Historical Significance of Bowhead Whales in Arctic Exploration
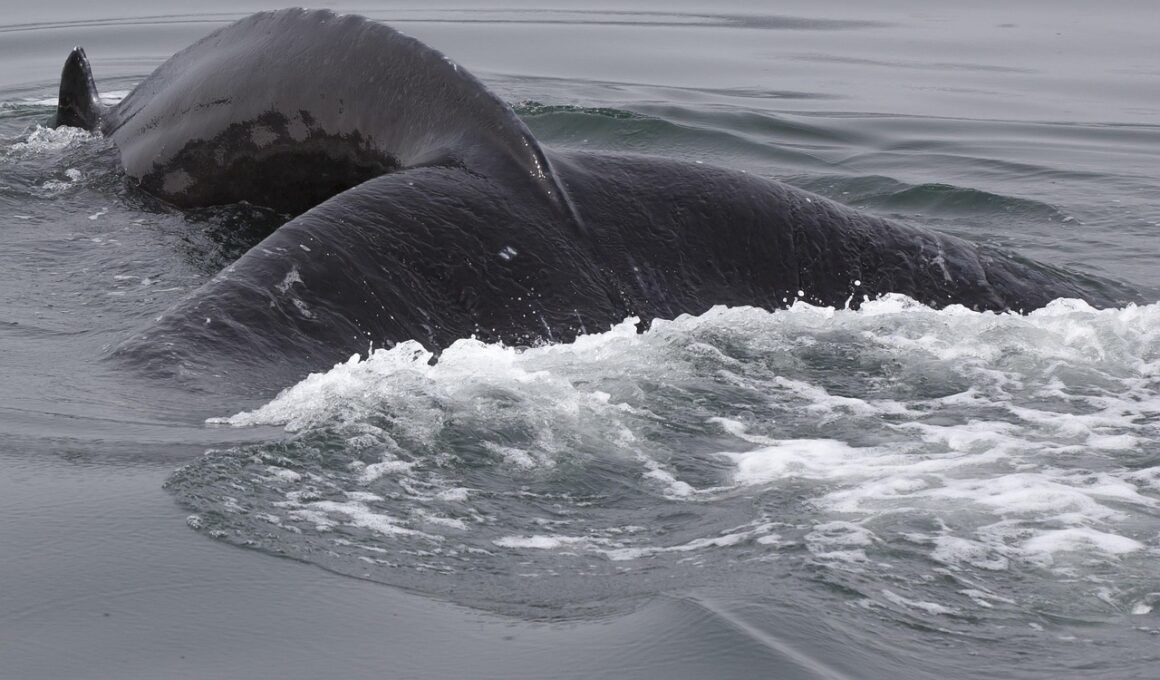
The Bowhead Whale, scientifically known as Balaena mysticetus, has played an important role in the history of human exploration in the Arctic. These magnificent creatures are well adapted to the icy waters and have provided crucial resources to indigenous communities for centuries. Bowhead Whales are unique in their ability to break through thick ice, which allows them to flourish in polar environments. Historically, they were vital to the subsistence of Native Alaskan tribes who relied on their meat, blubber, and baleen for nutrition and cultural practices. The Bowhead Whale’s significance transcends subsistence, as they are also an indicator of ocean health, affecting local ecosystems and, by extension, the livelihoods of people who depend on these waters for survival. Their migratory patterns have guided explorers seeking new trade routes, revealing the interconnectedness between human endeavors and cetacean behavior. The Bowhead’s adaptations and behaviors reflect the environmental changes facing the Arctic, reminding us of the historical interconnectedness of humankind and marine species. Efforts to study these whales illuminate modern conservation challenges as well, emphasizing the challenges we face in a changing climate.
As explorations progressed in the Arctic, the Bowhead Whale became the center of attention for whalers during the 18th and 19th centuries. The blubber of Bowhead Whales was rendered for oil, which became an important industrial product during the whale oil boom. The large quantities of oil extracted fueled lamps and lubricated machinery in a rapidly industrializing world. Whalers ventured deep into icy territories, encountering and documenting various Arctic species while exploiting Bowheads for commercial gain. Methods of hunting evolved, with techniques adapted not only for efficiency but also for survival in harsh conditions. The insatiable demand for whale oil led to significant population declines, pushing conservation measures into the political arena in later years. Today, these historical practices serve as valuable lessons in resource management and responsibility. The cultural resonance of Bowhead Whales continues among Arctic communities, emphasizing sustainable practices and respect for biodiversity. The Bowhead Whale’s remarkable longevity and reproductive strategies further underscore their resilience. As we reflect on whaling’s impact, it sparks important conversations about balance, coexistence, and lessons learned from the past.
The Role of Bowhead Whales in Indigenous Cultures
Across the Arctic, Bowhead Whales hold deep cultural significance for Indigenous Peoples. From Alaska’s Iñupiat to Greenland’s Kalaallit, these whales represent more than a food source; they symbolize livelihood, tradition, and identity. Annual whale hunts, often accompanied by rituals, are integral to sustaining cultural practices and community identity. Bowhead hunting reflects a profound respect for nature, emphasizing sustainability and heritage. Using every part of the whale post-hunting speaks to the resourcefulness intrinsic to Indigenous cultures. Traditional ecological knowledge passed through generations continues to offer insights into balancing resource use and conservation. This knowledge enhances modern scientific understandings of marine ecosystems, collaboration, and conservation efforts. The Bowhead Whale’s presence also fuels artistic expression in Indigenous communities, inspiring artworks, stories, and songs that celebrate their legacy. These cultural narratives imbue the Bowhead Whale with significance well beyond its biological existence. Modern Indigenous voices continue to advocate for conservation measures rooted in tradition and science, ensuring that future generations maintain this vital connection. This synergy of culture and conservation illustrates the profound bond shared between Indigenous peoples and Bowhead Whales, highlighting an essential aspect of Arctic anthropology.
Scientific studies of Bowhead Whales have evolved significantly, contributing to our understanding of the Arctic’s ecological dynamics. Researchers utilize sophisticated methods to track population stability, reproductive health, and migration patterns. Innovative techniques such as tagging and acoustic monitoring provide invaluable data on Bowhead behavior and interactions with the changing environment. These findings underscore the impacts of climate change on their habitat and migration routes, revealing vulnerabilities in the species’ survival amid rapid environmental alterations. The Bowhead Whale is unique among marine mammals for its impressive lifespan, with some individuals known to reach over 200 years old. This longevity presents research opportunities, particularly concerning their health and adaptive responses to climate pressures. Scientists actively collaborate with Indigenous knowledge holders to assimilate long-standing observations into contemporary research practices. Enhancing mutual understanding enhances the conservation framework aimed at protecting Bowhead Whale populations and their habitats. This collaborative approach signifies a blend of scientific rigor and traditional wisdom, fostering respect and effective stewardship of marine life. Increased regulations and protective measures have emerged in light of these findings, emphasizing the commitment to preserving this iconic species for posterity.
Bowhead Whales and Climate Change
Climate change poses unprecedented challenges for Bowhead Whales and the Arctic ecosystem. As ice melts due to warming temperatures, these whales face alterations in their habitat and food sources, impacting their migratory patterns and feeding behavior. Their primary prey, zooplankton, relies heavily on a stable and cold marine environment. Disruptions to these dynamics can lead to mismatches in availability, jeopardizing the survival of Bowhead Whale calf populations. Changes in sea ice not only affect hunting conditions for these whales but also influence their social structures and breeding success. Understanding these connections illuminates the crucial link between climate, marine life, and indigenous communities. The adaptation strategies Bowhead Whales employ offer insights into how species can respond to environmental changes. Collaborative initiatives involving scientists and indigenous communities work toward monitoring these changes’ ramifications and developing adaptive management strategies. Conservation organizations are increasingly advocating for policies to mitigate climate impacts while promoting sustainable practices among the populations that depend on marine resources. The plight of Bowhead Whales encapsulates the urgency for climate action, as safeguarding their future simultaneously protects the rich biodiversity of the Arctic regions.
The advancements in whaling regulations over the past century highlight the importance of protecting Bowhead Whale populations. Once hunted without restraint, stricter conservation laws now recognize the species’ endangered status. The International Whaling Commission has played a pivotal role in instituting protective measures, including designated harvest quotas and areas. These efforts aim to ensure Bowhead populations can thrive amid changing conditions. Active monitoring and community involvement help create a framework of responsibility and ethical management among whalers. The success of these initiatives reflects a growing conservation ethic among communities previously dependent on whaling. Success stories have emerged as Bowhead populations gradually recover, showcasing the effectiveness of community-based management approaches that respect traditional practices while addressing ecological sustainability. As Bowhead Whales rebound, educational initiatives raise awareness about their significance and ecological role among younger generations. Emphasizing preservation encourages societal shifts toward valuing biodiversity and understanding marine ecosystems. Moreover, the alignment of traditional ecological knowledge alongside modern science creates a deeper understanding of the complexities of Arctic marine life. The Bowhead Whale, once emblematic of human exploitation, now stands as a symbol of hope for a harmonized existence between nature and humanity.
Conclusion: The Future of Bowhead Whales
Looking ahead, the future of Bowhead Whales hinges on collective efforts to navigate the challenges posed by climate change and human activities. Continued collaboration between scientists, indigenous communities, and policymakers is essential for fostering sustainable cohabitation. The emphasis on adaptive strategies allows us to better prepare for uncertainties affecting Bowhead migratory and reproductive behaviors. Future research initiatives focusing on genetics, health, and behavioral ecology further assist in understanding their adaptive resilience. Creating policies that prioritize marine conservation while promoting traditional practices can benefit both Bowhead Whales and local communities. Moreover, educating the public about these whales’ roles will be critical in promoting advocacy and support for marine conservation efforts. Building awareness about Arctic ecosystems and their vulnerable species solidifies public engagement, particularly among the youth. The necessity for a unified front to confront climate change transcends borders, demanding cooperation across nations and disciplines. As stewards of the Earth, we bear the responsibility to safeguard these iconic marine mammals, ensuring the legacy of Bowhead Whales continues for generations to come. Respecting their historical significance in Arctic exploration and cultural connection helps establish a hopeful narrative for a sustainable future.
In conclusion, the Bowhead Whale’s historical significance reverberates throughout Arctic exploration, directly linking human ingenuity with ecological awareness. These majestic beings encapsulate an intricate story of survival amidst environmental challenges, cultural practices, and scientific advancements. Conservation strategies informed by traditional knowledge and scientific research can forge a path towards a sustainable coexistence among whales and humans. Recognizing their historical context encourages deeper empathy, respect, and solidarity in addressing the larger environmental issues confronting our world today.