Beluga Whales’ Role in Marine Biodiversity
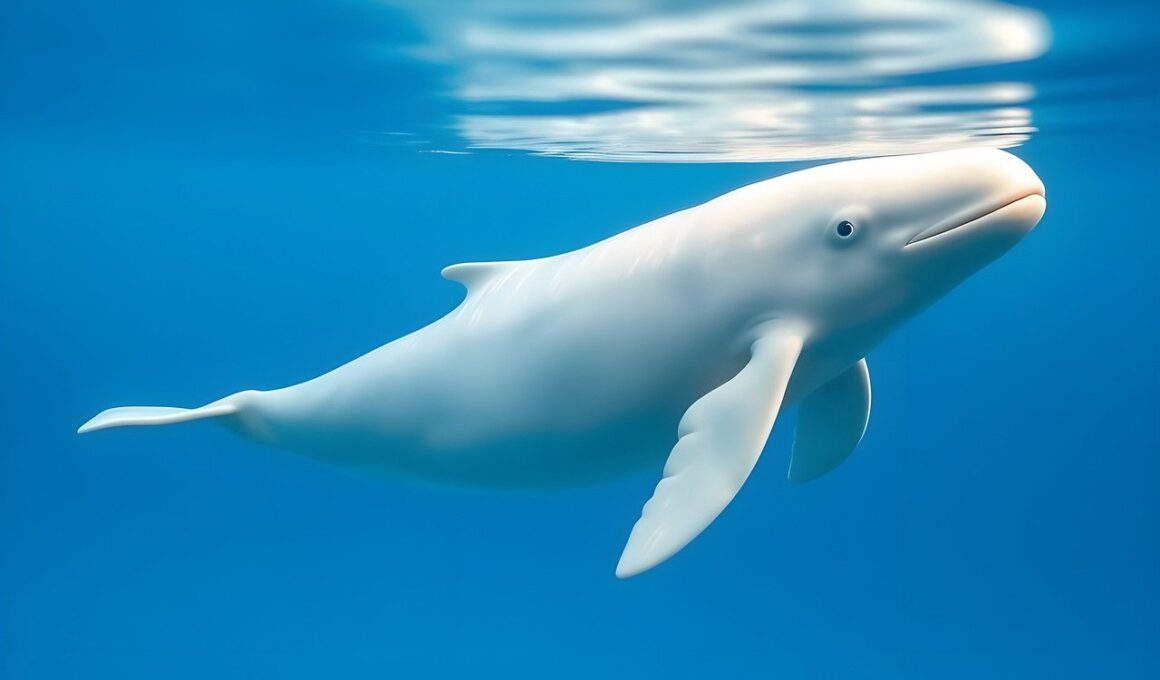
Beluga whales, also known as sea canaries, play a significant role in marine biodiversity and the overall health of their ecosystems. These gentle marine mammals inhabit the icy waters of the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. In doing so, they contribute to the marine food chain, influencing various oceanic life forms. The predatory habits of belugas allow them to maintain fish populations, particularly those that reside in cold-depth waters such as cod and salmon. By consuming these species, belugas help ensure their populations do not explode, which would lead to overgrazing and habitat degradation. Furthermore, the coastal ecosystems benefit from the nutrient cycling that belugas facilitate through their feeding and excretion patterns. Their movements through the water column as they hunt can stir sediments that promote the growth of phytoplankton and other essential forms of marine life. Healthy populations of beluga whales are thus indicative of balanced ecosystems, serving as a key species in understanding marine ecosystems’ health and resilience. As significant components of their ecosystems, belugas symbolize the complexity of marine life and highlight the need for ongoing research and conservation efforts.
Beluga whales are essential when considering the indicators for environmental health as they can be sensitive to changes in their surroundings. The presence of these whales suggests a balanced ecosystem, abundant in biodiversity. Belugas are known for their intelligence and social behaviors, often living in groups, or pods, that can range from 2 to 25 individuals. The structure of these pods can facilitate collaborative hunting strategies, showcasing their capabilities in communication and teamwork. Their vocalizations, which range from clicks to whistles, are not only a mode of communication but also reveal insights into their social structure. Additionally, the complexities of their communication serve as important behavioral studies for marine biologists, providing deeper understanding regarding the intricacies of social dynamics within pods. These social interactions reflect their adaptability to environmental factors and even to threats, such as hunting and climate change. Moreover, the evolving impact of climate change on their Arctic habitat affects prey availability and migratory patterns, illustrating the intertwined relationship between belugas and their environment. This incorporation emphasizes the urgency for conservation efforts pertaining to their species.
Conservational Importance of Beluga Whales
Conservation of beluga whales is critical to maintaining the balance of their marine ecosystems and understanding biodiversity’s full scope. These mammals face numerous threats including habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Human activities, such as industrial development, pose additional stress by disrupting their natural environments. Over the years, the number of beluga whales has declined due to increased shipping traffic and noise pollution that interfere with their communication. The changing climate alters ice coverage in the Arctic, which is detrimental to their breeding and nursing grounds. Organizations and governments worldwide have instituted protective measures to mitigate these threats. Policies encouraging sustainable practices in fishing and shipping industries, along with habitat protection laws, are crucial steps toward ensuring the survival of these species. Researchers are monitoring beluga populations to gather data which can inform conservation strategies. By preserving beluga habitats, we not only protect an important species but also the myriad of organisms that co-exist within their ecosystems. Promoting awareness of these marine mammals through educational campaigns can foster public support for conservation initiatives that directly benefit the well-being of these charismatic creatures.
Beluga whales contribute to the local economies of many coastal communities, underscoring their importance beyond ecological roles. As ecotourism grows in popularity, opportunities arise for communities to create sustainable tourism models centered around observing beluga whales in their natural environments. Tours offering encounters with these friendly creatures attract visitors from around the world, generating revenue while raising awareness about conservation. Tour operators can collaborate with local conservation agencies to ensure that all activities are responsible, minimizing disturbances to the animals’ natural behaviors. Moreover, educational materials distributed during tours, including information about beluga feeding habits and their role in the ecosystem, enhance the experience and promote conservation priorities among visitors. By engaging the public and building connections with local wildlife, tourism opportunities can contribute positively to beluga populations through funding and research support. Education and community involvement can foster stewardship of marine environments. Strengthening communities’ appreciation of local wildlife can catalyze ongoing dialogue about sustainable practices, engendering conservation efforts to ensure the long-term survival of beluga whales and their ecosystems.
The Impact of Climate Change on Belugas
Climate change has profound impacts on beluga whales and their habitats, affecting their food supply and breeding behaviors. As temperatures rise, Arctic waters are experiencing dramatic alterations with decreasing ice coverage. This loss of ice critically undermines the habitats vital for nursing and foraging. Belugas rely on ice for shelter and as a platform to rest. As the distribution of their prey shifts, so too does the migratory patterns of belugas. Food scarcity can lead to increased competition and even starvation. Additionally, warmer waters have encouraged the encroachment of new predators, further stressing beluga populations. The alteration of traditional migratory paths not only challenges belugas in finding food but also exposes them to increased human activity as they venture closer to coastlines. Marine traffic presents additional challenges, including increased noise pollution. This can interfere with their communication, reproduction, and hunting strategies. Monitoring these changes is essential for conservationists aiming to implement effective strategies to support beluga populations. Raising awareness about the vulnerabilities of belugas to climate change promotes collective efforts aimed at facilitating their protection amidst the shifting environmental landscape.
Understanding the life cycle of beluga whales is essential for effective conservation and management strategies. Female belugas typically give birth to one calf every three years after a gestation period of approximately fourteen months. Calves are born gray and darker in color, gradually transforming into their iconic white appearance as they mature. This change signifies the transition into adulthood, which is marked by social behaviors that develop within the pods. The maternal bond during early life is strong, as mothers guide calves in learning vital survival skills, like hunting and recognizing predators. As calves grow, they learn to communicate and socialize, building their roles within the pod. This familial structure is crucial for their survival and sustains their social hierarchy. The impacts of adversity, such as environmental stress or food shortages, can severely affect calf survival rates, thereby impacting population growth. To mitigate these consequences, conservation researchers can emphasize understanding the dynamics of families and pods, contributing to tailored conservation efforts. Research addressing reproductive success and calf survival can lead to implementing measures that specifically address the challenges faced during these early and vulnerable stages.
Future Prospects for Beluga Conservation
Looking ahead, there are several strategies proposed to enhance conservation efforts for beluga whales. These strategies hinge on collaborative approaches, embracing local communities, and scientific research that adapts to emerging threats. Conservationists stress the integration of indigenous knowledge into wildlife management plans. This collaboration can deliver insights into historical ranges and interactions of belugas, aiding in better understanding their ecological roles. Enhanced international cooperation is needed to address cross-border conservation challenges, as belugas traverse different nations’ waters. Developing marine protected areas could help safeguard crucial habitats from industrial activities and environmental degradation. Engaging the public through awareness campaigns and fostering partnerships among stakeholders, including fishermen, scientists, and local residents, reinforces the message of sustainability. By promoting practices that minimize human impacts, preserving genetic diversity within populations becomes achievable. Emphasis on monitoring population health will also direct efforts to proactively respond to any stresses faced by belugas. Scientific advancements, such as genetic tools and tracking technologies, can contribute valuable data to support their conservation. With these strategic steps, the future of beluga whales can be shaped positively, ensuring their continued presence in the changing marine environments.
Belugas’ cultural significance also plays an essential role in conservation initiatives, as storytelling and traditions often intertwine with marine life. In many indigenous cultures, these whales are celebrated in folklore and rituals, highlighting their deep connection with human history. This cultural heritage can drive conservation efforts by fostering a sense of responsibility within communities. Celebrating and respecting the significance of beluga whales can strengthen local engagement, nurturing advocacy for their protection. Incorporating local cultural narratives into educational efforts can enhance the awareness of conservation issues. Moreover, allowing communities to gain recognition and rights concerning their marine resources can empower residents. When stakeholders work collaboratively, the success of conservation efforts can lead to enhanced appreciation of these splendid creatures. Cultural initiatives can serve as catalysts, inspiring young generations to maintain these traditions and practice stewardship of the environment in ethical ways. Strengthening ties between cultural values and ecological awareness can enrich the conservation discourse. Ultimately, the integration of these dimensions can lead to more robust and resilient communities working towards the protection of beluga whales and maintaining the health of their coastal ecosystems.