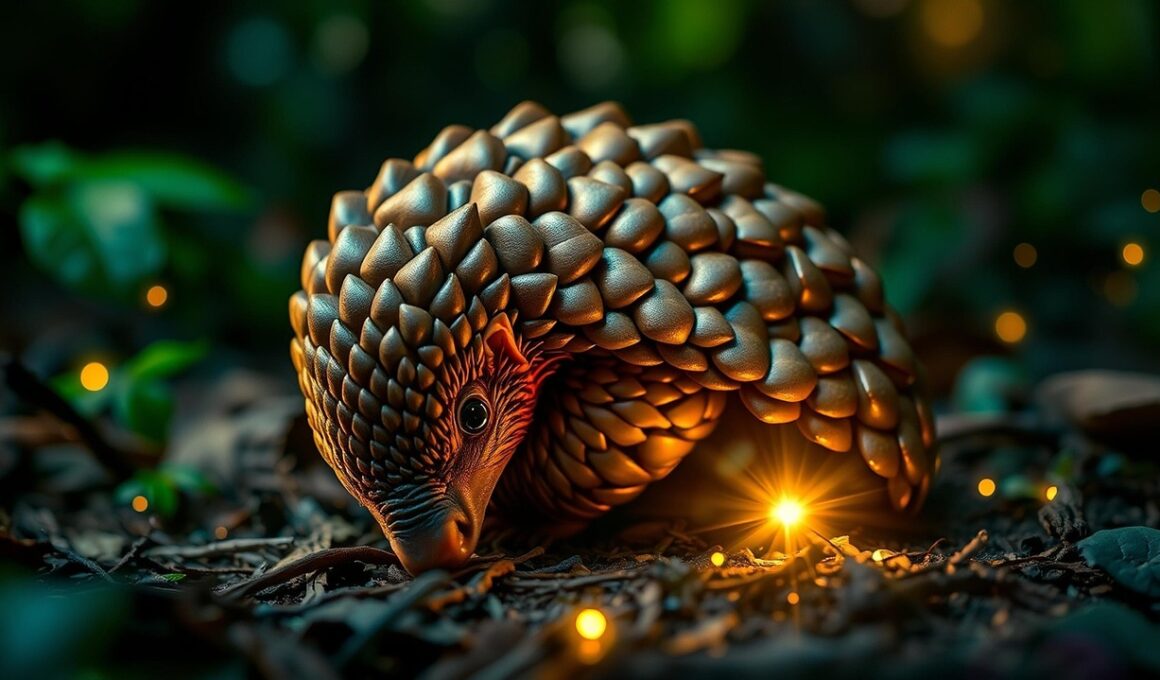
The Chinese pangolin, a unique anteater species, is a critically endangered mammal found primarily in Asia. Its scientific name is Manis pentadactyla, and it is known for its distinctive scales, which are made of keratin. Often referred to as the most trafficked mammal globally, the Chinese pangolin faces numerous threats that jeopardize its existence. Habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization is a significant concern. Furthermore, illegal poaching for their scales and meat contributes substantially to the decline of their populations. These pangolins are hunted relentlessly, primarily driven by demand in traditional Chinese medicine and as a delicacy in some cultures. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this species, but challenges remain high. Education and awareness are crucial in combating illegal trade and ensuring sustainable habitat management. Protecting forests and restoring habitats are vital to reversing population declines. Collaborative efforts among governments, NGOs, and local communities can foster a supportive environment for pangolin recovery. The role of law enforcement in cracking down on poaching and trafficking operations cannot be underestimated as well.
The impact of habitat destruction on the Chinese pangolin is substantial, leading to reduced food availability and increased human-wildlife conflict. As pangolins prefer forested areas, logging and agricultural expansion can destroy their natural habitats. Urban sprawl also forces these animals into fragmented patches which complicate their foraging behavior. They primarily feed on ants and termites, requiring extensive areas to secure adequate nutrition. As their habitat shrinks, finding enough food becomes increasingly challenging, leading to malnutrition and decreased reproductive success. In regions where these pangolins are found, conservationists advocate for sustainable land use practices that balance economic development and wildlife conservation. Community involvement is essential for the success of conservation strategies aimed at preserving the pangolin’s environment. Education programs focusing on the ecological role of pangolins can help local populations appreciate their value. Environmental laws and regulations must be enforced rigorously to limit destructive activities. Furthermore, establishing protected areas may provide safe havens for the remaining pangolin populations. Habitat restoration initiatives should focus on reforestation and promoting biodiversity to aid recovery efforts for both the pangolin and its ecosystem.
Threats from Poaching and Illegal Trade
Poaching poses an immediate and severe threat to the Chinese pangolin population. It is primarily driven by the illegal wildlife trade, where their scales are highly sought after for traditional medicine. Illegal markets in Asia are fueled by demand for these products, and pangolin scales are often falsely credited with healing properties. This has resulted in widespread hunting, leading to drastic declines in their numbers. In addition, pangolins are sometimes captured for their meat, which is considered a delicacy in several countries. The international trade in pangolins is banned under CITES, yet enforcement remains a challenge. Many countries still struggle with illegal poaching activities, as enforcement often lacks resources and capacity. The pangolin’s secretive and solitary nature makes them difficult to study, complicating population monitoring efforts. As a result, data on their abundance remains scarce. Conservationists emphasize the need for stronger policies and greater public awareness to diminish demand for pangolins and their parts. Community engagement plays a critical role in conservation by shifting local attitudes toward wildlife and creating sustainable livelihoods that discourage poaching.
Conservation measures targeting the Chinese pangolin must include a comprehensive approach involving locals. Effective strategies require education focused on the ecological importance of pangolins and the role they play in maintaining soil health and insect population control. When communities understand these benefits, they may be more inclined to protect these animals. Moreover, providing alternative livelihoods, such as eco-tourism, can reduce reliance on wildlife trafficking. Partnering with local NGOs to promote sustainable alternatives is essential for success. Support from governments is also necessary to create incentives for communities engaged in conservation efforts. It is vital to bolster legal frameworks surrounding wildlife protection to enhance enforcement capabilities against poaching. Resources should be allocated for training programs for local law enforcement. Furthermore, rehabilitating seized pangolins needs to become a priority within conservation agendas. Many captured animals end up in rehabilitation centers that are under-resourced and lack expertise in wildlife care. Additional funding and training for these facilities can greatly contribute to the recovery of populations in areas where they have been critically depleted.
International Collaboration in Conservation
The fight against the illegal pangolin trade necessitates international collaboration among various stakeholders. Wildlife trafficking often transcends national borders, making it crucial for nations to unite in enforcing laws. Global initiatives such as the TRAFFIC network work to monitor the trade and support local efforts to combat poaching through education and policy advocacy. Collaborative research, information sharing, and training can bolster local capacities for wildlife protection. Additionally, countries should work on joint patrols in wildlife trafficking hotspots to ensure continuous monitoring. Engagement with local communities remains essential as they often serve as the first line of defense. When locals are empowered with knowledge and resources, they can better help monitor and protect endangered species. International bodies need to facilitate assistance by providing funding for projects focused on pangolin conservation. Strengthening connections between conservation organizations, law enforcement agencies, and local communities can yield significant results. Sharing best practices and successful rehabilitation stories can inspire ongoing efforts in different regions battling with similar challenges. Collaborative approaches can enable effective conservation strategies that allow pangolins to thrive once more.
Government legislation and policy reform are pivotal in ensuring the protection of the Chinese pangolin. Countries must take legislative measures to enhance wildlife protection laws, including stiffer penalties for wildlife trafficking offenses. The implementation of comprehensive national action plans can outline clear strategies for conservation. This includes habitat management, anti-poaching initiatives, and public awareness campaigns to generate grassroots support. Governments should actively engage with conservation organizations to develop effective and evidence-based policies. Through international agreements, countries can commit to fighting wildlife trafficking on a global scale. It is imperative to establish strict wildlife protection laws and create dedicated wildlife crime units empowered to enforce laws effectively. Cooperation with customs and border control agencies can further assist in intercepting smuggled wildlife products. Public engagement efforts that advocate for the pangolin can lead to increased media attention, encouraging more citizens to participate in conservation activities. Sharing stories and successes in conservation can galvanize public support. Local engagement, supported by strong legislation, can provide essential backing for the protection of the Chinese pangolin and its habitat.
Overall, the conservation of the Chinese pangolin requires a multidimensional approach. Raising awareness, strengthening laws, and empowering communities are vital components of a successful conservation strategy. International collaboration plays a crucial role in addressing wildlife trafficking while promoting sustainable livelihoods in communities that rely on wildlife. A comprehensive understanding of the threats that pangolins face can foster targeted interventions aimed at reducing pressures on their populations. Conservation strategies should involve local populations, urging them to become stewards of their natural environment. Using innovative technology such as camera traps can enhance monitoring efforts, providing valuable data to guide conservation actions. Ongoing research is essential to understand the behavior and ecology of this elusive species. Ultimately, concerted efforts from governments, organizations, and individuals can contribute significantly to the preservation of the Chinese pangolin and the broader Asian biodiversity landscape. Protecting this unique species benefits ecosystems and highlights the need for a harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife.
Through these comprehensive conservation efforts, we can hope for a brighter future for the Chinese pangolin and the ecosystems it inhabits. Continued investments in community engagement and scientific research will pave the way for effective long-term strategies. As we address the pressing challenges facing pangolins today, the importance of global support and cooperation cannot be overstated. The survival of the Chinese pangolin relies not only on individual nations but on collective action from the international community. With increased awareness and a commitment to sustainable practices, we have the power to turn the tide for this remarkable species. Together, we can protect the Chinese pangolin and work towards achieving balance in our world, celebrating the rich biodiversity that sustains us all.