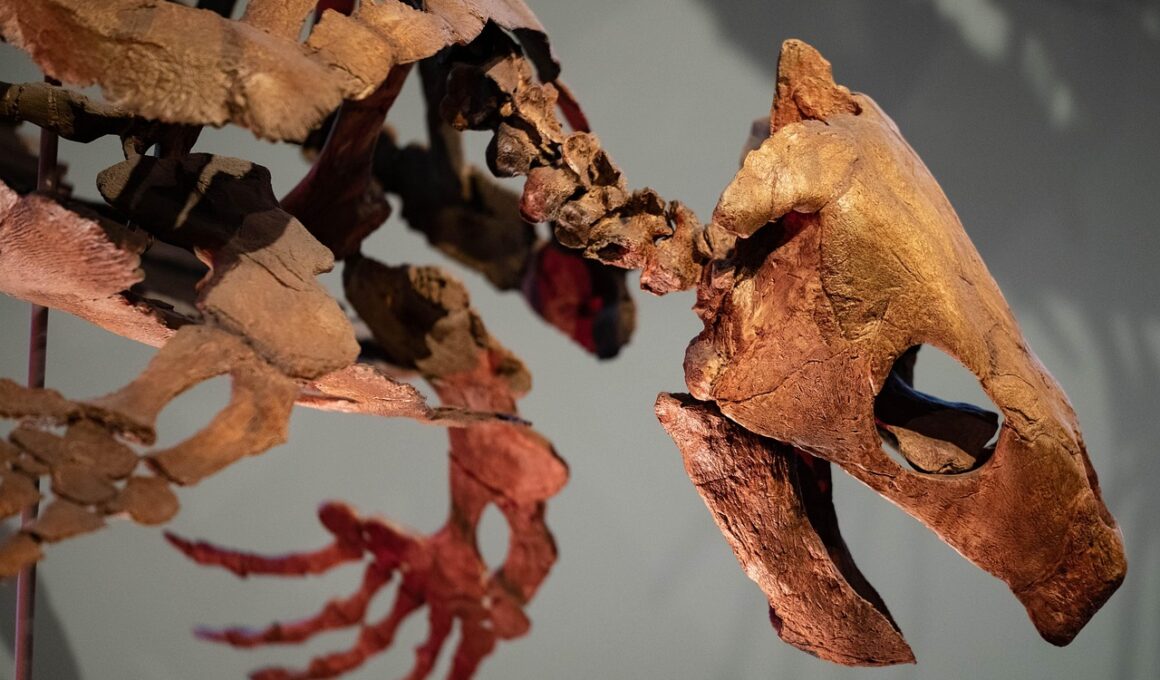
The Rise and Fall of the Gavialoids: Extinct Long-Snouted Crocodyliforms
The Gavialoids were a distinct group of long-snouted crocodyliforms that lived during the Late Cretaceous to the late Cenozoic. Known for their unmistakable appearance, Gavialoids had elongated jaws filled with slender, sharp teeth designed for catching agile prey like fish. They thrived in freshwater environments, particularly in river and lake ecosystems. As specialized predators, they displayed unique adaptations that distinguished them from other crocodilians. Their long snouts reduced drag while swimming, giving them significant advantages when hunting aquatic organisms. Fossil evidence shows they were distributed across various continents including Europe, Asia, and North America, suggesting they adapted to a range of environments. The evolutionary history of the Gavialoids tells a fascinating tale of adaptation and survival. Through the exploration of their fossil records, scientists can piece together their lifestyle and ecological roles. Understanding where they fit in the broader context of crocodyliform evolution provides insight into how these creatures interacted with their environment and each other. Despite their diverse adaptations, Gavialoids eventually faced extinction due to changing climates and ecological pressures.
The decline of Gavialoids was gradual yet significant, reflecting shifts in environmental conditions that challenged their existence. As their habitats transformed due to climate change and fluctuating water levels, these reptiles struggled to find suitable locations for hunting and breeding. Rival species, particularly more versatile crocodilians, began to outcompete them for resources. This competitive pressure was compounded by the expansion of terrestrial environments that drew prey away from aquatic habitats. Fossil records indicate a reduction in Gavialoid diversity toward the end of the Miocene epoch. Their likely failure to adapt quickly enough to these rapid changes in their ecosystems made them increasingly vulnerable. Researchers hypothesize that factors such as habitat fragmentation and competition may have collectively weakened their populations. Over time, the few remaining Gavialoid species gradually disappeared from various regions. The extinction of the Gavialoids serves as a potent reminder of the delicate balance within ecosystems and how quickly species can be affected by environmental changes. The layers of extinction reveal the complex interactions between species and underline the importance of biodiversity in sustaining life. Gavialoids’ ancient legacy continues to inform ongoing conservation efforts today.
Ecosystem Impact of Gavialoids
During their reign, Gavialoids played an essential role in their ecosystems. They were primarily piscivorous, meaning fish made up a significant part of their diet. Their hunting methods involved stealth and precision, allowing them to catch fast-moving aquatic prey efficiently. This predatory behavior likely helped regulate fish populations, maintaining balance within their habitats. By controlling fish numbers, Gavialoids indirectly promoted biodiversity, enabling other species to thrive alongside them. Their presence in the food web illustrates the importance of apex predators in sustaining ecological stability. When Gavialoids eventually went extinct, the absence of such top predators may have led to unpredictable shifts in aquatic ecosystems. Fish populations could have experienced explosive growth, negatively impacting plant life and causing other imbalances. Paleontological studies reveal a cascading effect following the extinction of apex predators. Cooperation among surviving species may become challenging without such ecological checks in place. As the dynamics shifted, smaller predators that previously had limited influence could have changed their feeding behaviors, leading to further unpredictability. Additionally, the overall health of river and lake systems may have declined without the natural filter systems provided by Gavialoids.
Throughout their existence, Gavialoids showcased remarkable adaptations to their aquatic environments. From their streamlined bodies to their specialized snout shapes, these characteristics highlight the evolutionary pressures they faced. Among the most fascinating features is the narrow, elongated jaw structure, designed for catching slippery prey. This distinctive adaptation is evident in modern gharials, which are their closest living relatives. Gavialoids exhibit notable convergent evolution, wherein distinct species develop similar traits because of comparable environmental pressures. By studying these adaptations, researchers can gain insight into the parallel challenges faced by these ancient reptiles and contemporary crocodilians. The morphological traits of Gavialoids adapted over time, demonstrating the relationship between form and function in evolutionary biology. Additionally, fossil discoveries of various Gavialoid species showcase a diverse range of adaptations catering to their ecological niches. The skeletal features from different habitats signify a lineage of animals that thrived in varied environments, illustrating their resilience. Paleocene records suggest these reptiles were experimenting with new shapes and sizes while adapting. Their multi-faceted evolutionary journey contributes to our understanding of how species might respond to future environmental changes.
Fossil Evidence and Discoveries
Fossil discoveries have vastly enriched our understanding of Gavialoid evolution and their ecological roles. Significant finds in regions such as India, North America, and Europe have illuminated aspects of their lives. These fossils provide critical insights into the morphology, behavior, and habitats of these extinct reptiles. Each fossil site reveals a unique snapshot of Gavialoid diversity, showcasing various species that once roamed the earth. Through sediment analysis, researchers reconstruct the environments in which Gavialoids thrived, deepening our appreciation for their adaptability. The abundance of fossilized remains often shows evolutionary patterns across great spans of time. Paleontologists often employ advanced techniques, utilizing CT scans and 3D modeling, to visualize internal structures. This approach allows for more precise interpretations of how these creatures functioned and lived. Each discovery raises more questions about the evolutionary lineage of crocodyliforms, with Gavialoids standing out as an example of successful adaptation. Examining these remains sheds light on the biodiversity of ancient ecosystems, presenting a profound understanding of the past. Their story also illustrates how science continues to incrementally uncover the mysteries surrounding extinct species.
The extinction of Gavialoids serves as a vital lesson in understanding biodiversity and the potential impacts of environmental changes. Their fate emphasizes the interconnectedness of species within ecosystems and highlights the cascading impacts that can occur when predators vanish. Changing climates and evolving habitats challenge both ancient and contemporary species. The loss of Gavialoids reiterates the critical need for ongoing conservation efforts, as many current crocodilian species face similar pressures. As environmental changes accelerate, lessons from the Gavialoids can inform strategies to protect vulnerable species. Preserving biodiversity ensures ecological resiliency in the face of inevitable shifts. Protecting habitats and reinforcing ecosystems can help maintain balance and stability across various environments. The survival of biodiversity can be supported by educating communities about species interdependence. Collaborative efforts between scientists and conservationists are pivotal in safeguarding contemporary ecosystems and raising awareness. The Gavialoids’ ancient legacy, coupled with contemporary challenges, illustrates the paramount importance of protecting the planet’s biodiversity. By drawing on the lessons learned from the extinction of these fascinating reptiles, we can strive toward a future where ecosystems flourish.
Conclusion: Lessons from Gavialoids
The saga of Gavialoids encapsulates both their remarkable adaptations and the vulnerabilities they faced. Understanding the factors contributing to their extinction provides vital insight into the consequences of changing environments. Their journey reflects broader themes of evolution, adaptation, and survival that resonate across the animal kingdom. By studying the Gavialoids, we acknowledge the delicate balance of ecosystems influenced by competition, climate, and ecological dynamics. The extinction of these ancient reptiles serves as a clarion call for conservation efforts today. As we face climate challenges and habitat loss, recognizing past extinction events can guide current decision-making. The principles drawn from the Gavialoids’ experiences underscore the urgency of preserving biodiversity in our ecosystems. Ensuring the survival of aquatic ecosystems and their inhabitants requires collective action and awareness. By addressing the factors that threaten modern species, we can work toward a sustainable future. Gavialoids remind us of the extraordinary richness of life that once existed and the responsibilities we hold in ensuring that future generations inherit a thriving planet.