Role of Tropical Mountain Animals in Seed Dispersal and Pollination
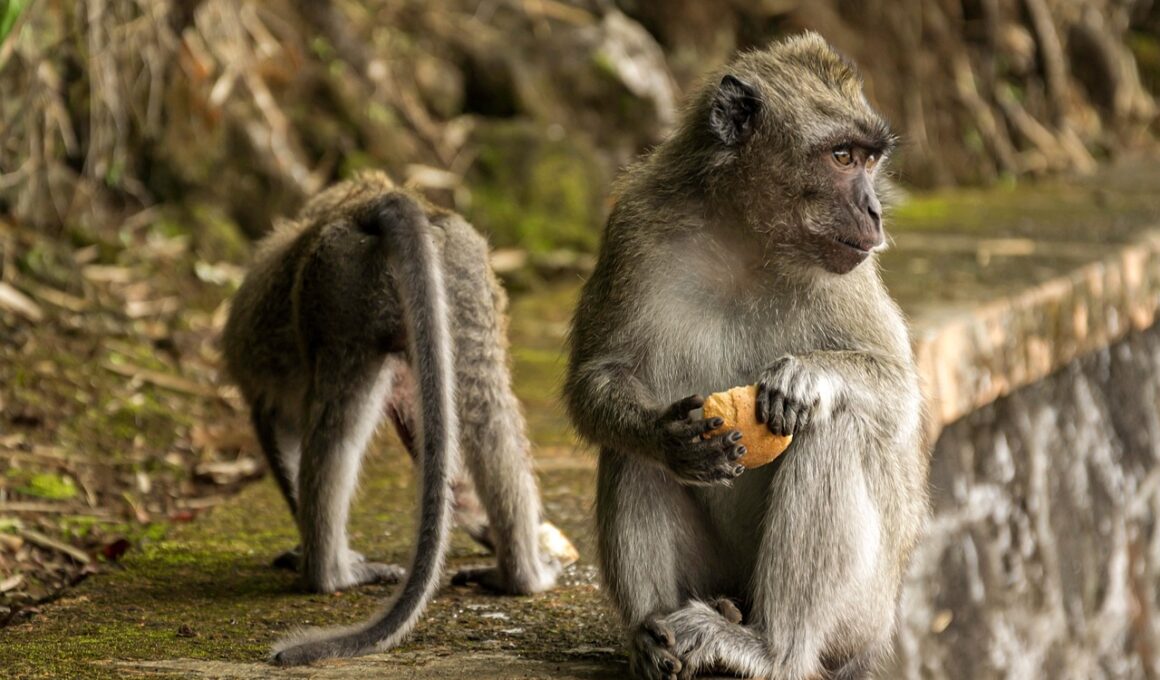
Tropical mountain animals play a pivotal role in ecosystems, particularly in seed dispersal and pollination. These animals include a wide range of species, from birds and bats to insects and mammals, all of which contribute significantly to the reproductive success of many plants. For instance, various bird species, such as the toucan and the hummingbird, are known to feed on nectar and fruits, inadvertently assisting in the transfer of pollen or the distribution of seeds over large areas. The movement of these animals across different altitudes in mountainous regions enhances genetic diversity among plant populations. Furthermore, some animals consume fruits and excrete the seeds far from the parent plant, enabling colonization in new locations. This process is essential for plant survival, especially in changing climates and fragmented habitats. Without these animal partners, many tropical mountain plants would struggle to reproduce effectively. The interdependence between flora and fauna in these ecosystems is a fascinating aspect of environmental science that shows importance in conservation efforts, aimed at preserving both animal and plant species, which are vital for healthy ecosystems.
Seed dispersal facilitated by tropical mountain animals also significantly impacts forest regeneration and habitat stability. Numerous animal species, such as howler monkeys and agoutis, consume fruits and carry seeds from one area to another, aiding in the creation of diverse plant communities. This variety in plant life not only serves as habitat for countless other species but reinforces the entire ecosystem’s resilience against disturbances like wildfires and extreme weather events. The relation is reciprocal, as healthy plant populations provide essential resources like food and shelter for animal species. Moreover, intact plant communities offer vital environmental services such as soil stabilization, preventing erosion, and regulating water flow. Particularly in mountainous regions, these functions are indispensable for protecting against landslides and maintaining ecosystem balance. Conservation initiatives focusing on protecting tropical mountain animals are therefore crucial for sustaining their roles in seed dispersal. Efforts such as the establishment of protected areas and wildlife corridors can encourage robust interactions between animals and plants. Continued research into these interdependencies will enhance our understanding of ecological dynamics and underscore the importance of biodiversity in maintaining global ecosystems.
Importance of Pollination
Pollination is another critical service provided by tropical mountain animals, with many species acting as pollinators for various flowering plants. Bees, butterflies, and bats are particularly noteworthy for their contributions to pollination processes. For instance, bats play a significant role in pollinating night-blooming species, supporting the reproductive cycle of plants that might otherwise go unpollinated. The loss of these pollinators due to habitat destruction or climate change can have dire consequences for many species and entire ecosystems. Studies have shown that when pollinator populations decline, it often leads to reduced plant diversity and decreased food resources for other species, creating a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem. As these animals visit flowers in search of nectar, they transfer pollen between plants, promoting genetic exchange and enhancing the vitality of plant populations. The effectiveness of pollination is influenced by factors such as the availability of diverse floral resources and the presence of suitable habitats for pollinator species. Efforts to preserve habitats that support both plants and their animal pollinators are essential for maintaining the ecological balance within these vibrant tropical mountain environments.
The significance of tropical mountain animals extends beyond just seed dispersal and pollination; these creatures also contribute to the overall health of ecosystems. For instance, some animals help in seed predation, where they consume seeds, thus regulating plant populations. This predatory relationship can control the abundance of certain species, allowing for increased biodiversity within the ecosystem. Moreover, various mammals and birds can even shape the growth of plants through their foraging behaviors. By selectively feeding on certain species, these animals can influence plant community composition and productivity. Tropical mountains serve as unique ecological niches, where these interactions between flora and fauna play essential roles in maintaining the life balance. Beyond ecological implications, these interactions have also inspired various cultural elements in local communities, highlighting the intrinsic connection between nature and humans. Indigenous peoples often recognize the importance of certain animals in their cultural practices, as these species have direct implications on agriculture and sustainability. Therefore, the conservation of tropical mountain animals and their habitats must also consider these socio-cultural dimensions and the myriad ways they enrich human life and contribute to ecosystem stability.
Conservation and Biodiversity
Conservation efforts are fundamental in protecting tropical mountain animals and their roles in ecosystems. As habitat loss and climate change pose significant threats, various strategies must be pursued to maintain biodiversity. Establishing protected areas and wildlife corridors has proven effective in allowing animals to migrate and thrive. Involving local communities in conservation initiatives also ensures that the cultural knowledge related to these species is preserved. Environmental education plays a significant role, raising awareness about the vital contributions of animals in ecological processes such as pollination and seed dispersal. Grassroots conservation efforts can empower local populations to safeguard their natural surroundings. Furthermore, scientific research can help identify at-risk species and create targeted conservation plans, ensuring that both flora and fauna can persist. Engaging with governments and global organizations can mobilize resources for tropical mountain conservation projects. The significance of preserving these ecosystems goes beyond ecological considerations; it aligns with global sustainable development goals aimed at achieving food security and safeguarding diverse ecological resources. A holistic approach that integrates ecological science with community involvement is crucial for the long-term survival of tropical mountain animals and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Furthermore, the interconnectedness between seed dispersal, pollination, and animal species illustrates the complexity of tropical mountain ecosystems. Eradicating one link in this chain can have far-reaching consequences that disrupt not just plant life, but the entire ecosystem’s function. Moreover, the threat posed by invasive species further complicates these ecological relationships. Invasive species can outcompete native plants and pollinators, eventually leading to a decline in native biodiversity. Consequently, targeted management practices are necessary to control invasive organisms and protect native species. Sustainable land use practices also play a significant role in maintaining the balance within these habitats. Integrating agriculture with natural ecosystems helps preserve biodiversity and allows for coexistence between farming and wildlife conservation. Implementing agroforestry systems can enhance habitat connectivity and improve overall ecosystem health. Promoting policies that support biodiversity alongside agricultural development can also foster resilience against climatic changes. Tropical mountain regions, with their unique challenges and rich biodiversity, must be prioritized in national and international conservation agendas. Recognizing the critical role of animals in maintaining ecosystem health will be essential for effective conservation strategies.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, tropical mountain animals play indispensable roles in seed dispersal and pollination, showcasing the intricate relationships within these ecosystems. Their presence is vital for maintaining plant diversity, ensuring ecological balance, and providing essential ecosystem services. Ongoing conservation efforts must consider the multifaceted roles of these animals while addressing contemporary challenges posed by climate change and habitat loss. Future research should focus on understanding how these interactions are changing and what these shifts mean for ecosystem resilience. Engaging local communities in these efforts can enhance the effectiveness of conservation strategies by incorporating traditional knowledge and fostering stewardship for local biodiversity. Moreover, collaboration among stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and researchers, can amplify the impacts of conservation initiatives. Strategies must be adaptive, responding to ecological changes and utilizing scientific findings to inform management decisions. The future of tropical mountain ecosystems depends on recognizing the significance of their animal inhabitants and actively working to ensure their survival. By protecting these animals, we safeguard the intricate web of life they support, highlighting the need for continued commitment to conservation and biodiversity on a global scale.
Ultimately, a holistic approach to conservation, combining ecological understanding, community engagement, and sustainable practices, will be essential. As we learn more about the vital contributions of tropical mountain animals, we can create informed policies and initiatives that promote biodiversity and resilience in these rich ecosystems. Protecting tropical mountain animals and their habitats is not merely an ecological necessity; it is a commitment to preserving the intricate interconnections of life on Earth for generations to come.