The Enigma of the Flores Giant Rat: Extinct Island Rodents
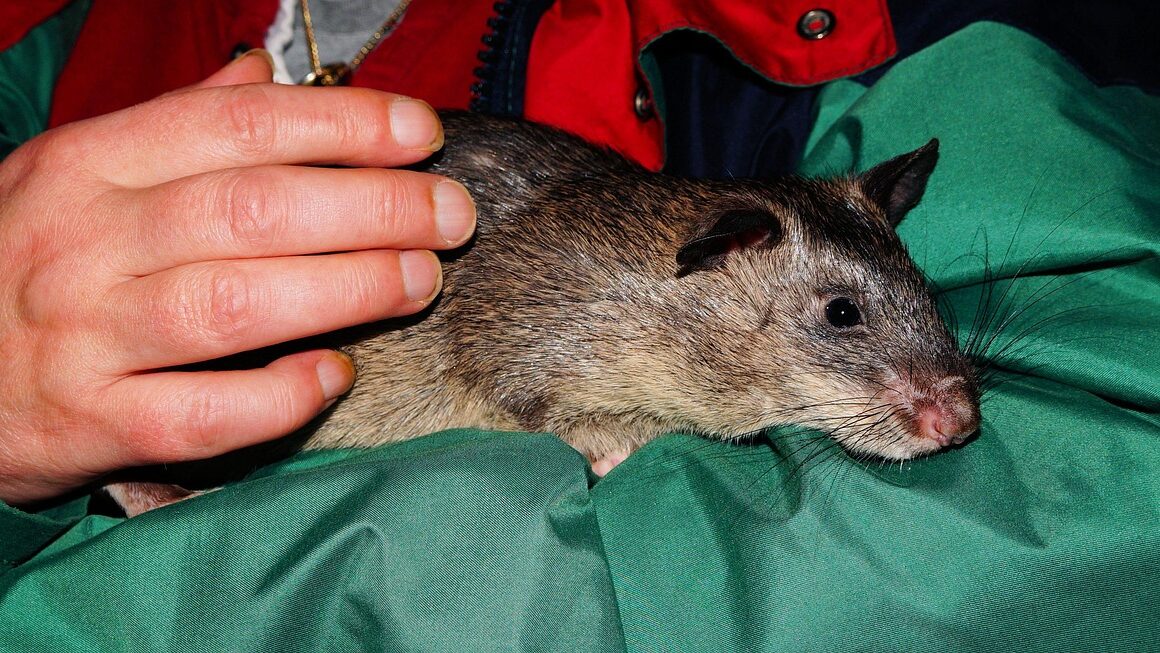
The Flores Giant Rat, known scientifically as “Komodomys rintjanus,” was an intriguing species that inhabited the island of Flores in Indonesia. These rodents are a part of the marvelous yet enigmatic ecosystem of this island. They lived around 1,000 years ago, coexisting with early human settlers who arrived at the island. The presence of such large rodents raised many questions about their evolutionary adaptations and ecological roles. Despite being lost to time, evidence shows they were almost the size of cats, showcasing an unusual instance of island gigantism. One of the reasons for the extinction of the Flores Giant Rat may have been the environmental changes on the island. The arrival of humans likely introduced competition and predation, impacting the fragile ecosystem. Other species that shared the island also faced similar pressures. The Flores Giant Rat is not alone in its extinction saga, as many island species have succumbed to similar fates. Understanding their history is crucial for biodiversity conservation, helping us learn about the consequences of human activity on ecosystems and the importance of maintaining ecological balance for future generations.
Physical Characteristics of the Flores Giant Rat
The physical characteristics of the Flores Giant Rat were strikingly unique. These rodents were significantly larger than their mainland counterparts, which hints at the phenomenon of island gigantism. They could weigh over a kilogram, making them an extraordinary sight on the island. Their features included a robust body, dense fur, and strong teeth, which allowed them to thrive in their environment. These adaptations indicate that they were likely generalist feeders, allowing them to consume a variety of plant materials prevalent on Flores. While their exact diet remains unclear, it is believed they fed on fruits, seeds, and roots. The relatively large size may have aided them in avoiding certain predators, though they were not entirely free from threats. Fossil evidence suggests that they faced competition from other rodents or even introduced species by early humans. Furthermore, the anatomical structure reveals adaptations that align with survival in dense forest habitats. Investigating their morphology provides insight into evolutionary processes inherent in isolated ecosystems. The study of these extinct species emphasizes the intricate connections in nature that can easily be disrupted.
Understanding the ecological niche of the Flores Giant Rat is essential. This rodent played a significant role in its ecosystem as a herbivore, influencing the landscape of the island. By eating various plants, they likely contributed to seed dispersal, thus facilitating the growth of different flora. Their interactions with plant life exemplify the interconnectedness of species within an ecosystem. Moreover, their extinction inevitably left gaps in the ecological web, altering food chains and the dynamics of their habitat. When species become extinct, their absence can lead to overpopulation of certain species, creating imbalances. Consequently, understanding the ecological roles of such extinct species is crucial. Documenting their existence allows researchers to draw parallels with modern-day species facing similar threats. Improving biodiversity management strategies requires not only studying existing species but also examining those lost to extinction. Each species plays a distinctive role, contributing to the broader ecological tapestry. Learning from the past can guide conservation efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity for future generations, helping to ensure that current ecosystems remain resilient against human influence.
Causes of Extinction
The extinction of the Flores Giant Rat is closely linked to various factors, primarily human activities and environmental changes. The arrival of humans on Flores brought agricultural practices that disrupted native habitats. Deforestation for farming reduced the natural landscape that rodents depended on. Additionally, the introduction of livestock and non-native species may have increased competition for resources. These factors combined likely led to overexploitation of their food sources and habitat destruction. As human populations grew, the pressure on the island’s ecosystem intensified. The limited area and resources of Flores can accelerate extinction rates when faced with such challenges. Other extinctions have occurred on islands worldwide as similar patterns of human impact emerged. Historical records show that island species, being isolated, have less resilience to changes compared to mainland populations. Conservation strategies must prioritize understanding the complex interplay between species and their environments. Mitigating the effects of human activities remains crucial for preserving what is left of unique ecosystems. Future efforts should focus on protecting remaining habitats, thus safeguarding any vulnerable species still clinging to existence.
Research into the Flores Giant Rat has inspired interest in other extinct island fauna. This fascination helps to shed light on broader questions of evolution and extinction. Scientists are keen to explore how isolation on islands can result in unique evolutionary paths like that of the Flores Giant Rat. By examining their habitats and relationships with contemporary species, researchers gain insights into adaptive traits. Such studies reveal the intricacies of natural selection processes that drive the emergence of distinct species. Moreover, by understanding consequences of extinction events, conservationists can develop better strategies to protect endangered species. The case of the Flores Giant Rat exemplifies the dynamics of island ecosystems and their vulnerabilities. It provokes thoughtful discussion on preserving biodiversity in the face of environmental change. Educational efforts to inform the public about these extinct species can foster a deeper appreciation for the planet’s biodiversity. Increased awareness may inspire protective measures for existing species. Ultimately, the legacy of the Flores Giant Rat serves as a cautionary tale for humanity, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices in conservation and ecological health.
Conclusion: The Legacy of the Flores Giant Rat
The legacy of the Flores Giant Rat offers profound insights into the fragility of island ecosystems. As a species lost to time, their story emphasizes the need for informed conservation efforts. While we can never bring back extinct species, studying them helps illuminate the mechanisms behind their extinction. Education plays a pivotal role in promoting conservation awareness and preserving remaining biodiversity. The natural world is interconnected, and its health relies on balance. Extinct species like the Flores Giant Rat remind us of the consequences of human actions on fragile ecosystems. They highlight the importance of protecting habitats and ensuring sustainability moving forward. We must take lessons from the past to shape a better future for the planet’s wildlife. Continued research and exploration have opportunities for discovering more about our natural world. There’s merit in understanding our ecological history, creating a path toward preserving it. As we strive to protect our planet, the contributions of extinct species should never be overlooked. Embracing this legacy empowers future generations to cherish and protect the delicate balance of our dwindling ecosystems.
In essence, the tale of the Flores Giant Rat is intertwined with larger narratives regarding conservation and extinction. Understanding the past aids us in forging a sustainable path into the future for both wildlife and humanity. Each species carries a story worth telling, and the ripple effects of extinction can resonate through generations. The extinction of island fauna prompts urgent consideration of strategies to protect biodiversity. Acknowledging the lost giants of Flores reinforces the need for proactive measures to safeguard remaining species. Engaging communities in conservation efforts can forge a collective responsibility for environmental stewardship. Through education and advocacy, we can inspire action grounded in empathy toward all living beings. The preservation of biodiversity necessitates collaborative endeavors across various disciplines and sectors. By working together, we can ensure the vibrancy of natural ecosystems across the globe. This responsibility extends beyond geographical bounds, reminding us that biodiversity is a shared treasure to be valued. The Flores Giant Rat may be gone, but it serves as a poignant reminder of what we stand to lose if we fail to act today.
In conclusion, to truly safeguard future generations, we must prioritize the conservation of both existing and historically significant species. The story of the Flores Giant Rat encapsulates a broader lesson about humanity’s impact on nature. As we confront the ongoing biodiversity crisis, let this extinct island rodent remind us of the fragility of natural balance. Communities united in conservation efforts can yield profound change, potentially preventing more extinctions. Understanding the ecological roles of extinct species enriches our knowledge base. It equips us to tackle the challenges that lie ahead. Ultimately, through concerted actions and a commitment to sustainability, we can work toward protecting our natural heritage. By valuing the existence of all species, we foster a future where both wildlife and people thrive. The legacy left by the Flores Giant Rat encourages a profound respect for biodiversity. Its extinction serves as a driving force behind the need for a more just and equitable relationship with the natural world. Acknowledging the past propels us to envision a future where conservation is a shared responsibility, creating a harmonious existence for all.