The Role of Communication in Maintaining Social Hierarchies
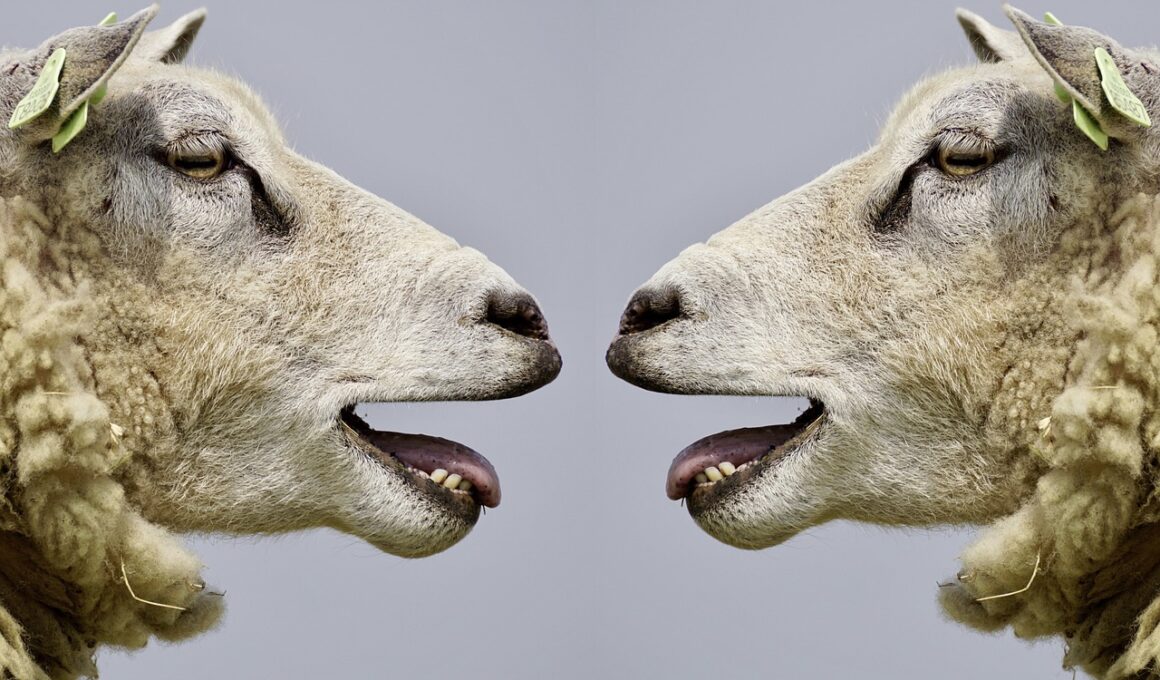
In the wild, communication plays a vital role in the establishment and maintenance of social hierarchies among animal species. Various methods, such as vocalizations, body language, and scent marking are utilized to convey status and intentions. In many species, dominant individuals often display specific traits that communicate their status to others. For instance, the louder vocalizations of dominant males in primate groups serve to assert their position. Observations show that these vocalizations can deter rivals and attract mates. Body language, including posturing and grooming behaviors, also conveys hierarchical status. Moreover, non-verbal communication is crucial in minimizing conflicts in tightly knit social groups, as animals learn to interpret subtle cues. Through these signals, lower-ranking individuals receive information about their status, which influences their behavior. Understanding and reacting to these communications help maintain group stability. In essence, the interplay of signals within social structures lines up with evolutionary adaptations that bolster group cohesion. Thus, by effectively communicating their ranks, animals navigate the complex dynamics that define social hierarchies.
Another significant aspect of communication in social hierarchies involves the display of aggression or submission. Aggressive behaviors are often overtly communicated through various displays consisting of growling, showing teeth, or even physical confrontations. Such displays are crucial, particularly in territorial species where maintaining dominance over an area ensures access to resources. These aggressive displays can preempt physical conflicts since they effectively communicate intentions to rivals. Conversely, submissive signals also play an essential role in keeping the peace. Lower-ranking individuals tend to exhibit behaviors such as turning away or lowering themselves to indicate their position in the hierarchy. This submission avoids unnecessary confrontations and helps maintain social order. Animals like wolves and dogs engage in these behaviors regularly, ensuring that the pack stays cohesive. Additionally, the effectiveness of these communications lies in their clarity, with each signal precisely understood within the context of the social environment. The balance between aggression and submission is tightly woven within the social fabric, showcasing remarkable behavioral adaptations that ensure the survival of the group.
Vocal Communication as a Dominance Tool
Vocal communication is particularly important in species that rely on auditory signals to maintain their social hierarchy. In social birds, for example, intricate songs and calls convey information about individual fitness and social rank. Dominant males often have more elaborate calls, which can deter rivals and attract females. Studies have shown that females prefer males with more complex vocalizations, as they often signal better health and genetic quality. In contrast, subordinates might produce softer, less complex sounds to avoid drawing attention to themselves. The difference in vocalization styles can lead to a clearer understanding of social ranks. Additionally, vocal communication helps facilitate group coordination, as seen in species like dolphins and elephants, where calls are used to maintain contact and unity within the group. This cohesion is vital when navigating environments or during foraging. Thus, the ability to communicate effectively through vocalizations not only serves to establish dominance but also enhances the overall stability and functionality of social groups within animal communities.
Visual cues also play an important role in maintaining social hierarchies in various animal species. In many primates and birds, visual displays such as bright plumage, specific body postures, or unique facial expressions signify dominance or submission. For instance, male peacocks display their vibrant feathers to attract females and intimidate rivals simultaneously. These displays communicate not just individual health but also genetic fitness. Similarly, in primate societies, visual signals, like facial expressions, can indicate emotions such as aggression or submission, allowing individuals to assess each other’s intentions in social interactions. This is particularly evident during encounters that could lead to conflict. The dynamic interplay of visual cues augments verbal communication and supplements the understanding of social ranks. Furthermore, animals may shift their visual signals depending on the social context, showcasing remarkable adaptability. Animals adept at reading these subtle cues navigate social hierarchies more effectively than those who are not. In essence, visual communication strategies are paramount in reinforcing social order and facilitating interactions among group members.
Impact of Scent Communication
Scent marking is another crucial method of communication in many social species. Animals like wolves, cats, and rodents utilize scent to communicate their reproductive status, territorial boundaries, and individual hierarchy. Scent marking involves depositing pheromones in various locations, allowing other members of the species to gather information over time. For example, dominant males may leave stronger scent marks than lower-ranking individuals, signaling their presence and reinforcing their status. This olfactory communication is essential during mating season, as it affects female mate selection based on the quality of scent signals. Moreover, scent plays a role in conflict avoidance. Members of a social group can differentiate between dominant and subordinate individuals through scent, helping to establish and maintain social order without the need for physical encounters. By being able to identify each other’s social rank through scent, animals can reduce the frequency of aggressive interactions. This sophisticated use of scent highlights the complexity of communication strategies animals deploy to sustain their social structures, emphasizing an often-overlooked facet of social behavior.
The interplay of multiple communication methods is seen in species with complex social structures. For example, elephants use vocalizations, visual cues, and scent markings to navigate their social landscapes. This multimodal communication allows elephants to express their hierarchy and coordinate group movement effectively. When a matriarch calls, other members of the herd respond with vocalizations and body language that indicates their social cohesion. The matriarch’s role as a leader is reinforced by her ability to communicate effectively through these various channels. Additionally, elephants display physical interactions such as trunk wrestling, which further solidifies their social bonds. By engaging in these behaviors, elephants maintain group stability, ensuring everyone knows their rank. The dynamic relationships among individuals emphasize the need for varied communication methods within social hierarchy contexts. As social structures become more complex, the reliance on multimodal communication appears to enhance group functionality. This adaptability showcases an evolutionary response to the challenges posed by living in intricate social groups.
Conclusion: The Essential Nature of Communication
In summary, communication serves as a critical component in maintaining social hierarchies across various animal species. Through auditory, visual, and olfactory signals, animals establish and reinforce their ranks, resulting in structured social systems. The balance of aggression and submission in social interactions is paramount for avoiding conflicts and enhancing group cohesion. Research in behavioral sciences continues to unveil the intricacies of these communication strategies, shedding light on their effectiveness in ensuring social stability. Understanding the role of communication in social hierarchies also has implications for the conservation and management of species. By recognizing how these communication channels operate, wildlife biologists can develop more effective strategies for preserving species in their natural habitats. As our understanding of animal behavior deepens, we become better positioned to safeguard these complex social structures. Thus, communication not only enriches our understanding of animal societies but also highlights the fundamental nature of these interactions, ultimately reminding us of the interconnectedness present among all living beings.
The study of animal communication is a fascinating realm that enhances our understanding of social dynamics among species. Each communication method serves a purpose, whether it be signaling aggression, asserting dominance, or fostering relationships. As researchers continue to explore these themes, the nuances of social hierarchies will become increasingly clear. The insights gained will further uncover how interconnected animal societies are impacted by their communicative strategies. Therefore, recognizing the underlying significance of communication in maintaining social hierarchies is crucial, not only to better understand animal behavior but also to appreciate the complex networks that exist within nature. By honoring the interrelationships and communication within these societal structures, we can foster a greater appreciation for the intricacies of life on Earth.