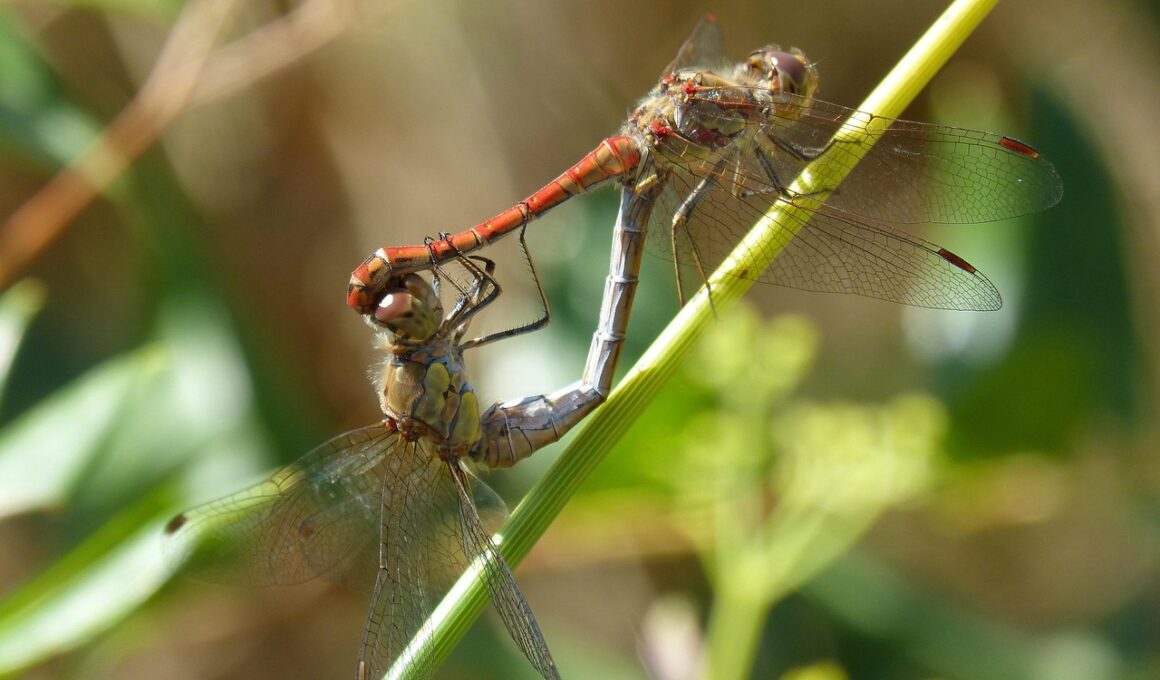
Sensory Mechanisms Behind Synchronization of Mating Activities
The world of animal mating rituals is deeply intertwined with their sensory capabilities. Various species utilize distinct sensory cues during these rituals, which are important for enhancing reproductive success. For instance, the visual, auditory, and chemical senses play significant roles in attracting potential mates. These sensory modalities serve as signals to convey the fitness and readiness of individuals to reproduce. Some species of birds, like the peacock, flaunt their vivid plumage to attract partners, relying on sight. However, other animals, such as insects or mammals, may depend on pheromonal cues, which are often undetectable by human senses yet crucial for initiating reproductive behaviors. Timing is essential in mating synchronization, ensuring that males and females are ready to mate at the same time. This method prevents energy loss in unsuccessful mating attempts. Understanding these synchronization mechanisms can shed light on the delicate balance of ecology and mating dynamics, revealing how environmental factors influence these behaviors. Recognizing the importance of sensory cues is vital for conservation efforts aimed at protecting these species in changing habitats.
In addition to the visual and chemical signals used during mating, auditory cues also play significant roles in many species’ courtship rituals. Birds, for example, produce various songs and calls that serve multiple purposes, including territory declaration and attracting mates. Males often engage in elaborate vocal performances, demonstrating their strength and genetic fitness to potential female partners. These sounds can convey vital information about a male’s health, age, and even availability. Furthermore, the quality of a bird’s song can be a determining factor in mate selection. Similarly, frogs and crickets rely heavily on mating calls, producing distinct sounds to attract the opposite sex. Their calls often vary in pitch and volume, depending on the environmental conditions, which can influence their mating success. Male crickets, for instance, will alter their calls in response to background noise levels. This adaptation highlights the importance of fine-tuning sensory outputs in response to external factors. Understanding these auditory mechanisms further emphasizes the sophisticated nature of mating in animal species and demonstrates the intricate relationship between sensory biology and reproductive strategies.
Chemical Cues in Mating Behavior
Chemical signals, particularly pheromones, are vital in the mating rituals of various animal species. These substances are secreted by individuals to convey messages regarding reproductive status, territory boundaries, or genetic compatibility. Many insects, such as pheromone-sensitive moths and ants, heavily depend on chemical communication for mate attraction. Female moths release specific pheromones to signal their readiness for mating, which can attract males from considerable distances. This chemical cue is potent enough to ensure successful partnerships by guiding males directly to receptive females. Similarly, mammals utilize pheromones to determine reproductive readiness and facilitate mate selection. For example, studies have shown that rodents can detect pheromonal cues through their vomeronasal organ, which plays a significant role in their mating behavior. Olfactory preferences in mate choice can lead to selective breeding, enhancing genetic diversity within populations. By investigating these intricate chemical communication pathways, researchers can develop a better understanding of reproductive strategies and their implications within ecosystems, highlighting the essential role of olfactory cues in animal behavior.
In many species, the interplay between visual, auditory, and chemical signals results in synchronized mating activities that optimize reproductive success. For example, synchrony in reproductive behaviors is crucial among many amphibians and insects, ensuring that males and females engage in mating simultaneously. This timing reduces the chances of wasted energy and increases the likelihood of successful copulation. Environmental cues, such as temperature, moon phases, and social interactions, can significantly influence mating synchronization. Some species, like fireflies, utilize bioluminescent signals to achieve synchronized flashing patterns, attracting mates while creating a visually captivating display. Coordination among individuals is achieved through an impressive response to light stimuli, leading to clouds of flashing individuals. The biological significance of such synchronization extends beyond mere attraction; it can enhance collective reproductive success by ensuring that more eggs are fertilized at the same time, maximizing the survival rate of offspring. Investigating the mechanisms behind this synchronization provides insights into the adaptability of these species in response to ecological factors, ensuring their ongoing survival amidst a changing environment.
Role of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping the sensory cues involved in mating synchronization. Changes in habitat, including seasonal alterations, temperature fluctuations, and food availability, can influence the timing and efficiency of mating activities. For example, many amphibians breed during specific seasons when environmental conditions are most favorable for the survival of their offspring. Temp fluctuations can affect hormone levels in these species, thereby triggering mating behavior at optimal times. Additionally, urbanization poses challenges for many animals, altering their natural habitats and sensory environments. Urban noise pollution can disrupt the mating calls of birds and insects, making communication more difficult and potentially leading to decreased reproductive success. Observing how animals adapt to these changes is crucial for understanding the ongoing impact of anthropogenic influences on wildlife. Furthermore, conservation efforts aimed at preserving natural habitats must account for these environmental challenges to enhance the chances of successful mating and ultimately ensure species survival. The ongoing research into the impacts of environmental factors is critical for developing effective conservation strategies that support the maintenance of healthy and interconnected ecosystems.
In recent years, advancements in technology, such as bioacoustics and olfactometry, have allowed scientists to study animal mating cues more comprehensively than ever before. These modern tools enable researchers to analyze the complex communication systems used in mating synchronizations across various species. By recording and quantifying sound waves, scientists can investigate the rare calls of endangered species or discover new vocalizations that may play roles in mate attraction. Similarly, advancements in detecting pheromones empower researchers to conduct controlled experiments that reveal how different chemical cues influence mate selection. By understanding the intricacies of these sensory mechanisms, we can uncover the vital connections between sensory biology and reproductive success. Moreover, these insights can contribute directly to conservation strategies aimed at preserving vulnerable species by considering their unique sensory requirements. For instance, habitat restoration initiatives can be developed based on knowledge about specific auditory or chemical cues vital to these species. The integration of technology and research is vital for unraveling the complexities surrounding animal reproduction, with the potential to inform future conservation efforts effectively.
Future Directions of Research
Looking ahead, the exploration of sensory cues in mating synchronization represents a vibrant field of research ripe with potential discoveries. New studies should address the impacts of climate change on animal behavior, particularly concerning changes in mating patterns and sensory communication. Investigating how altered environmental conditions affect sensory outputs can provide insights into the resilience of various species. Furthermore, the effects of pollution, urbanization, and habitat destruction on sensory mechanisms are increasingly vital for understanding species decline. Long-term studies focused on the adaptability of these sensory cues over time can unveil strategies animals employ to cope with ecological pressures. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches combining ecology, behavioral science, and technology offer promising avenues for research. Collaborative efforts can lead to greater advancements in conservation and species management, utilizing knowledge gained from sensory studies to develop more holistic ecological strategies. Awareness and understanding of these intricate mating dynamics will ultimately shape our approach to wildlife conservation, ensuring that species can thrive even amidst rapidly changing environments. Continued exploration in this field will undoubtedly yield valuable insights into animal behavior and the importance of sensory cues in securing reproductive success.
In conclusion, understanding the sensory mechanisms behind synchronization of mating activities provides critical insights into the complex relationships between species and their environments. Animal mating strategies are inherently linked to the effectiveness of sensory cues in attracting mates, facilitating reproductive success while navigating challenging ecosystems. The interactions among visual, auditory, and chemical signals shape not only individual mating successes but also broader population dynamics within various habitats. As technological advancements enhance our ability to study these mechanisms, researchers will gain a more profound comprehension of the critical roles sensory cues play in animal behavior. By prioritizing this research, conservationists can devise more effective strategies to protect vulnerable species as they adapt to environmental changes. Addressing the various factors influencing mating synchronization, including subtle environmental cues, will foster an appreciation for the delicate balance of ecosystems. Thus, a comprehensive understanding of mating mechanisms will inspire conservation efforts, ultimately ensuring the survival of diverse species amidst shifting conditions. Efforts to preserve these intricate relationships will encourage sustainable interactions between animals and their environments, contributing to the greater ecological stability of our planet.