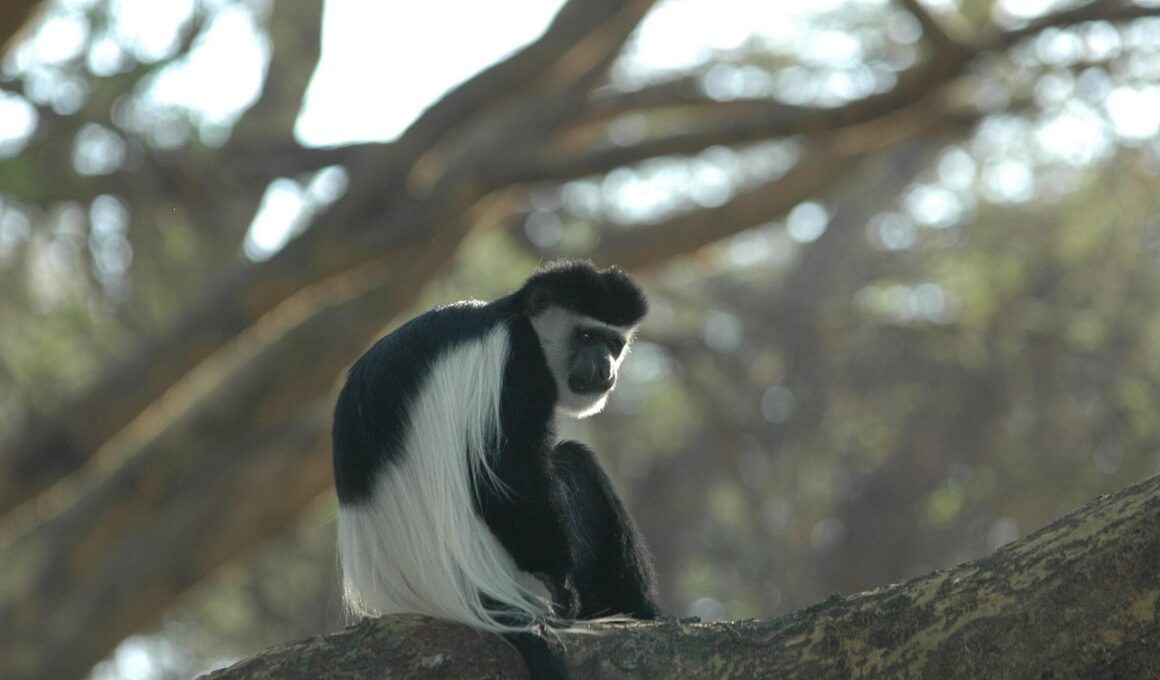
Interactions Between Colobus Monkeys and Other Forest Animals
Colobus monkeys inhabit tropical and subtropical forests, particularly known for their unique adaptation to a leaf-based diet. Their interactions with other forest animals are crucial to understanding the biodiversity of their habitat. Colobus monkeys primarily feed on young leaves, fruits, and flowers, which promotes healthy growth in forest ecosystems. By foraging, they inadvertently assist seed dispersal of various plant species, contributing to forest regeneration. These monkeys are typically social creatures, living in mixed-gender groups, facilitating interactions with other forest fauna. They share their habitat with various herbivores, small mammals, and a variety of bird species. Additionally, they might encounter predators such as leopards or eagles, impacting their behavior and social structures. Other primates, such as baboons or share similar habitats, and competition for food may arise. The presence of larger grazers might also affect the availability of foliage, leading to changes in foraging behavior. Overall, these interactions between colobus monkeys and other animals are dynamic and form an essential part of their ecological niche.
Colobus monkeys have developed various strategies to navigate their relationships with other species in the forest environment. They are known for creating vocalizations that carry over significant distances, which helps to maintain group cohesion and communicate with potential allies. In addition to vocal communication, body language plays an important role; they often engage in grooming behaviors that strengthen social bonds within their groups. These grooming habits may also extend to other species, fostering interspecies relationships, which can be beneficial for cooperative behavioral strategies. Furthermore, when feeding on fruits, they often disturb the environment, attracting small animals eager for leftover scraps. This behavior can establish a connection between colobus monkeys and smaller mammals, as these animals benefit from the remnants of their meals. The interactions can also lead to mutualism, where both parties gain from their relationship. Understanding these dynamics offers insight into the complexity of ecological interactions in the forest, indicating that colobus monkeys act not just as herbivores, but as integral participants in the multi-species community that inhabits their ecosystem.
Social Behaviors Impacting Interactions
Colobus monkeys demonstrate complex social behaviors that influence their interactions with other animals. These primates typically exhibit strong relationships within their groups, marked by intricate social hierarchies and bonds. Their social structures are essential for survival, providing alliances that help in predator avoidance and resource sharing. During their daily activities, they interact with various forest herbivores, from elephants to antelopes, which can indirectly reshape the feeding dynamics of the forest undergrowth. For instance, larger grazers often flatten vegetation, making it easier for colobus monkeys to forage on the resulting regrowth. These interactions illustrate the concept of a shared habitat, where the actions of one species profoundly affect opportunities for others. By understanding these connections, researchers can identify the importance of respecting social structures among primates and other animals. The forest ecosystem operates as a complex web of interactions, where each species plays a role and where changes to one element can ripple across various levels of the community. Colobus monkeys thrive within this intricate system, showcasing how social behaviors can effect ecological balance.
Colobus monkeys also engage in seasonal migrations that can alter their interactions with fellow forest animals. When food sources become scarce during certain times of the year, these monkeys may relocate to areas with better foraging opportunities. This movement can bring them into the territories of other primates, leading to various social encounters that may range from peaceful coexistence to aggressive competition. Non-aggressive interactions often facilitate the sharing of vital resources amongst different species, allowing for cooperation rather than conflict. Their ability to adapt to seasonal changes also reflects their resilience as herbivores within a changing environment. As they migrate and adapt their feeding habits, colobus monkeys will likely discover new relationships with species previously unseen. This adaptability demonstrates the critical nature of flexibility in feeding behavior for colobus monkeys and how it impacts their interactions with others. Ultimately, their seasonal movements illustrate the interconnectedness of species within the forest, emphasizing that survival often hinges on collaborative interactions among various inhabitants.
Influence on Plant Communities
Interactions involving colobus monkeys significantly influence forest plant communities due to their unique feeding behavior and preferences. As primarily folivores, they selectively consume young leaves from various tree species, aiding in shaping the growth patterns of those plants. This consumption promotes the growth of other vegetation, ensuring a diverse range of plant life flourishes in their habitat. The way monkeys forage can influence the richness of plant species, as certain plants may thrive while others decline due to selective browsing. Additionally, their foraging habits can create microhabitats that support other forms of wildlife. For example, the droppings of colobus monkeys not only enrich the soil but also promote the growth of diverse flora that can support various fauna. Their role in seed dispersal contributes to the propagation of plants across the forest, helping maintain the ecosystem’s balance and health. Thus, their feeding strategies are vital, impacting not just their survival but allowing for the support of intricate food webs, showcasing the cascading effects of a single herbivore within a diverse community.
Colobus monkeys play an essential role in the conduct of forest ecosystem processes through their interactions with other forest animals. These monkeys have a particular significance in maintaining the balance among herbivores, as their browsing habits influence the abundance of plant species that serve as critical food sources. Their presence can also affect the feeding behaviors of other animals; for instance, smaller herbivores may adjust their feeding timelines based on colobus monkeys’ activities, establishing dietary niches within overlapping environments. Mutualistic interactions are common in these ecosystems, as other animals, such as birds, can benefit from insects stirred up by colobus monkeys browsing. By studying these relationships, scientists can better understand how such dynamics shape habitats and forge cooperation pathways among species. As these interactions are examined further, it becomes increasingly evident that each species contributes to the stability of the forest ecosystem. Furthermore, as environmental pressures mount due to climate change and habitat loss, understanding these relationships will help in conservation efforts aimed at preserving both the colobus monkeys and their forest communities.
Conservation Implications
To fully appreciate the importance of colobus monkeys, one must consider their role and interactions within the forest ecosystem regarding conservation efforts. Recognizing that they facilitate essential ecological processes highlights that the decline of their populations can result in adverse effects on forest health. Such implications underscore the necessity of protecting colobus monkeys and their habitats from threats, including deforestation, poaching, and agriculture encroachment. Conservation programs must promote awareness about the various roles these monkeys hold in the forest community. Collaborative conservation efforts engaging local communities ensure that the needs of both wildlife and people are met. Programs based on habitat restoration and sustainable resource management are instrumental in preserving the colobus monkey populations while fostering coexistence with other species. Governments, NGOs, and local stakeholders must work together in implementing effective conservation strategies to safeguard colobus monkeys’ ecological presence. By valuing their contributions to forest health, we can work towards a more biodiversity-rich future, acknowledging the intertwined fates of colobus monkeys and their forest environment, ultimately contributing to global ecological resilience.
In summary, the interactions between colobus monkeys and various forest animals depict a rich tapestry of ecological relationships. These monkeys play a fundamental role not only in their communities but in the broader forest ecosystem. Their feeding habits shape plant communities, influence the behavior of other animals, and foster critical interspecies relationships that can benefit diverse forest inhabitants. Acknowledging their importance in maintaining ecological balance through their interactions results in more effective conservation strategies. As we continue to provide suitable habitats for the colobus monkeys, we promote biodiversity and the health of the ecosystems they inhabit. Their presence is undeniably significant, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts that protect not only the colobus monkeys themselves but the delicate balance of their forest homes. Understanding this intricate web of interactions continues to inspire awareness, illustrating that the survival of individual species is inextricably linked to healthy ecosystems. Future research in this domain remains essential to uncover further insights into these dynamics, advancing our efforts in preserving the invaluable connections in nature and ensuring a flourishing forest environment.