Future Directions in Sawfly Conservation and Study
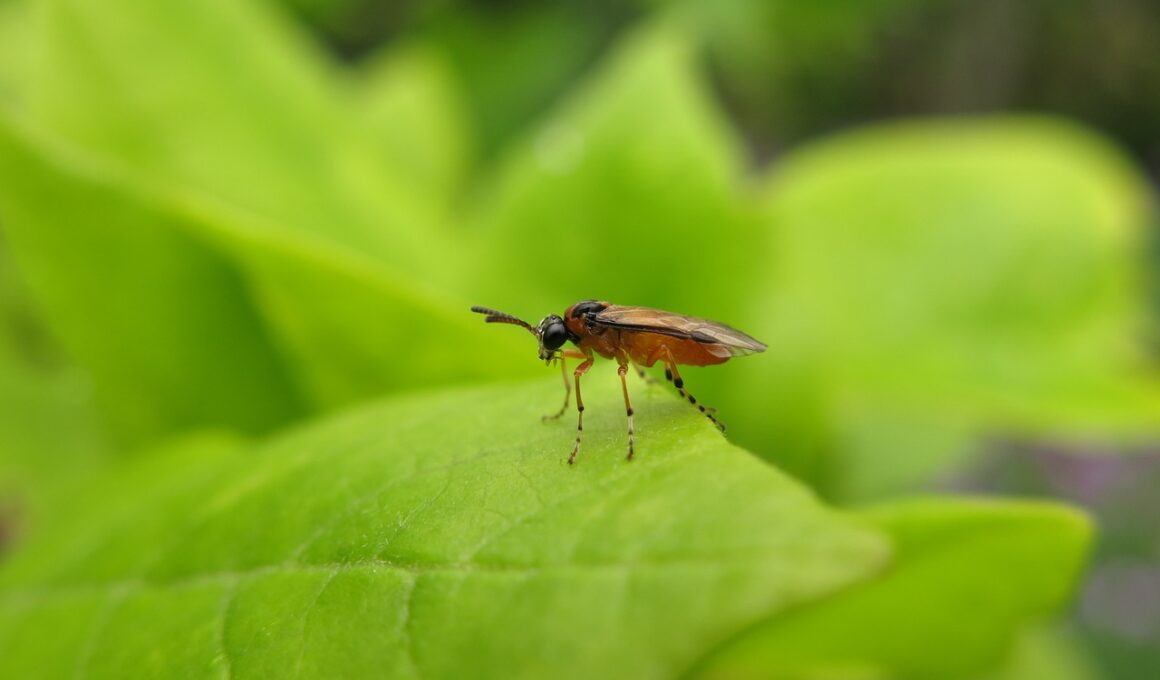
Sawflies, belonging to the order Hymenoptera, represent a diverse and ecologically significant group of insects. They contribute to natural ecosystems through roles such as pollinators and herbivores. Understanding their species diversity is essential for effective conservation efforts. Future research should prioritize the identification and classification of various sawfly species across different ecosystems. This can be accomplished through collaborative efforts involving field studies and genetic analysis. As habitat loss and climate change continue to threaten these insects, it is crucial to establish conservation strategies that address their specific needs. Educating the public about sawflies can also foster appreciation for their ecological contributions. Outreach programs can promote awareness about their roles in food webs and the importance of biodiversity in sustaining healthy ecosystems. Involving local communities in conservation initiatives can enhance the protection of these species. Additionally, researchers can utilize citizen science to gather data on sawfly populations and distribution, improving our understanding of their ecology. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach that incorporates scientific research, community involvement, and educational outreach will be vital for the successful conservation of sawflies.
Ongoing studies about sawflies should also focus on their interaction with various plant species. By examining these relationships, researchers can gain insights into the ecological dynamics within ecosystems. Understanding how sawflies affect plant populations can help guide management practices. For instance, if certain sawfly species are recognized as pests, targeted strategies can be designed to mitigate their impacts while maintaining ecological balance. Moreover, research into habitat preferences of different sawfly species is essential for effective conservation. Identifying critical habitats can inform restoration projects that prioritize areas supporting these insects. Incorporating native plant species into restoration efforts can create a suitable environment for sawflies to thrive. Partnerships with agricultural systems will also be beneficial, as sawflies play a critical role in pest management. Encouraging biodiversity within farming practices can lead to healthier ecosystems and greater resilience against pest pressures. Collaborative initiatives with farmers can help improve land-use strategies that favor both agricultural productivity and sawfly conservation. Ultimately, ongoing research needs to encompass all dimensions of sawfly ecology, creating a holistic framework. This will ensure that conservation efforts are science-based and effectively address the challenges faced by sawflies.
Impact of Climate Change on Sawflies
Climate change poses significant threats to sawfly populations globally. Rising temperatures can alter the distribution of both sawflies and their host plants, disrupting established ecological relationships. Researchers must investigate the potential impacts of climate variations on sawfly life cycles and phenology. Shifts in timing of life stages can affect reproduction and survival rates. Understanding how different sawfly species respond to temperature and precipitation changes is critical for predicting future population dynamics. This knowledge will enable better conservation management. Furthermore, climate change can exacerbate existing threats such as habitat loss and invasive species competition. Developing adaptive strategies requires an understanding of sawfly resilience to these stressors. For instance, identifying sawfly species capable of thriving under changing climate conditions can guide conservation priorities. This can be achieved through experimental studies that simulate future climate scenarios. Additionally, researchers should explore the potential of assisted migration for vulnerable sawfly species. This approach involves facilitating the movement of populations toward more suitable habitats as conditions change. By preparing adaptive management frameworks, scientists and conservationists can collaborate effectively to enhance the survival of sawflies amid climate uncertainty.
Furthermore, the role of genetic diversity within sawfly populations needs further investigation. Genetic variation can provide resilience against environmental changes and diseases, contributing to long-term survival. Future studies should involve genetic mapping of sawfly populations across diverse habitats. This will enable researchers to determine genetic health and identify populations most at risk. Addressing issues of genetic bottlenecks and ensuring gene flow between isolated populations is vital. Implementing translocation strategies may help facilitate gene diversity where necessary. Moreover, innovations in biotechnology provide potential solutions for conservation efforts. For instance, techniques like environmental DNA (eDNA) can enhance detection and monitoring of sawfly species within specific areas. This non-invasive method will improve data collection, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of their distribution. Integrating technological advances with traditional conservation methods strengthens overall conservation strategies. The emphasis on genetic research also enhances the conservation of interrelated species and ecosystems that contribute to sawfly habitats. Future research efforts should prioritize collaboration between geneticists, ecologists, and conservationists. A multifaceted approach to conserving sawflies will ultimately yield better ecological outcomes.
Community Involvement in Conservation
Involving local communities in sawfly conservation creates an essential framework for success. Citizen engagement can lead to increased awareness and appreciation of these insects. Community-driven initiatives can foster active participation in monitoring and reporting sawfly sightings. Schools and educational organizations can implement programs that teach children about sawflies and their ecological roles. This grassroots involvement not only educates the public but also creates a sense of stewardship toward the environment. Furthermore, forming partnerships with local conservation organizations can enhance conservation efforts. Collaborating with these groups enables resource sharing and access to local knowledge about sawfly habitats. Workshops and training sessions can empower community volunteers to identify and document sawfly species in their regions. Online platforms and social media can facilitate reporting and sharing of sightings, creating a dynamic database that supports ongoing research. Through these community efforts, researchers gain valuable data while fostering a culture of environmental responsibility. Encouraging citizen science initiatives will ultimately benefit sawfly populations and broader conservation efforts. Therefore, establishing robust community partnerships should be a priority for future conservation planning.
In addition to community involvement, interdisciplinary collaboration plays a vital role in sawfly conservation. By bringing together experts from various fields, researchers can tackle complex ecological challenges. Biologists, agronomists, and conservationists can collaboratively develop effective pest management solutions. This collaboration will ensure that agricultural practices align with preserving sawfly populations. Research addressing agricultural impacts on sawflies should also incorporate economic assessments. Any conservation strategy must consider the socioeconomic implications for farming communities. Balancing agricultural productivity with ecosystem health is essential for sustainable practices. Furthermore, political advocacy for policy changes supporting sawfly protection will be crucial. Funding research initiatives and conservation programs at local, national, and international levels requires a coordinated effort across disciplines. Engaging policymakers and stakeholders in conversations around sawfly conservation can ensure their critical role within ecosystems is recognized. Creating policy frameworks that support research and conservation initiatives will ultimately result in better outcomes for these important insects. Therefore, interdisciplinary collaboration and policy advocacy stand as pillars of successful sawfly conservation strategies moving forward.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of sawfly conservation and study hinges upon a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates community involvement, genetic research, technological innovation, and policy advocacy. As our understanding of these insects improves, we can develop targeted conservation strategies that address their specific needs and challenges. Engaging local communities will be paramount, fostering stewardship while collecting vital data for researchers. Furthermore, incorporating genetic research and biotechnology will enhance our ability to monitor and manage sawfly populations effectively. Climate change poses numerous threats to this group, and adaptive strategies will become increasingly necessary. Interdisciplinary collaboration will equip us to navigate these challenges as ecological systems continue to evolve. Additionally, progressive policies must support conservation efforts, ensuring sustainable futures for not only sawflies but entire ecosystems reliant on their presence. The comprehensive initiatives outlined in this article emphasize the importance of integrated conservation efforts. By prioritizing collaborative research, community engagement, and adaptive management, we can create a sustaining environment for sawflies. Ultimately, the continued study of sawflies and their conservation must remain a dynamic and adaptive process that responds to our changing world.
By integrating the recommendations and strategies mentioned above, conservationists can better navigate the complexities of preserving sawfly populations globally. Addressing the unique ecological roles filled by sawflies will help clarify the need for focused efforts to enhance their conservation. The combination of scientific inquiry with fieldwork ensures a robust understanding of their requirements, which can effectively guide conservation programs. Additionally, fostering partnerships with agronomists and ecologists encourages a multidisciplinary approach vital for comprehensive solutions. The collaborative approach will not only support sawfly conservation but also promote sustainability within agricultural practices. Furthermore, the emphasis on technology and innovative techniques can streamline data collection and analysis, ultimately improving research outcomes. As environmental challenges exacerbate due to human activities, proactive measures must be taken to preserve biodiversity, particularly for lesser-known species like sawflies. Continued dialogue among stakeholders will strengthen conservation frameworks while empowering local communities through education. Ensuring that future generations recognize the value of sawflies and their ecosystems is crucial for long-term success. Through combined efforts and shared responsibility, we can sustain the delicate balance of our ecosystems while protecting the future of sawflies.