Effects of Climate Change on Greenland Shark Populations
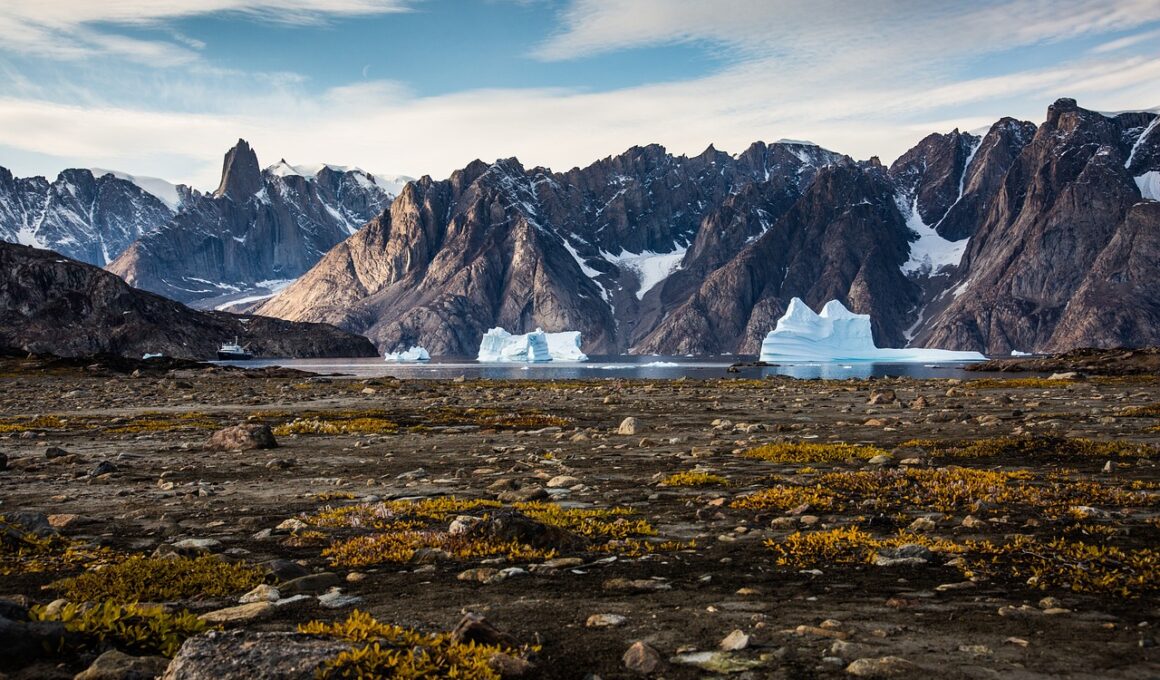
Greenland sharks are unique creatures, thriving in the cold waters of the Arctic. These fascinating animals, known for their slow growth and longevity, face various threats due to climate change. One significant effect concerns the rising ocean temperatures, which can alter their habitats. As the temperature increases, it may affect their prey availability, forcing them to adapt or relocate. This change can lead to decreased survival rates and reproductive success. Furthermore, warmer waters could encourage the migration of other species into their environment, resulting in increased competition for resources. The delicate balance of the Arctic ecosystem is at stake, significantly impacting the Greenland shark populations. Researchers study these impacts extensively, using tracking technology to monitor movements and behaviors. Nevertheless, the effects of changing sea ice conditions also pose a challenge. For instance, melting ice reduces available hunting grounds, which may hinder their ability to thrive and decrease overall population numbers. In harmony with marine conservation efforts, understanding these impacts is crucial to ensure the survival of this remarkable species in a changing world.
Greenland sharks have remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive in frigid waters. They are often found at depths between 200 to 600 meters, where the water remains perpetually cold. However, climate change disrupts these stable environments. Changes in ocean currents can lead to unexpected shifts in habitat and food sources for these sharks. Increased ocean temperatures might also affect their metabolism and growth rate. Research indicates that warmer waters could lead to earlier breeding seasons, impacting their reproductive cycle. Additionally, Greenland sharks are known to have a remarkably slow reproduction rate, resulting in a long wait for populations to recover from declines. As the climate continues to warm, alterations in their breeding patterns may lead to further complications in population sustainability. The interplay between climate conditions and their lifecycle highlights the urgency for conservation awareness. Organizations dedicated to Arctic wildlife are working to raise awareness and gather data on these incredible creatures. Collaborations among scientists, policymakers, and conservationists are necessary to develop effective strategies. By prioritizing shark protection initiatives, we have an opportunity to preserve their populations for future generations.
Human Impact on Greenland Shark Populations
Human activities significantly contribute to the challenges faced by Greenland shark populations. Overfishing remains a pressing concern, as it disrupts the food chain. By depleting fish stocks, overfishing reduces the availability of prey for these sharks. Moreover, bycatch in commercial fisheries also results in the accidental capture of Greenland sharks. This unintended catch can often lead to mortality, undermining population growth efforts. Climate change compounds these issues, as it alters prey distribution and abundance across their habitats. Insufficient understanding of their ecological role can lead to mismanagement of fisheries. Consequently, the population dynamics of Greenland sharks continue to be unstable. Education and awareness are vital to mitigate human impact on these majestic creatures. By informing fishermen about sustainable practices, we can minimize negative interactions. This includes advocating for catch-and-release practices, reducing bycatch, and protecting critical habitats. Additionally, better legal protections could help ensure the survival of Greenland sharks. Fostering community engagement is essential for creating long-term change. Partnerships with local fishery communities can lead to improved conservation efforts, benefiting both their livelihoods and shark populations.
Research into the biology and behavior of Greenland sharks is crucial for understanding their role in the Arctic ecosystem. Scientists employ various methods, including tagging and tracking technology, to gather data on their migrations and breeding habits. Such research is vital for assessing the impact of environmental changes on their population dynamics. The Greenland shark’s unique biology includes an impressive longevity, with some individuals living for over 400 years. This extended lifespan plays a significant role in their slow reproductive rates, complicating conservation efforts. An aging population can be more susceptible to environmental stressors due to the heightened risk of diseases. Investigating their diet is another essential aspect of research. Greenland sharks are opportunistic feeders, consuming fish, carcasses, and even other sharks. This variety in diet underscores their adaptability as predators. However, declining prey availability due to overfishing and climate change poses a threat to their survival. By expanding our understanding of Greenland sharks, we can create data-driven strategies tailored to their conservation. This knowledge will ultimately help establish a thriving, resilient population amidst the rapid changes occurring in the Arctic.
Conservation Efforts for Greenland Sharks
Conservation efforts focused on Greenland sharks are essential for their survival and long-term population stability. Researchers and conservation organizations are advocating for stronger protections and sustainable practices. Collaborating with local communities and fishery industries is critical in this regard. Sustainable fishing practices can help mitigate the effects of overfishing on Greenland shark populations. Initiatives aimed at monitoring shark populations are also underway globally. Data collection enhances our understanding of their conservation needs. Additionally, creating marine protected areas can provide safe havens for these vulnerable species. Such protected spaces are crucial for facilitating breeding and maintaining prey availability. Public awareness campaigns also play a significant role in conservation. Educating communities and stakeholders about the importance of Greenland sharks fosters a sense of responsibility for their future. Moreover, research partnerships empower local environments to track changes while recommending evidence-based policies. Incorporating indigenous knowledge about local environments enriches the conservation perspective and adds value. The road to successful conservation of Greenland shark populations requires a combined effort from researchers, policymakers, and local communities passionate about protecting their Arctic waters.
Looking forward, the future of Greenland sharks is uncertain amidst ongoing climate change. As temperatures continue to rise, the effects on their populations remain unpredictable. Several questions arise concerning their adaptive capacity in response to shifting ecosystems. These inquiries necessitate ongoing research to monitor populations closely and assess the ecological impact of these adaptations. Maintaining healthy, stable Greenland shark populations is vital for the broader Arctic marine ecosystem. Their presence maintains balance and stability in the food web, making their conservation critical. Climate models predict that further ice melt could significantly alter their habitats and patterns. Implementing conservation measures proactively may help buffer against these changes. Emphasizing collaboration and adaptive management strategies will allow stakeholders to respond to climate impacts effectively. Creating supplemental research initiatives focused on the interconnectedness of species can yield valuable insights. This holistic approach provides a better understanding of how climatic changes affect various marine life forms. Assessing Greenland shark populations’ health is paramount, ensuring their role within the ecosystem is preserved through climate resilience and conservation planning.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the effects of climate change on Greenland shark populations highlight the need for urgent attention. Rising temperatures, habitat destruction, and human impacts pose significant threats to their survival. Conservation strategies and proactive management approaches are mandatory to ensure their long-term viability. Continuous monitoring of populations and fishing practices creates opportunities for recovery and restoration. Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and local communities will strengthen conservation efforts and yield meaningful results. Education about the Greenland shark’s ecological importance will inspire action toward their protection. Selecting conservation strategies with the flexibility to adapt to ongoing changes is essential. As the Arctic environment evolves, so too must our approaches to safeguard these creatures. Each species in the Arctic plays an integral role, sustaining an interconnected ecosystem facing numerous challenges. As advocates for the environment, it is our responsibility to amplify awareness and deploy strategies that protect Greenland sharks for future generations. Their survival is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of the Arctic environment, urging us to act deliberately and foster a commitment to conservation.
This closing section emphasizes the significance of studying and protecting Greenland sharks due to the profound effects of climate change. Additionally, understanding how these creatures adapt to their shifting environment is vital for enhancing conservation efforts. Collective responsibility manifests through individual actions, from reducing plastic pollution to supporting sustainable seafood initiatives. Recognizing the impacts of human activity on wildlife can foster environmental stewardship. In acknowledging their ecosystems’ complexity, we are reminded that preserving the Greenland shark invites respect for the entire Arctic habitat. Collaboration among scientists, local communities, and policymakers enables comprehensive solutions to ensure these species thrive despite rapid changes. The Arctic’s future hinges upon our commitment to conserving such unique wildlife within its boundaries. By being proactive, we can support the delicate interactions forming the backbone of the Arctic marine ecosystem, enabling Greenland sharks to continue flourishing for generations to come. Through innovative strategies and adaptive management, there’s an opportunity to safeguard their future amid climate challenges. Protecting Greenland sharks can inspire broader initiatives that benefit all Arctic wildlife, creating a ripple effect for marine conservation worldwide.