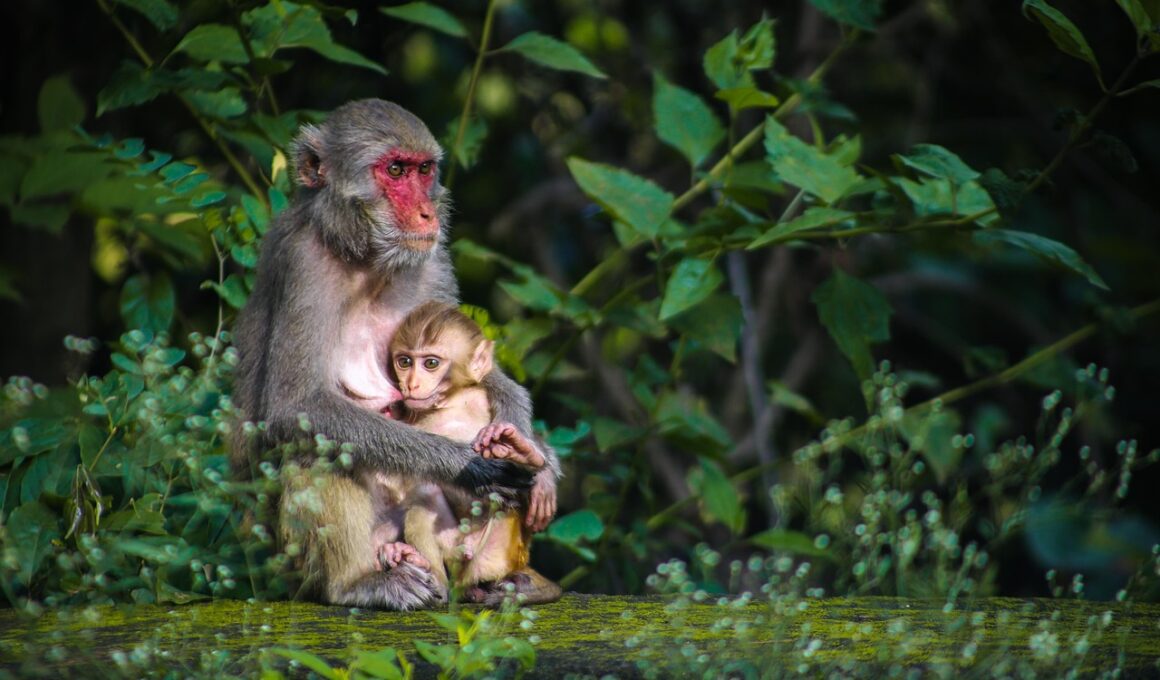
Territoriality and Social Dynamics of Diurnal Monkeys
Diurnal monkeys exhibit complex social structures largely shaped by territoriality. These social dynamics are influenced by factors such as habitat, availability of resources, and group cohesion. Territoriality serves as a mechanism for resource protection, ensuring that groups have access to food, mates, and safe sleeping sites. Monkeys mark their territories through vocalizations, scent marking, and physical displays, sending signals to neighboring groups. Research has shown that territorial disputes often occur, leading to aggressive interactions. Understanding these dynamics reveals much about their social organization and behavior. In many cases, territories are established and defended aggressively, especially by males. However, females may also play critical roles in territory defense. With the pressures of habitat loss and environmental changes, understanding these territorial behaviors and social structures becomes increasingly essential for conservation efforts. Group sizes, composition, and dynamics also shift in response to social pressures, influencing reproductive success and survival rates. Consequently, studying territoriality and social dynamics is not only vital for understanding diurnal monkey behavior but also important for their conservation in a rapidly changing world.
In the fascinating realm of diurnal monkeys, the social structures can vary dramatically based on species and environmental conditions. For example, some species like the vervet monkeys display strong group cohesion and complex hierarchies, while others, like the spider monkeys, exhibit more fluid social dynamics. The differences in these structures often correlate with their respective territorial behaviors. Groups tend to be matrilineal or patrilineal, influencing how territory is established and defended. In some species, males may leave their natal group to join other territories, whereas females often remain. This dynamic can affect the genetic diversity within and among groups. Understanding the intricacies of their social structures provides insight into their survival strategies. Groups that maintain strong social bonds are better at defending resources and protecting their young. Observations of intergroup interactions reveal how territoriality is not only a function of resource availability but also a reflection of social relationships. Through these interactions, we witness a rich tapestry of alliances, rivalries, and kinship that defines their day-to-day lives.
Territory and Resource Allocation
Resource allocation is a crucial factor dictating the territorial behavior of diurnal monkeys. The availability of food and water sources largely determines how territories are marked and defended. Groups that inhabit areas with abundant resources tend to have more stable territories, while those in resource-scarce environments exhibit more fluid boundaries. This variability impacts intergroup relations as competition for limited resources can lead to heightened aggression. Observation has shown that vocalizations play a significant role in territorial defense. For example, the howler monkeys emit loud calls to assert their territory, deterring potential intruders. Males typically lead these vocal displays to attract females and warn rival males. Additionally, physical displays, like grooming and play, serve to reinforce social bonds within the group, strengthening the overall social fabric. Over time, these behaviors have evolved, contributing to their adaptability in changing environments. Furthermore, the social structures among groups reveal preferences for particular types of habitats, often aligning with specific resource distribution patterns. Thus, territoriality among diurnal monkeys is deeply intertwined with resource management and group dynamics.
The social interactions of diurnal monkeys extend beyond territoriality, incorporating complex communication strategies. Their ability to convey information quickly and effectively is crucial for group survival. Monkeys utilize a variety of vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language to communicate different messages. For instance, alarm calls can warn other group members of approaching predators, while calls for food can attract fellow foragers. Understanding how these communication methods influence group dynamics offers fascinating insights into their social structures. Moreover, the nuances in communication can signal changes in group hierarchy or dynamics. Rank within the group often influences which individuals are more dominant in social interactions. Higher-ranking individuals typically receive preferential access to resources, while lower-ranking members may need to rely on social tactics to navigate these dynamics. Social learning also plays a vital role, as younger monkeys observe and mimic older members of their group. Through these social interactions, knowledge of their environment and social structures is passed down. As such, communication and social learning are essential for understanding how diurnal monkeys maintain their intricate social networks.
Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors significantly influence the territoriality and social dynamics of diurnal monkeys. As habitats change due to climate variations or human activities, the availability of resources becomes more unpredictable. Many species of diurnal monkeys face challenges such as deforestation, which limits their habitat range and access to food. These pressures can lead to increased competition among neighboring groups, resulting in more aggressive and territorial behavior. Furthermore, alterations in food availability may push groups to expand their territorial boundaries. When resources are insufficient, monkeys may resort to new, often risky behaviors, such as raiding neighboring territories. These adaptations illustrate the resilience and flexibility of their social structures in response to changing environments. In studies of specific species, scientists have noted shifts in social interactions. Changes can result in higher levels of stress and conflict among individuals, ultimately affecting reproduction and health. Monitoring these trends is essential for conservation strategies. Understanding how environmental factors shape territories and social dynamics allows for better management and preservation of monkey populations as habitats continue to evolve.
Territorial disputes among diurnal monkeys can provide valuable insights into their social behavior. Observing these confrontations gives researchers the opportunity to study aggression, negotiation, and alliances within and between groups. In many species, conflicts are not always physical; they can often be resolved through displays of dominance or vocal signals that establish hierarchy. For example, tease displays or
h3>Sexual Selection and Territoriality
It’s essential to understand the role of sexual selection in shaping the territorial behaviors of diurnal monkeys. Males in many species defend territories not only to secure resources for themselves but also to attract potential mates. The quality of a male’s territory can significantly influence reproductive success. Females often prefer males with the most resource-rich territories, associating habitat quality with their genetic fitness. Consequently, males invest considerable effort in defending these areas against rivals. This leads to the evolution of complex social strategies, including displays of strength or intelligence during contests with other males. The significance of mate selection reinforces the interconnectedness of territory, resources, and social dynamics. Moreover, females are not merely passive; they can play an active role in choosing mates based on their social standing and territory quality. These dynamics underline the importance of understanding sexual selection in the broader context of diurnal monkey social structures. By examining the intersection of territoriality and mating behaviors, researchers can gain fresh insights into their population dynamics and social evolution.
Conclusion: Importance for Conservation
Understanding the territoriality and social dynamics of diurnal monkeys is vital for their conservation and management. As their habitats are increasingly threatened, knowledge of their social structures and behaviors allows conservationists to develop effective strategies. The interdependencies between territoriality, resource management, and social interactions highlight the complex adaptations these species have developed. Protecting their habitats, maintaining resource availability, and mitigating human impact is essential for the survival of these remarkable animals. Consequently, research efforts must continue to monitor the changing landscapes and their effects on social dynamics. Conservation programs that consider the social fabric of diurnal monkeys can better guarantee their long-term survival. By fostering collaborations between researchers, local communities, and conservation organizations, strategies can be created that not only focus on habitat protection but also support the social systems of these unique primates. In a world of rapid environmental change, prioritizing the understanding of social structures will be crucial. Sustaining the delicate balance of intergroup relations, territory dynamics, and environmental health can ultimately lead to a more secure future for diurnal monkeys.