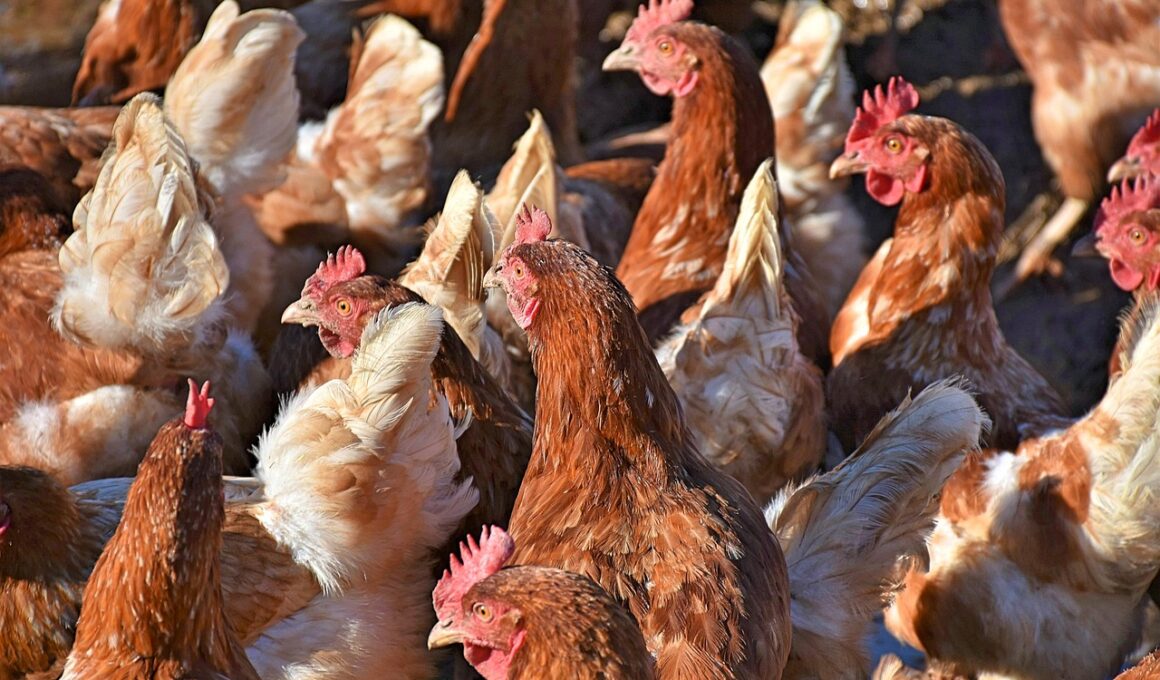
The Importance of Social Structures in Chicken Flocks
Chickens are not just farm animals; they exhibit complex social behaviors that are essential to their well-being. The structure of chicken flocks can be likened to a social community. This community helps to maintain order and ensure survival by establishing roles that each bird takes on within the group. In natural settings, chickens form hierarchical orders, often referred to as a pecking order. The establishment of a pecking order is crucial for minimizing conflict amongst birds. Through social interactions, chickens assert dominance and establish their position, ensuring peace and stability. Understanding this dynamic helps us recognize not only the necessity of keeping chickens in flocks but also how the ratios should be balanced. Proper flock management can greatly affect their health and productivity. When birds are socialized face-to-face, they develop their behavioral patterns better compared to isolated settings. Emotional well-being also comes into play within chicken communities. Recognizing feather pecking or aggression as symptoms of a disrupted social structure is vital. Overall, the social structures in chicken flocks are indispensable to their survival and success.
Chickens engage in various social activities that promote necessary bonding and interactions within their flocks. These activities include roosting, foraging, and dust bathing, showcasing their social needs. Each of these behaviors contributes to reinforcing their social bonds and maintaining unity within the flock. Additionally, chickens communicate through various vocalizations and body language, further emphasizing their social structure. By interpreting each other’s signals, chickens can easily establish relationships and roles. This communication can prevent potential conflicts, thereby fostering a cohesive living environment. Factors such as group dynamics and environmental conditions influence interactions. The presence of a few dominant birds can dictate the movement and behavior of the flock. Interestingly, the absence of these dominant members can lead to chaos amongst the rest. When a sudden change occurs, like introducing new members, establishing a new pecking order is essential. This adjustment may cause temporary discomfort, yet it ultimately leads to a more harmonious living situation. Observing how a flock reacts to changes can provide insights into their social structures. Thus, understanding these social dynamics is essential for optimal flock management.
Benefits of Strong Social Structures
Strong social structures within chicken flocks have numerous benefits that impact their overall health and productivity. A well-structured flock faces fewer issues related to stress, which can lead to illness. When chickens feel secure in their social hierarchy, they are less likely to display aggressive behaviors. This leads to a peaceful environment that promotes better growth and egg production. In addition to immediate benefits, strong social ties ensure long-term viability of the flock. Chickens with supportive social structures tend to forage better and find food more efficiently. Their cooperative behavior ensures that resources are shared, reducing anxiety related to competition for vital materials. Moreover, a stronger flock may have better defense mechanisms against potential predators. When chickens work together, either through vocalizations or physical formations, they can better alert each other to danger. This coordination is pivotal for survival in the wild. Therefore, farmers and poultry enthusiasts should pay close attention to the social dynamics of their chickens. Creating a harmonious environment leads to increased productivity, happier birds, and ultimately a more successful farming experience.
Another crucial aspect of social structures in chicken flocks is how they affect the well-being of individual birds. Social isolation can lead to significant stress and subsequent health issues. Birds that are separated from their flock may display signs of depression, aggression, and an overall lack of interest in their surroundings. A cohesive social environment mitigates these risks by offering emotional support. Each bird can engage in normal behavior when they feel safe within their group. Additionally, chickens learn from observing others in their flock, further emphasizing the importance of social structures. Young chickens tend to mimic older, more experienced birds, adopting beneficial habits that could enhance their survival. This youth-to-adult learning dynamic is vital for cultivating a healthy flock. Recognizing when a member feels marginalized and addressing these social needs is crucial for maintaining flock integrity. Adjustments, such as rearranging social structures or providing additional companionship, can alleviate issues. Thus, attentive management of social dynamics ensures that the flock flourishes as a whole, while each individual bird receives the support it needs for optimal living.
Predator Awareness and Social Patterns
Interestingly, social structures also play a crucial role in how chickens respond to potential threats, such as predators. Chickens rely heavily on their flock for safety. In a tightly-knit group, individual birds establish a protective network. When a threat is perceived, chickens often display specific behaviors that alert the rest of the flock. This collective awareness is what enables chickens to strategize for their protection. Those on the lookout can spot danger and sound alarms, allowing the flock to act quickly. Strong social ties mean that the coordination in these scenarios is efficient. Birds with friendly relationships are more likely to follow one another’s lead during stressful situations. Research has shown that flocks that maintain strong relationships are more successful in avoiding danger. Behaviorally, this means that an alarmed bird can initiate a quick response from the group. Thus, encouraging healthy social structures within henhouses is vital. By fostering cooperative behaviors, owners can ensure their flocks are well-prepared for any threats. A robust social awareness is a cornerstone for both safety and survival within the chicken community.
The implications of social structures are not limited to their behavioral aspects; they also extend to breeding dynamics within chicken flocks. Understanding these dynamics helps poultry managers make informed decisions about breeding choices. Strong social structures allow for better monitoring of reproductive behaviors, ensuring that mating occurs within a supportive environment. This translates into better hatch rates and healthier chicks emerging from eggs. Flocks that are harmonious also have lower incidences of nesting issues, helping ensure that each clutch of eggs is protected and nurtured properly. Each bird’s position within the social hierarchy can influence its breeding success, as dominant birds often have preferential access to mates. Thus, knowing the social structure can provide insights into potential breeding outcomes. Additionally, managers may utilize this knowledge to prevent inbreeding by monitoring genetic backgrounds in a social context. This situational awareness supports long-term flock health and vigor. Therefore, a keen understanding of social interactions can shape effective breeding programs, enhancing both productivity and genetic diversity. Healthy social structures ultimately lead to superior chickens with better productivity and hardiness.
Conclusion
In summary, the importance of social structures in chicken flocks cannot be overstated. From promoting positive behaviors to ensuring overall health, these dynamics are essential for success in domestic chicken farming. By recognizing and nurturing the social needs of chickens, farmers create environments that support natural interactions and bonding among the flock. This ultimately leads to high productivity, robust health, and a sustainable breeding process. Future research in poultry science can further refine our understanding, leading to improved flock management practices. Social structures serve as the backbone of a thriving chicken community. Appropriate management means farmers are more likely to enjoy better results, whether in egg production or meat quality. Therefore, ensuring that chickens flourish in social environments offers opportunities that enhance profitability and animal welfare. Keeping a watchful eye on behavioral patterns, emotional health, and dynamics become inseparable for those invested in poultry farming. Understanding these aspects equips farmers with the necessary tools to adapt to their flocks’ changing needs. In essence, their unique social structures are foundational for nurturing healthy and happy chickens.