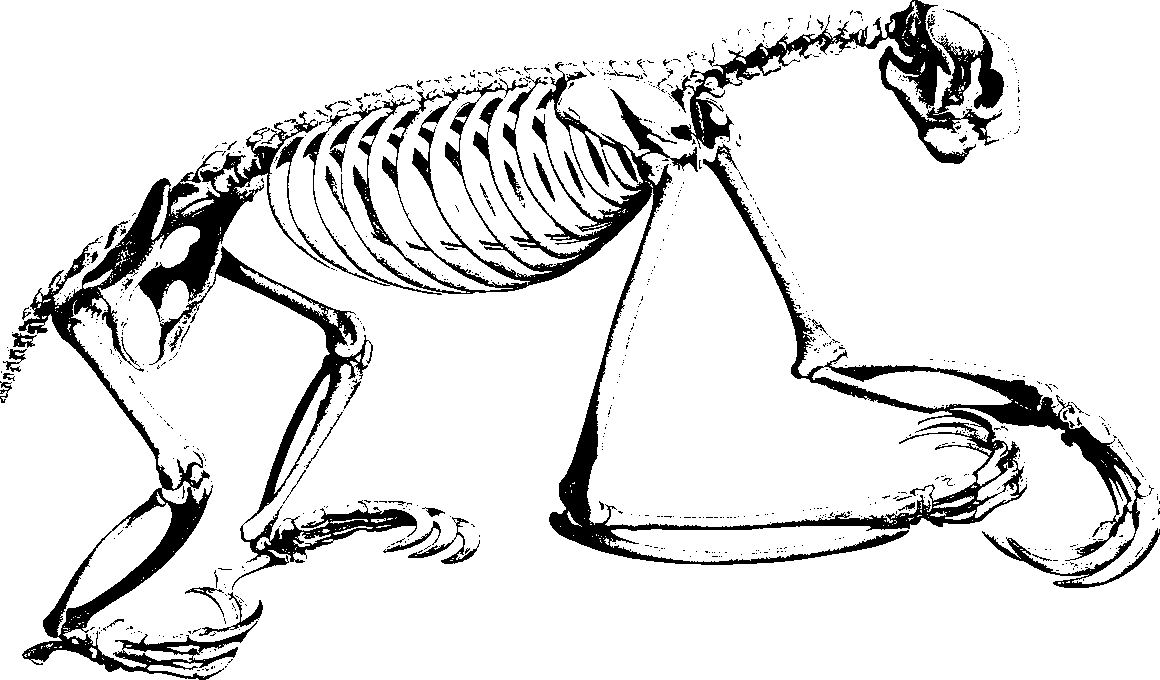
Famous Giant Ground Sloth Fossil Sites Around the World
The world is home to several remarkable fossil sites that capture the history of the giant ground sloth, a fascinating creature from prehistoric times. One of the most famous locations is the La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles, California. Here, the sticky tar traps have preserved an abundance of fossils, including those of the giant ground sloth. Excavations continue to reveal insights into the lifestyle and environment of these ancient animals. The Tar Pits provide not only sloth remains but also many other species, giving context to their existence during the Pleistocene epoch. Another notable location is the Cueva de las Manos in Argentina, famous for its prehistoric cave paintings and sloth remains. Visitors can marvel at the art and the significance it carries about the giant ground sloth’s role in ancient ecosystems. In this site, studies reveal how humans interacted with these massive creatures. Each discovery contributes to addressing questions about biodiversity and extinction patterns. One fact that astounds researchers is the variety of sizes and species found across different locations around the globe.
In addition to La Brea and Cueva de las Manos, the Southern Patagonian Ice Field in Argentina is another significant site. This region has yielded numerous fossils, revealing a wealth of information about the various ground sloth species that once roamed vast expanses of land. Discoveries here have provided valuable insight into the adaptations of these animals to harsh cold climates, reflecting their remarkable evolutionary journey. Most notably, the fossils recovered are from a species known as Megatherium, which were among the largest ground sloths. Another important site is the Folsom site located in New Mexico. This location is historically noteworthy due to its association with early human artifacts, alongside fossil remains of the giant ground sloth. These finds present a compelling narrative about human and sloth coexistence. Researchers here continue to explore the implications of how climate changes may have influenced their eventual extinction. As excavations progress, the potential to learn about environmental interactions between humans and megafauna remains ever present. These discoveries reinforce the importance of such sites in understanding both past ecosystems and modern conservation efforts.
A unique discovery site is the Devonian Hills in Argentina, which is particularly rich in Megatherium fossils. The findings here have contributed substantially to our knowledge of ground sloths and their adaptation mechanisms. This area has yielded stunning remains, from bones to skeletal structures, that help reconstruct the physical characteristics of these creatures. The Devonian Hills showcase how geographic and climatic conditions influenced the evolution of giant ground sloths. Similarly, the Tarija Valley in Bolivia represents another fascinating location where sloth fossils have been unearthed. Researchers here have pieced together important aspects regarding sloth diets and their habitat preferences based on the fossil evidence found. The sediments in the valley suggest a once lush habitat, offering essential information on how the climate changed over time. An integral part of ongoing studies, the Tarija Valley is crucial in understanding extinction drivers. Additionally, the famous location of Isla de Santiago in the Galápagos Islands has presented unique findings. The isolation of this island provided different evolutionary pressures on the ground sloths that lived there, leading to significant divergences from continental relatives that can inform current biodiversity studies.
Impact of Climate on Ground Sloth Fossils
Climate has played a significant role in the fossilization processes found at these various sites. For example, the warmer conditions during certain eras aided in the preservation of remains at La Brea Tar Pits. Conversely, the colder conditions observed in places like the Southern Patagonian Ice Field resulted in unique preservation states. By exploring these sites and understanding the climate’s influence, researchers can better address how adaptability and extinction are connected. The premised relationship between ground sloth fossils and climate change is imperative, as it highlights how previous species responded to environmental shifts. In a modern context, this understanding sheds light on how current species may react to ongoing climate variations. A thorough mining of data regarding these ancient interactions is invaluable for intelligent conservation efforts today. Fossils thus serve as instructive artifacts, painting a vivid image of life and survival during changing climates. Rich content gathered through studies of giant ground sloth fossils demonstrates the broader narratives regarding nature’s resilience, adaptation, and eventual extinction under certain pressures. Recognition of these factors is significant for understanding life’s continuous cycle.
The study of giant ground sloth fossils is not limited to the Americas. European finds also contribute valuable data. In places such as Spain and Italy, unique sloth fossils have been discovered, indicating that some species may have migrated across continents during ancient times. These discoveries suggest more complex interactions between species than previously understood. The findings show remnants of sloths that thrived in diverse climates across the continents, offering insight into their adaptability. The genetic studies derived from these fossils can potentially reveal migration patterns, contributing to the overall understanding of prehistoric life. These sites illustrate the interconnectedness among environments, species, and climatic conditions across the globe. Furthermore, understanding the relationship between terrestrial and environmental changes gives essential lessons on today’s biodiversity challenges. Addressing how current species may respond to changing climates is crucial, paralleling ancient lessons learned from the existence of the giant ground sloth. Gathering and analyzing fossils from varied locations continues to enrich the understanding of how these magnificent creatures lived and why they eventually disappeared, marking essential milestones in the biological history of Earth.
The fossil sites of giant ground sloths are not merely locations of past discovery; they hold the keys to understanding ancient ecosystems and their changes. The continuation of excavations at places like La Brea Tar Pits and other worldwide sites offers opportunities for education and insight. By showcasing the evidence of extinction, these fossil sites serve to remind us of biodiversity’s fragility. Educational programs and exhibits based on these findings foster awareness about past life forms, promoting conservation efforts needed for current endangered species. Public engagement through these efforts aids in spreading knowledge and emphasizes the importance of preserving natural habitats today. Zoos and educational centers can incorporate fossil findings to illustrate ancient species’ lifestyles and environmental adaptations, cultivating interest in paleontology and ecology. As significant educational resources, these sites inform future generations about environmental stewardship. Incorporating findings into community dialogues can bring awareness to how climate and human activity affect both past and present ecosystems. By connecting the past with present conservation approaches, we underscore our role in protecting biodiversity for the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fossil sites of giant ground sloths offer astonishing insights into a world long past. Each site, from La Brea to the Southern Patagonian Ice Field, contributes unique tales of adaptation, interaction, and extinction. The study of these fossils enriches our understanding of ancient environments and life cycles. As we deepen our knowledge of climate impacts, ancient ecosystems become more relevant. The ongoing discoveries from these sites not only enrich our historical narrative but also serve as essential cautionary tales about current environmental challenges. Embracing the stories told by these fossils may inspire actions leading to improved conservation efforts for today’s ecological landscapes. The lessons learned from giant ground sloth fossils teach us about resilience, adaptability, and the need for vigilance in preserving biodiversity. It is through understanding these complex interactions that we can foster future research paths and conservation strategies. Protecting our planet’s richness today ensures that the stories of future generations remain alive. The past informs our future, reminding us that nature’s history plays a pivotal role in ensuring a sustainable ecological balance across the world.