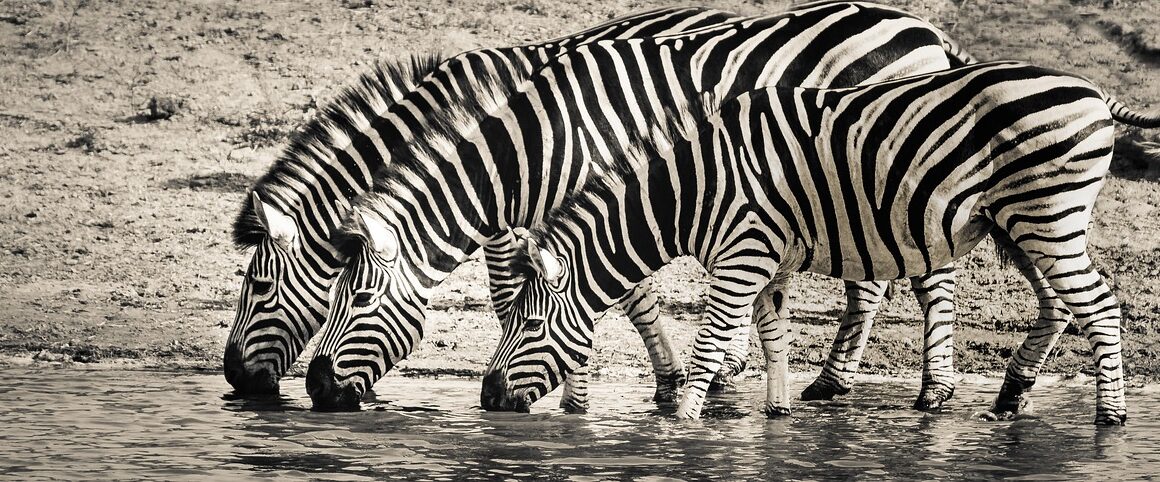
Savanna Mammals and Their Water Conservation Techniques
The savanna ecosystem, characterized by grassy plains and scattered trees, supports a rich diversity of mammals that have developed remarkable water conservation techniques. These adaptations are vital for their survival in an environment where water is often scarce, particularly during the dry seasons. Notable examples of these mammals include elephants, antelopes, and lions. Each species uniquely tackles the challenge of limited water resources. For instance, elephants are known to dig wells to access underground water. Antelopes typically graze during cooler periods, conserving moisture in their bodies and minimizing the need for water. Lions, on the other hand, may go days without drinking. Instead, they obtain moisture from their prey, optimizing their water intake. The interplay between these mammals and their environment enhances the savanna’s ecological balance. Understanding these survival strategies encourages further research and conservation efforts. By emphasizing the importance of preserving their habitats, we can help ensure that these incredible animals continue to thrive in their native landscapes. Successful conservation depends on addressing both water management and habitat preservation for long-term ecological health.
Another profound adaptation found among savanna mammals relates to the structure of their kidneys. Various species, particularly herbivores like giraffes and zebras, have highly efficient renal systems that effectively filter and conserve water. These adaptations allow them to maintain hydration while consuming plants that may contain high amounts of salt. Living in such harsh conditions forces these animals to adapt to survive, with revolutionary changes in their physiological makeup. For instance, the ability to produce concentrated urine means that they can expel excess minerals while retaining valuable water. Additionally, some mammals can tolerate dehydration to a more significant extent than other animals. Consequently, they have the ability to withstand longer periods without drinking water directly, relying on the moisture found in their food. Furthermore, by being active mainly at night or during cooler periods of the day, these mammals lessen water loss due to evaporation. As this adaptability highlights, the intricate relationships between species and their habitats are essential for survival in the savanna. Overall, these water conservation techniques illuminate the resilience of wildlife amid climate variability and habitat changes.
Behavioral Adaptations That Ensure Survival
Many savanna mammals exhibit behavioral adaptations that enhance their chances of survival in arid environments. Social structures often dictate foraging strategies and water gathering. For example, elephants frequently travel in family groups, which allows them to share information about water sources. Through communication, these groups can locate hidden wells during the dry season, ensuring the whole family has access to drinking water. Other species, like meerkats, maintain intricate social structures that benefit group survival. By ensuring that some members stay on lookout, they can efficiently forage while mitigating the risks associated with predation. Grazing animals, such as buffalo or wildebeest, often migrate across vast distances in search of greener pastures and available water. This seasonal movement allows them to exploit resources more efficiently. As environments shift due to climate change, behaviors will also adapt over time, which could significantly impact species survival. Understanding these social and behavioral strategies is crucial for conservation efforts aimed at preserving the intricate web of life within savanna ecosystems. These adaptations signify the importance of community in a challenging environment where every water source becomes a lifeline.
Moreover, the way savanna mammals regulate their body temperature plays a pivotal role in their water conservation efforts. Many species develop behaviors that minimize sun exposure and prevent overheating, which directly conserves water within their systems. For example, animals like the African wild dog often rest in the shade during peak sunlight hours, thereby reducing their metabolic rate while conserving moisture. This behavioral trait is essential, especially during the hot summer months when dehydration risks escalate. Conversely, species such as the brown hyena exhibit nocturnal habits, primarily hunting at dusk or in the early morning hours. Such adaptations ensure they remain cooler, preventing excessive water loss through sweating. Additionally, several mammals adjust their activity levels according to temperature fluctuations, aligning their eating and drinking schedules with optimal weather conditions. By employing these strategies, savanna mammals enhance their chances of survival in conditions where water scarcity is a constant threat. These adaptations not only highlight their resilience but also underline the significant relationship between an animal’s behavior and its ability to thrive in the harsh savanna ecosystem.
The Role of Diet in Water Conservation
Diet choices are another critical factor influencing water conservation strategies among savanna mammals. The diets of these animals are abundant in fibrous plants, fruits, and leaves, each containing varying moisture levels. Herbivores such as elephants and giraffes consume significant quantities of moisture-rich vegetation. By doing this, they fulfill part of their hydration needs through their diet. Giraffes, for instance, are known to feed on acacia leaves, which provide both nutrition and water. On the other hand, carnivorous mammals like lions adapt their diet to hunt prey that can supply them with necessary moisture. Prey animals contain a higher percentage of water, enabling lions to meet their hydration requirements. Additionally, some mammals develop foraging habits geared toward seeking out water-rich plants, particularly during times of drought when access to free-standing water is limited. By adapting their dietary habits, these mammals optimize their nutrition while concurrently minimizing their dehydration risks. Recognizing these dietary behaviors provides valuable insights into the intricate connections between savanna mammals and their environments.
When it comes to landscape changes, savanna mammals exhibit exceptional adaptability, allowing them to respond to environmental challenges effectively. Climate change, habitat destruction, and other anthropogenic factors significantly impact water availability in savanna ecosystems. Some mammals, such as migratory animals like wildebeests, demonstrate considerable resilience against these evolving conditions. They can adapt their migration patterns in response to shifting water sources caused by climate change. Consequently, these adaptive journeys enable them to seek food and water, promoting their chances of survival despite habitat fluctuations. Alterations to grazing areas require animals to adjust their routes and social structures, which can influence overall herd dynamics. These shifts in behavior ultimately reshape savanna landscapes, reflecting the delicate interplay between animals and their ecosystems. Conservation strategies targeting the protection of migratory routes and critical habitats are vital to ensure the survival of these mammal populations amid ongoing environmental changes. By committing to habitat preservation efforts, communities can support the overall health of savanna ecosystems along with the diverse wildlife that depend on them.
Conclusion: The Importance of Conservation
In conclusion, the remarkable water conservation techniques observed in savanna mammals illustrate their capability to thrive amidst challenging environments. From behavioral adaptations to sophisticated dietary choices, these animals demonstrate a complex understanding of their habitats. Additionally, their resilience in response to changing landscapes emphasizes the need for continued conservation efforts. Without proper stewardship, ongoing climate change and habitat destruction threaten the delicate balance of savanna ecosystems. By implementing effective conservation practices and prioritizing the preservation of habitats, we can protect these incredible animals. This ensures the survival of not just individual species, but entire communities within the savanna ecosystem. Awareness and education play crucial roles in advocating for wildlife conservation and instilling values in future generations. By fostering a culture of sustainability and ecological responsibility, we empower communities to take action for the benefit of wildlife and their habitats. The future of savanna mammals depends on our commitment to preserving the intricate connections between species and their environments. Together, we can work towards a sustainable coexistence that benefits all living forms in these vibrant ecosystems.
Ultimately, collaborating with local communities and stakeholders is key to ensuring successful conservation initiatives. Engaging those who live in close proximity to savanna ecosystems can help inform strategies tailored to specific regional challenges. Local knowledge and involvement can significantly enhance the effectiveness of conservation efforts. By ensuring that the voices of local communities are heard, a sense of shared ownership over wildlife preservation can be cultivated. This community-based approach not only fosters environmental stewardship but also enhances social and economic livelihoods for those reliant on natural resources. Educating and empowering local populations regarding sustainable practices is instrumental in forging pathways toward ecological resilience. As we develop innovative conservation measures, an integrated approach that values both biological diversity and cultural heritage will yield beneficial outcomes for all. The delicate balance of savanna ecosystems can only be maintained through collaborative efforts that respect ecological systems and local traditions. Ultimately, the future of savanna mammals hinges upon our collective responsibility to advocate for their survival, safeguarding the natural resources that sustain these magnificent creatures in a world increasingly marked by change.