Glaucous Gulls and Their Role in Arctic Food Chains
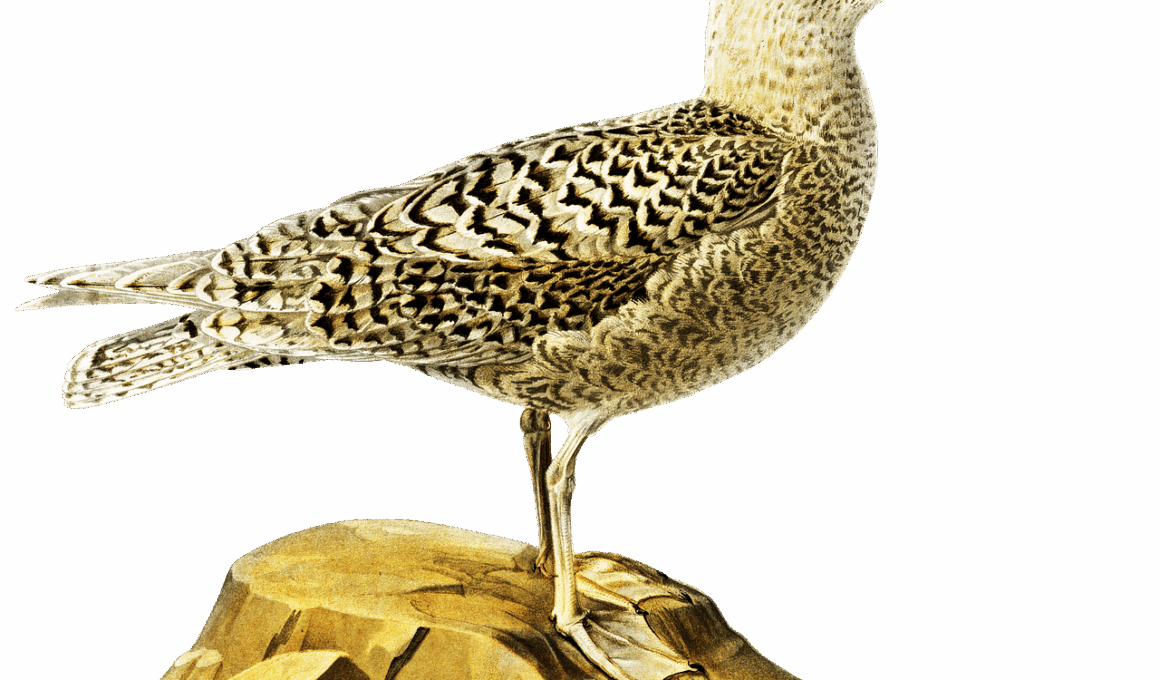
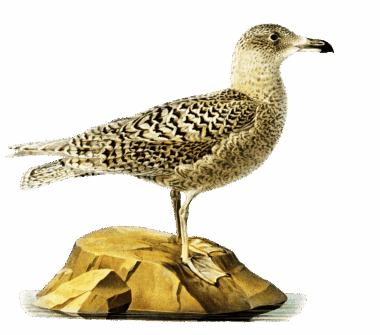
Glaucous gulls (Larus hyperboreus) are fascinating birds that serve a critical role in the Arctic ecosystem. Their large, robust bodies and striking pale plumage make them easily recognizable. Glaucous gulls are often seen soaring over the frigid landscapes or perched on cliffs, waiting for opportunities. They inhabit various regions across the Arctic, including coasts, islands, and tundra. These gulls are opportunistic feeders, consuming a diverse diet composed of marine animals. Their primary food sources include fish, marine invertebrates, and carrion. Consequently, they significantly contribute to the energy transfer within the Arctic food chains. Furthermore, Glaucous gulls are pivotal in controlling the populations of smaller birds and marine species. This predatory behavior can help maintain ecological balance. As scavengers, they play a vital role in recycling nutrients back into the environment. Their foraging habits also influence the distribution of other wildlife in the area. With ongoing climate change, these birds face new challenges. Understanding their role in the Arctic ecosystem is crucial for conservation efforts.
Dietary Habits of Glaucous Gulls
Glaucous gulls display diverse dietary habits, which profoundly impact the Arctic food web. These birds are skilled hunters, often preying on fish and smaller seabirds. They also exhibit scavenging behavior, taking advantage of carcasses left by other predators. Their adaptability in diet is vital for survival in the extreme Arctic conditions. During summer, they hunt and consume various fish species, ensuring they have sufficient energy for breeding and raising chicks. In contrast, during winter, their diet shifts as food becomes scarce. They then rely heavily on scavenging. Observing their feeding behavior provides insight into the health of marine ecosystems. Moreover, interactions with other species, such as Arctic foxes or polar bears, highlight complex relationships within the food chain. These interactions demonstrate the interdependencies of species in the Arctic tundra and coastal regions. Glaucous gulls also influence the population dynamics of species like eggs or chicks of smaller seabirds, contributing to natural regulation mechanisms. Their role as apex predators illustrates the intricate balance within Arctic environments. As such, Glaucous gulls are invaluable indicators of broader ecological changes.
Reproductive habits of Glaucous gulls are fascinating and crucial for maintaining their population. They typically nest on cliff edges or in isolated tundra areas, providing safety from predators. Their nests consist of a simple scrape lined with grasses and feathers, making them somewhat vulnerable. A typical clutch contains two to four eggs, which are incubated primarily by the female. Both parents are involved in raising the young gulls. One of the fascinating aspects of their reproduction is the timing; they breed during the brief Arctic summer when food is plentiful. This ensures that the chicks have access to ample resources, aiding their rapid growth. After hatching, the chicks rely on their parents for food, learning essential hunting and foraging skills within weeks. Glaucous gull chicks exhibit a strong instinct to fledge quickly, allowing them to become more independent and adapt to their harsh environment. As they mature, they gradually become proficient at capturing food themselves. The reproductive success of Glaucous gulls is vital for the stability of their populations. Monitoring breeding success rates is essential for understanding the impact of environmental changes on these iconic Arctic residents.
Glaucous Gulls: Adaptations for Survival
Glaucous gulls have developed numerous adaptations essential for surviving in harsh Arctic climates. Their large body size, thick plumage, and strong wings help them endure extreme cold and strong winds typically experienced in their habitat. The feathers of adult Glaucous gulls are designed to provide thermal insulation, keeping them warm during frigid temperatures. Additionally, they possess sharp eyesight that enables them to spot prey from great distances. Their keen vision is particularly beneficial when hunting for food. Furthermore, the strong beaks of these birds are adapted for tearing flesh and opening shells, allowing them to access various food sources. Their powerful legs enable swift movement across ice and rocky terrains. Glaucous gulls are also known for their vocalizations, which serve critical roles in communication, especially during mating season. They engage in a wide range of calls to defend territory or signal distress. The resiliency of Glaucous gulls against environmental challenges showcases their evolutionary success. Studying these adaptations provides insight into avian life in the Arctic and can inform conservation strategies for similar species facing climate change.
Climate change poses significant threats to the populations of Glaucous gulls and their habitats. As temperatures rise and sea ice diminishes, their breeding grounds face potential disruption. The reduction of ice affects the availability of their primary food sources, leading to decreased survival rates. Shifts in marine ecosystems can alter fish populations, which are crucial for gull survival. Additionally, changing weather patterns can impact the timing of breeding and availability of food for chicks. If Glaucous gulls cannot adapt quickly enough to these changes, their populations may decline. Increased human activity in Arctic regions also poses risks to their habitats. Pollution, commercial fishing, and tourism can disrupt their natural behaviors and feeding grounds. Conservation efforts focusing on protecting Arctic ecosystems are essential for ensuring the survival of Glaucous gulls. Strategies may include establishing protected areas and regulating human activities. Furthermore, scientific research is needed to monitor population trends and dietary changes resulting from climate impacts. By understanding these dynamics, we can better support Glaucous gulls in overcoming the challenges they face in a rapidly changing environment.
Ecological Importance of Glaucous Gulls
The ecological importance of Glaucous gulls extends beyond their role as predators and scavengers. These birds play an integral part in nutrient cycling within Arctic ecosystems. By consuming marine organisms and carrion, they facilitate the return of nutrients to the environment, promoting a healthy ecosystem. Their feeding habits help control prey populations, ensuring that no single species dominates the environment. Additionally, their presence influences the behaviors of other wildlife, creating a complex web of interactions. Glaucous gulls can also serve as indicators of ecological health. Changes in their population dynamics may reflect broader environmental changes within their habitats. For instance, declining populations could signal shifts in marine ecosystem health or availability of food resources. Protecting Glaucous gulls thus contributes not only to their conservation but also to maintaining ecological balance in Arctic regions. As apex consumers, they contribute significantly to the food web’s integrity, ensuring a dynamic and diverse ecosystem thrives. Understanding their role in these ecosystems can guide effective conservation strategies that encompass multiple species within the fragile Arctic environment.
In summary, Glaucous gulls occupy a vital role within Arctic food chains. Their adaptability, hunting skills, and reproductive success all contribute to their ecological significance. While they face numerous challenges from climate change and human activity, understanding their role can inform conservation strategies. Protecting Glaucous gulls goes hand in hand with safeguarding the health of the Arctic ecosystem. As researchers study the complexities of these interactions, it becomes increasingly clear that every species plays a part in the intricate web of life. These birds not only illustrate the beauty and resilience of Arctic wildlife but also remind us of the urgent need for conservation efforts. Environmental changes threaten not only Glaucous gulls but the delicate balance of ecosystems they inhabit. Collaborative conservation efforts, awareness, and actions on climate change can help secure the future of Glaucous gulls and, by extension, the Arctic environment. Engaging local communities, policymakers, and researchers in conservation efforts is essential. The survival of these remarkable birds relies on our understanding and commitment to protecting their Arctic habitats.
As they interact with multiple species in their environment, Glaucous gulls enhance the biodiversity of the Arctic. Without them, certain species’ populations could explode, leading to resource scarcity. The influence of Glaucous gulls extends into the marine food web and terrestrial ecosystems. Their feeding behavior shapes the distribution and dynamics of numerous species. Additionally, they engage in complex behaviors that reflect their intelligence and adaptability. Glaucous gulls are known for their ability to learn from experiences and modify their strategies accordingly. Their keen problem-solving skills enable them to thrive in ever-changing environments. The interplay between Glaucous gulls and other wildlife also affects nutrient flows and energy distribution across various trophic levels. As apex predators, they exemplify the importance of each species in maintaining balance within these ecosystems. Their resilience in the face of environmental stressors speaks volumes about their evolutionary capabilities. The survival of Glaucous gulls will depend on ongoing research and conservation efforts aimed at sustaining Arctic ecosystems. By reinforcing the arrangements of diverse life forms, we ensure the continuance of those environments that have historically forged unique animal behavior. The essence of Glaucous gulls reminds us of our intrinsic ties to nature.