The Malagasy Thylacine: A Mysterious Extinct Predator
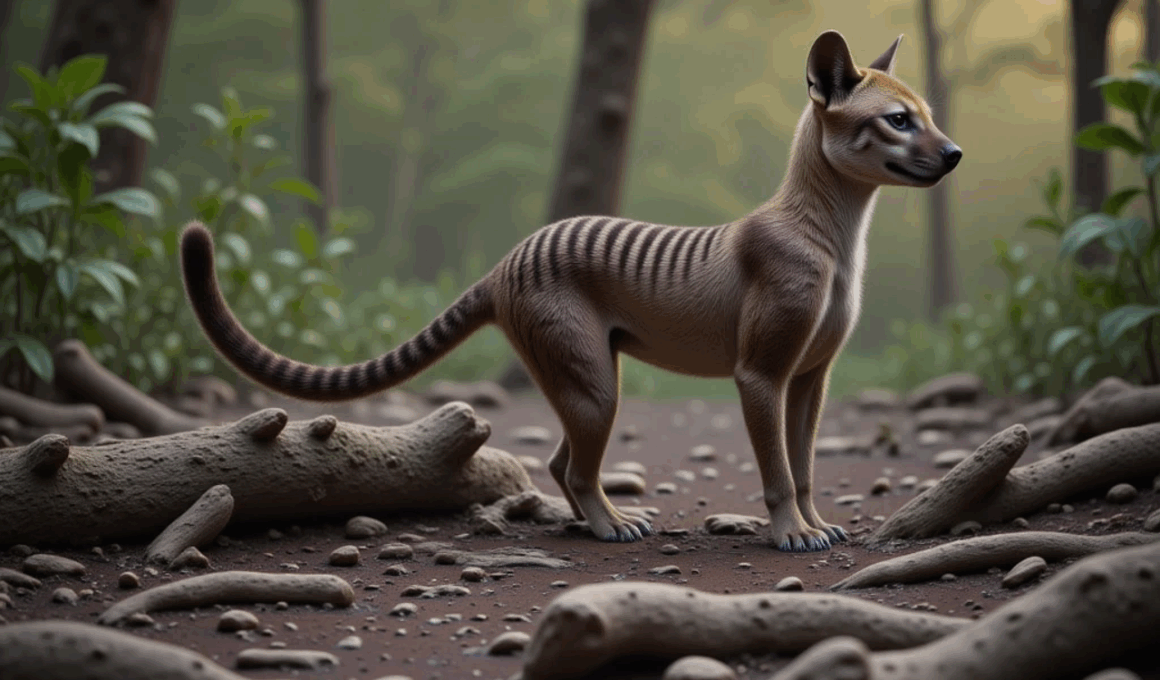
The Malagasy Thylacine, often referred to as the Tasmanian Tiger, was a carnivorous marsupial that inhabited Madagascar. This unique creature became extinct during historical times, leaving behind various myths and mysteries. Its general appearance resembled a large dog, characterized by distinctive stripes along its back, which accounts for its nickname. The disappearance of this predator has puzzled scientists and historians for decades. It is believed that hunting pressure, habitat destruction, and competition with introduced species led to its decline. The extinction of the Malagasy Thylacine presents a crucial case study in understanding how human activities can disrupt ecosystems. Its importance goes beyond mere extinction; it holds insights for biodiversity preservation and conservation efforts worldwide. The Thylacine played a significant role in the balance of its ecosystem, as it was a top predator, naturally controlling the populations of herbivores and smaller carnivores. The loss of such a species can have cascading effects on plant and animal life, ultimately affecting the environment significantly. Efforts to resurrect the memory of the Malagasy Thylacine continue within conservation circles, emphasizing the lessons learned from its past.
Physical Characteristics and Habitat
The Malagasy Thylacine’s physical characteristics were remarkable, making it a fascinating subject of study. This predator typically exhibited a lean build, with powerful limbs and a long snout. Its fur was coarse and had a sandy or brownish color, adorned with dark stripes extending from its neck to its tail. These stripes provided excellent camouflage against the vegetation found in Madagascar’s forests. The Malagasy Thylacine preferred humid, forested regions near rivers and lakes, indicating its reliance on specific habitats. This adaptation was critical for hunting its prey, which included various small mammals and birds. The unique morphology and behavior of the Thylacine helped it navigate its environment effectively, but these specialized traits made it vulnerable when face-to-face with environmental changes introduced by human interference. While this predator thrived in its natural habitat, it also faced challenges due to shifting climate conditions, which ultimately affected its distribution. Understanding the habitat requirements of the Malagasy Thylacine can provide invaluable information for current conservation efforts targeting similar ecosystems experiencing instability. The analysis of this species shows how critical habitat preservation is for maintaining biodiversity.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Malagasy Thylacine is its evolutionary history. Classified as a member of the family Thylacinidae, this predator is closely related to both modern-day Tasmanian devils and quolls. The evolutionary journey of the Malagasy Thylacine can be traced back millions of years, showcasing a unique divergence in the marsupial lineage. As a result, its distinct traits can be attributed to adaptations required for survival in its native ecosystem. Fossil evidence indicates that ancestral Thylacine species roamed across Asia and Australia before eventually finding their way to Madagascar. This geographical isolation allowed the Malagasy Thylacine to develop unique characteristics not seen in its relatives. The study of its evolutionary path is significant as it contributes to understanding adaptive evolution and species survival. Investigating the genetic variation among the Thylacine population may also provide clues about resilience against extinction pressures. The fascinating evolutionary saga of the Malagasy Thylacine not only deepens our understanding of predator dynamics but also enriches our knowledge of marsupial diversity within prehistoric ecosystems. These insights hold immense value for evolving conservation methodologies.
Ecological Role
As a top predator in Madagascar, the Malagasy Thylacine played a vital role in maintaining ecological balance within its habitat. This ancient predator primarily fed on small to medium-sized mammals, thereby regulating prey populations crucial to the ecosystem’s health. By controlling herbivore populations, the Thylacine indirectly influenced vegetation patterns, facilitating a stable environment for many other species. The loss of such a significant predator leads to potential overpopulation of these smaller species, which may ultimately result in vegetation degradation and habitat destruction. The cascading effects of removing the Malagasy Thylacine from its environment illustrate the intricate interdependencies prevalent in ecosystems. In restoring balance after a species disappearance, smaller predators might have to fill the ecological void, but they may not be equipped for such adjustments. An imbalance can lead to further extinction events, demonstrating how critical top predators are to ecosystem dynamics. The study of the Thylacine’s role in its ecosystem provides essential insights for current wildlife managers. Recognizing the importance of predator-prey relationships is fundamental for conservationists engaged in habitat restoration and wildlife protection efforts.
Despite its extinction, the Malagasy Thylacine continues to captivate the imagination of many around the globe. Numerous sightings have been reported, leading to speculative theories about its possible survival in remote areas of Madagascar. These claims often find their way into popular culture, enhancing the creature’s legacy. Such sightings range from anecdotal tales to credible reports, sparking curiosity among cryptozoologists and researchers alike. The mythology surrounding the Malagasy Thylacine not only fuels interest in this extinct predator but also emphasizes the human fascination with lost species. Various documentaries, articles, and books have explored the history and mystery surrounding the Thylacine, underscoring its significance in discussions on conservation and extinction. In addition, this creature serves as a cautionary tale regarding humanity’s impact on wildlife. As ongoing efforts aim to stabilize ecosystems, the Malagasy Thylacine’s story resonates strongly, reminding us to safeguard existing wildlife. This fascination with extinction narratives cultivates awareness of our environmental responsibilities, encouraging support for conservation initiatives worldwide. The enduring legacy of the Malagasy Thylacine epitomizes humanity’s desire to learn from the past.
Conservation Lessons
The story of the Malagasy Thylacine presents several key conservation lessons that remain relevant today. First, it highlights the importance of recognizing the interconnectedness of species within ecosystems. Every species plays a unique role, and losing one can have unforeseen consequences on others. The Thylacine’s decline exemplifies how human-induced pressures, such as habitat destruction and hunting, can lead to extinction. Therefore, proactive measures must be taken to prevent similar tragedies from occurring with existing at-risk species. Conservation efforts must prioritize habitat preservation to ensure ecosystems remain intact and functional. It also emphasizes the need for rigorous scientific research to monitor wildlife populations and assess their health. Establishing protected areas can also benefit to safeguard vital habitats from exploitation. Furthermore, engaging local communities in conservation initiatives is crucial to ensure sustainable practices. The legacy of the Malagasy Thylacine stands as a reminder of the delicate balance within ecosystems and the potential consequences of human interference. Learning from these lessons, conservationists can foster a more sustainable relationship with nature, ultimately securing a better future for both wildlife and ourselves.
The Malagasy Thylacine remains an emblem of extinction, resonating deeply with those who seek to understand the complexities of species conservation. Its mysterious existence encourages ongoing research, inspiring scientists and conservationists to unearth lessons from its history. By fostering awareness regarding the importance of every species, we can ensure a more balanced ecological system. Educating communities about the intricate dynamics of nature may spark a sense of responsibility, prompting individuals to advocate for wildlife protection. The tale of the Malagasy Thylacine underscores the value of maintaining biodiversity, as each species contributes to the web of life that supports our planet. Ensuring that this story endures will motivate future generations to act as stewards of the earth. The Malagasy Thylacine’s plight is a call to action, urging humanity to reevaluate our relationship with the natural world. Continued advocacy for conservation and ecological integrity remains paramount as we work to prevent further extinctions. As we strive for a sustainable future, embracing the teachings left behind by the Malagasy Thylacine must remain at the forefront of our conservation endeavors.
Final Thoughts
Concluding the discussion on the Malagasy Thylacine prompts reflection on its significant role in understanding extinction and conservation efforts. This unique predator, now lost to time, acts as a guidepost for exploring our responsibilities towards preserving biodiversity. As conversations about environmental stewardship evolve, the legacy of the Thylacine emphasizes the critical importance of protecting habitats and engaging in sustainable practices. Furthermore, it serves as a reminder of the actions required to enhance ecological resilience amid climate change and human impact. By studying the lives and challenges faced by extinct species like the Malagasy Thylacine, society can gain insights into preserving the rich tapestry of life on Earth. The extinction narrative reminds us that while some species may be lost, their stories can fuel a movement towards greater appreciation for biodiversity. It is crucial to harness this knowledge in efforts to protect at-risk species from a similar fate. The history of the Malagasy Thylacine ultimately urges us to act more compassionately and responsibly toward our environment, ensuring the legacy of this enigmatic predator lives on through ongoing conservation endeavors.