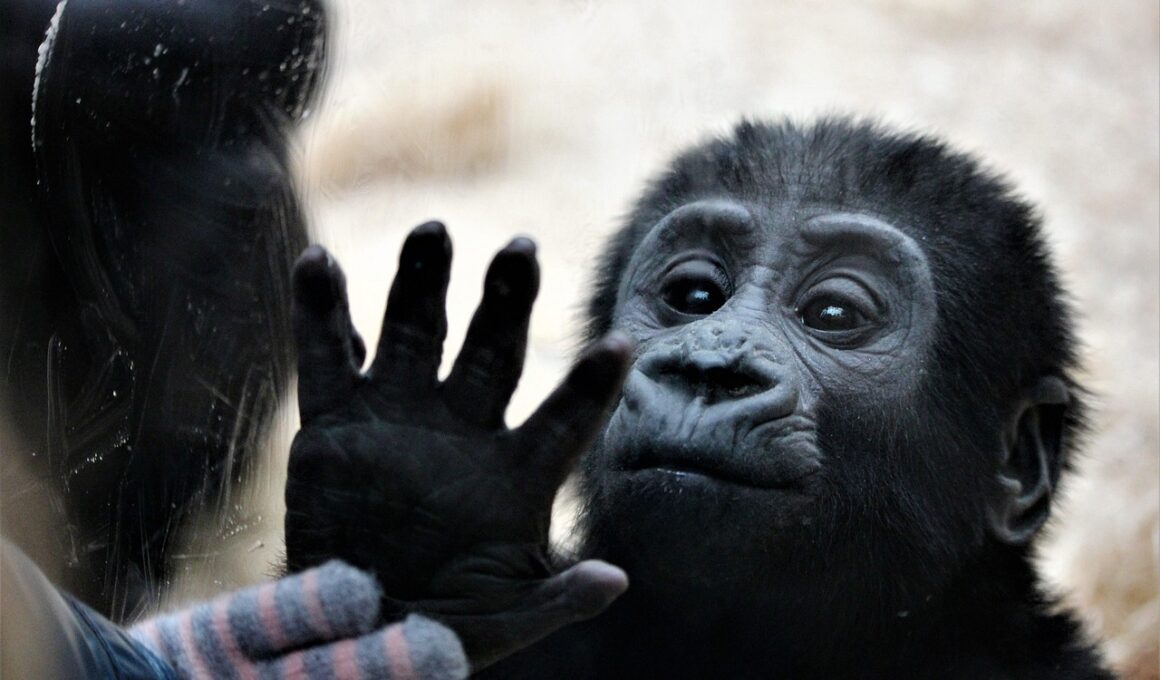
Animal Communication Through Touch and Movement
Animal communication encompasses various modes, including vocalization, body language, and physical interactions such as touch and movement. These forms allow animals to convey critical information about their intentions, emotions, and needs to one another. Understanding how animals communicate through touch and movement can enhance our knowledge of their social structures and behaviors. For instance, many social species use grooming as a form of bonding. In primates, grooming goes beyond mere cleaning; it serves to strengthen social ties and maintain group cohesion. Similarly, elephants engage in tactile communication, using their trunks to touch one another, which can express affection or reassurance. Furthermore, in certain species, such as dolphins, physical interactions often play a pivotal role in their complex social interactions. This highlights the necessity to observe and interpret these behaviors for a comprehensive understanding of animal interactions. By observing how various species interact using touch and movement, researchers can learn more about their social dynamics and emotional states. Each action is laden with meaning, which can inform us about the evolutionary traits that have developed in these species over time.
Touch can convey different emotions in animals, which makes it an essential part of their communication toolkit. For instance, when dogs greet one another, they often engage in a form of touch through sniffing and gentle nudging, indicating friendliness or curiosity. Similarly, cats may utilize gentle pawing or rubbing against another cat to initiate play or affection. In contrast, aggressive encounters may involve more forceful movements, such as biting or swatting. Understanding these subtle nuances in touch can assist pet owners and wildlife enthusiasts in interpreting animal behavior accurately. It also underlines the value of touch in establishing relationships among species. For instance, in social insects like bees, physical contact conveys important information about foraging and colony status through specific movements. Touch can often communicate a multitude of feelings ranging from comfort to hostility, depending on the context and species involved. By studying these behaviors, researchers can gain insights into how animals prioritize social interactions and exhibit preferences for particular social bonds. The interplay between touch and movement demonstrates the complexity of animal communication quite effectively.
Movement as a Form of Expression
Movement in animals is another vital aspect of communication, functioning in both subtle and overt ways. For instance, animals may use body language to communicate dominance or submission. A wolf that raises its tail and stands tall is conveying confidence, while a cowering wolf with a lowered tail signals submission. In social species, movement can also signify readiness to interact or a desire to play. Playful movements, such as hopping or bounding, illustrate excitement and can prompt a reciprocal response from others. Observing these movement patterns can shed light on social hierarchies and relationships among individuals within a group. Furthermore, migratory species often use movement as a means of communicating seasonal changes. For example, birds migrating south indicate changes in weather and food availability. This behavior is instinctual and reflects a collective understanding among the species. By studying these patterns, scientists can understand how animals adapt to their environments and make critical decisions for survival. Overall, the study of movement in animal communication demonstrates the diversity of methods used in social interaction.
In underwater ecosystems, fish use movement to convey information as well. Certain species display vivid coloration or change their swimming patterns to signal threats or attract mates. For instance, the vibrant displays of male bettas during mating rituals are accompanied by fluid movements that demonstrate their vitality. In contrast, when threatened by predators, many fish might exhibit sudden changes in speed or direction to evade capture. Understanding these behaviors is essential for appreciating the intricate language of aquatic life. Moreover, observing how fish use their fins and bodies to communicate reinforces the idea that movement serves various functions across different environments. In terrestrial habitats, animals also exhibit interesting communication techniques through movement. Horses, for example, often use their ears and body posture to express mood and intent, which fellow equines can easily pick up on. This highlights that communication through movement is not only about physical actions but also about how those actions are interpreted by others. Taking note of these cues can enhance our understanding of wildlife behavior and support effective interaction with these magnificent creatures.
Touch and Movement in Pets
Understanding how pets communicate through touch and movement can foster deeper human-animal bonds. For example, dogs often wag their tails to convey excitement or happiness, while a slow wag may indicate caution or uncertainty. This nuanced communication encourages pet owners to be observant and responsive to their pets’ emotional states. Similarly, cats exhibit a range of movements, such as playful pouncing or slow blinks, to signal affection and contentment. Recognizing these movements can help owners cultivate an enriching environment that meets their pets’ emotional needs. Insight into animal behavior promotes cooperation not only between pets and their owners but also among pets themselves. Such understanding emphasizes the role that touch and movement play in reinforcing social bonds in multi-pet households. Moreover, interaction through touch, such as stroking or gentle petting, can be mutually beneficial, reducing stress in both pets and owners. Enhancing these bonds contributes to well-being and happiness within the home. It also draws attention to the importance of recognizing and adapting to the unique communication styles exhibited by different species and breeds.
In conclusion, exploring animal communication through touch and movement reveals a rich tapestry of interactions that provide vital information about emotions, intentions, and relationships within and between species. The diverse tactics animals employ — from the gentle nudging of a dog to the intricate body language of a chimpanzee — illustrate the sophistication of their communicative abilities. Each movement and touch serves a purpose, conveying messages that can be critical for survival, reproduction, and social bonding. By understanding these modes of communication better, we can cultivate more harmonious relationships with the animals in our lives. Furthermore, as we delve deeper into the intricacies of animal communication, we can appreciate the evolutionary significance of these behaviors. The challenges and adaptations experienced by different species encourage a broader perspective on animal welfare and conservation efforts. As we move forward, researchers continue to unearth the complexities of how animals interact, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living beings. Ultimately, recognizing the significance of touch and movement in animal communication enhances our understanding of the natural world.
A potential future endeavour could focus on investigating the implications of human interference in natural animal communication. For instance, urbanization and technology have significantly altered how animals interact within their habitats. As researchers continue to document changes in animal behavior due to these factors, it becomes crucial to address how these alterations shape their communication patterns. Consequently, we may need to explore strategies aimed at preserving natural communication channels among animals. Enhancing our understanding of animal communication through touch and movement will not only enrich our experience with pets but also foster a greater respect for wildlife. Engaging in activities, such as wildlife observation and habitat preservation, can help raise awareness about this fascinating area of study. By nurturing an appreciation for how animals communicate, we empower ourselves to create environments that support their well-being and facilitate natural interactions. In the end, this holistic understanding will contribute positively to conservation initiatives aimed at ensuring the survival of countless species. By recognizing the intricate language of touch and movement, we can enhance our shared habitat and protect the wildlife that enriches our world.
As we reflect on the nuances of animal communication, it becomes evident that touch and movement play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between species. The more we understand these communicative forms, the better we can advocate for animal welfare and conservation strategies. The unique interplay between touch and movement not only strengthens social bonds but also illuminates the emotional lives of animals. Whether we are observing the gentle nudge of a cat or the exuberant playfulness of a dog, we grasp the significant impact of these interactions on their well-being. It encourages us to forge deeper connections with the animals sharing our lives, recognizing their need for social interaction and emotional expression. By cherishing these moments of communication, we foster not just companionship but also respect for the rich tapestry of life surrounding us. Animals have much to teach us about social relationships, emotional expression, and the importance of communication in every aspect of life. As we grow in our understanding of animal communication, we become better stewards of their world, ensuring a harmonious existence for all species.