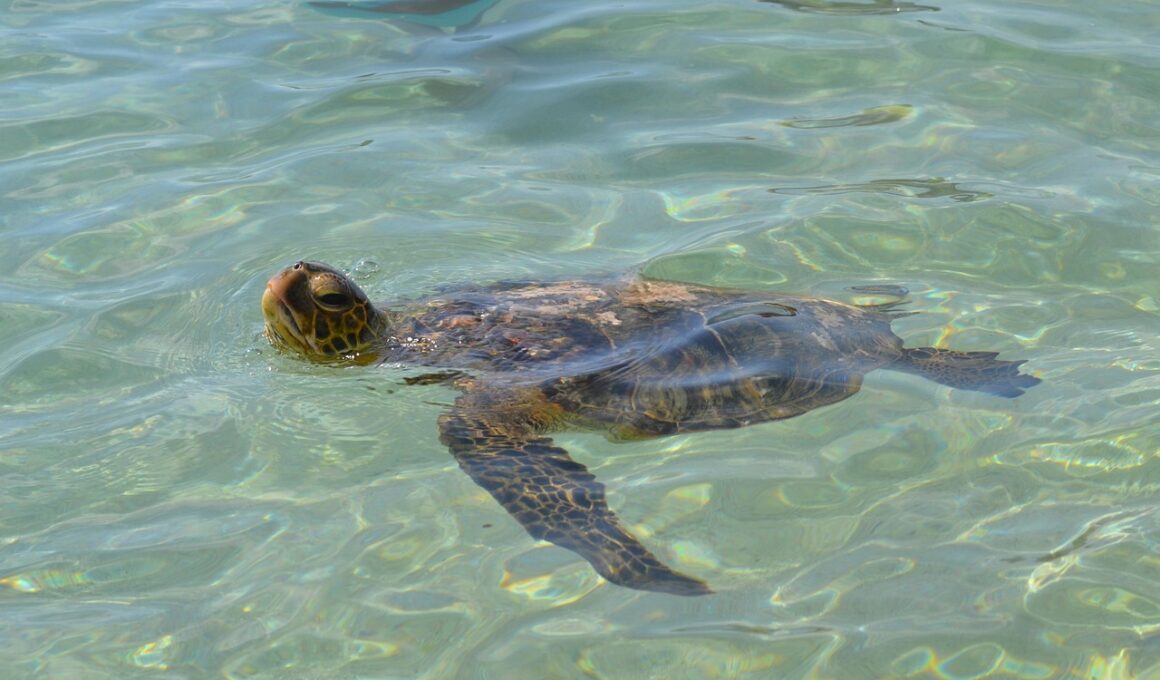
Understanding Endangered Marine Animals
Marine animals are critical components of Earth’s ecosystems, yet many face dire threats due to human activities. Overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change contribute to the declining populations of various species, prompting urgent conservation efforts. Key endangered marine animals include the Hawksbill Turtle, Vaquita, and Blue Whale, each suffering from distinct challenges. The Hawksbill Turtle, for instance, is hunted for its beautiful shell, while the Vaquita, a small porpoise, suffers from bycatch in fishing nets. The Blue Whale, despite being the largest animal on Earth, is endangered primarily due to ship strikes and entanglement. Understanding these threats enables us to develop effective conservation strategies tailored to each species. Marine protected areas (MPAs) have become vital tools in safeguarding habitats. However, the commitment to sustainable fishing practices and regulations is equally crucial. Public awareness and education are essential for fostering community involvement in conservation. Protecting these splendid creatures not only preserves biodiversity but also sustains the health of our oceans, benefiting countless future generations. Each small step towards conservation plays a significant role in ensuring that marine ecosystems continue to thrive sustainably.
Threats Facing Marine Species
The threats jeopardizing marine species’ survival are multifaceted and interconnected. Climate change is warming oceans and disrupting habitats, affecting food webs and reproductive patterns. In addition, ocean acidification poses severe risks to coral reefs, essential for many marine organisms. Pollution, particularly plastic waste, directly threatens marine life. Animals ingest or become entangled in plastic debris, leading to suffering and death. Furthermore, unsustainable fishing practices deplete fish stocks and harm ecosystems. Bycatch, the unintended capture of non-target species, is particularly devastating, endangering species like sea turtles and dolphins. Increased shipping and maritime traffic also pose threats through ship strikes and noise pollution, disrupting communication among marine animals like whales. Habitat destruction from coastal development further exacerbates pressures on these species. Consequently, urgent action is required to address these challenges. Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and local communities is essential for developing and implementing conservation initiatives effective in reducing these threats. Comprehensive policies focusing on habitat restoration, pollution control, and sustainable fishing practices can significantly mitigate adverse effects. Engaging the public in conservation efforts raises awareness and promotes stewardship, ensuring marine species are preserved for future generations.
Conservation Success Stories
Despite the significant challenges facing marine species, there are notable conservation success stories that inspire optimism and drive further efforts. One exemplary case is the recovery of the California Sea Lion, which once faced severe population declines due to hunting and habitat loss. Through protective regulations and habitat restoration, their population has rebounded dramatically, showcasing the impact of effective management strategies. Another heartening story is that of the Green Sea Turtle, which has shown signs of recovery thanks to the implementation of marine protected areas and global conservation initiatives. Collaborative efforts among governments, scientists, and local communities have reduced bycatch and improved nesting sites. The return of the Beluga Whale in certain regions demonstrates the success of conservation measures aimed at reducing ship traffic and underwater noise pollution. These stories exemplify that and illustrate how concerted efforts can yield tangible benefits. They also highlight the importance of continuous monitoring and adaptation of strategies, ensuring they remain effective. By celebrating these victories, we can foster a culture of conservation that encourages innovative solutions and collective responsibility in protecting marine ecosystems and the creatures that inhabit them.
Engaging Communities in Conservation
Local communities play a pivotal role in marine conservation, which fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards local ecosystems. Engaging communities in conservation initiatives leads to more sustainable practices and better outcomes for endangered species. Education programs targeting schools raise awareness about marine conservation, emphasizing how local actions can impact global issues. Workshops that teach sustainable fishing methods empower local fishermen, allowing them to profit while protecting marine habitats. Successful programs focus on the integration of traditional knowledge with modern conservation techniques, resulting in innovative solutions tailored to unique challenges faced by communities. For instance, involving local fishers in monitoring and research fosters a collaborative spirit and ensures that their expertise informs management decisions. Community-led marine reserves have shown remarkable success in preserving biodiversity and enhancing fish stocks. Furthermore, involving communities in eco-tourism initiatives creates alternative livelihoods, incentivizing the conservation of marine environments. Promoting stewardship in local populations is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. By highlighting the direct benefits of healthy marine environments, we cultivate a collective commitment to protecting these vital ecosystems and the incredible species that inhabit them, ensuring their survival for generations to come.
International Agreements and Frameworks
International agreements play a crucial role in advancing marine conservation efforts worldwide. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) aims to enhance and protect biodiversity, including marine ecosystems, by promoting collaboration among countries. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) prioritize the conservation and sustainable use of oceans, highlighting the importance of international cooperation in addressing marine challenges. Another crucial agreement is the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which regulates trade in endangered species and plays a pivotal role in protecting vulnerable marine animals like sharks and sea turtles from over-exploitation. Additionally, regional organizations like the International Whaling Commission (IWC) work towards the conservation and management of whale populations, setting sustainable quotas and implementing protection measures. Effective implementation of these agreements requires strong governance, commitment, and collaboration among nations to enforce regulations and monitor compliance. By fostering international dialogue and cooperative actions, we can build a more sustainable future for marine species. Ultimately, these frameworks unite efforts across borders, emphasizing collective responsibility for ocean stewardship and the vital need to protect endangered marine life on a global scale.
Innovative Technologies in Marine Conservation
Advancements in technology have revolutionized marine conservation, introducing innovative tools and methods to monitor and protect endangered species. Satellite tracking is one of the most significant breakthroughs, allowing researchers to follow the migratory patterns of marine animals, such as sea turtles and whales, providing insights vital for conservation efforts. Drones are also proving to be invaluable for monitoring marine habitats, conducting aerial surveys, and detecting illegal fishing activities, enhancing surveillance capabilities for conservationists. Artificial Intelligence (AI) contributes to analyzing large data sets, facilitating the identification of trends and patterns in marine species populations. Underwater cameras and acoustic monitoring devices help in gathering data about elusive species and understanding their behavior, improving conservation strategies. Moreover, advancements in bioacoustics enable researchers to monitor marine mammal communication, ensuring better management of underwater noise pollution. Citizen science initiatives leverage technology by encouraging public participation in data collection, fostering a sense of community ownership in conservation efforts. By integrating innovative technologies into marine conservation practices, we significantly enhance our ability to protect endangered species while fostering collaborative efforts among researchers, communities, and stakeholders.
The Path Forward for Marine Conservation
The future of marine conservation relies on our commitment to protect endangered species and restore marine ecosystems. Strategies should incorporate community engagement, emphasizing the shared responsibility for safeguarding marine life. Implementing effective policies and regulations plays a vital role in preserving marine biodiversity. Additionally, the enforcement of established agreements is crucial for achieving long-term sustainability. Stakeholder collaborations among governments, NGOs, and local communities create a diverse network of support, empowering initiatives aimed at biodiversity conservation. Innovation must continue to drive marine conservation efforts, with a focus on embracing cutting-edge technologies for monitoring and protecting species. Raising public awareness and support can enhance conservation funding and increase community involvement. Educational programs will not only cultivate a generation of conservation leaders but will also inspire collective action toward sustainability. Lastly, continuous research is crucial for understanding the complex dynamics of marine ecosystems and species interactions. A holistic approach that incorporates diverse knowledge and perspectives can enhance robustness, resulting in more effective strategies. Ultimately, by working together, we can create thriving, resilient marine ecosystems, ensuring endangered species continue to flourish and contribute to the health of our planet.
Conclusion: Vital Importance of Marine Species
In conclusion, protecting endangered marine species is of paramount importance for maintaining ocean ecosystems and overall planetary health. As stewards of the environment, it is our duty to safeguard these species and their habitats from the looming threats caused by human activity. Successfully executing conservation efforts that combine policy enforcement, community engagement, technological innovation, and education can lead to substantial positive impacts on marine biodiversity. Every individual can contribute in meaningful ways through advocacy, responsible consumption, and supporting conservation initiatives. We must recognize that healthy oceans produce valuable resources, and preserving their integrity benefits all life on Earth. As we look to the future, it is essential we act collectively, fostering collaborations across borders and disciplines to ensure the survival of endangered marine species. By prioritizing marine conservation, we can work towards restoring balance within our oceans, protecting vulnerable wildlife, and ensuring sustainable fishing practices. The legacy we leave behind will determine the fate of these magnificent creatures and the health of our oceans for generations to come. It is a shared responsibility that requires dedication, action, and hope for a brighter future.