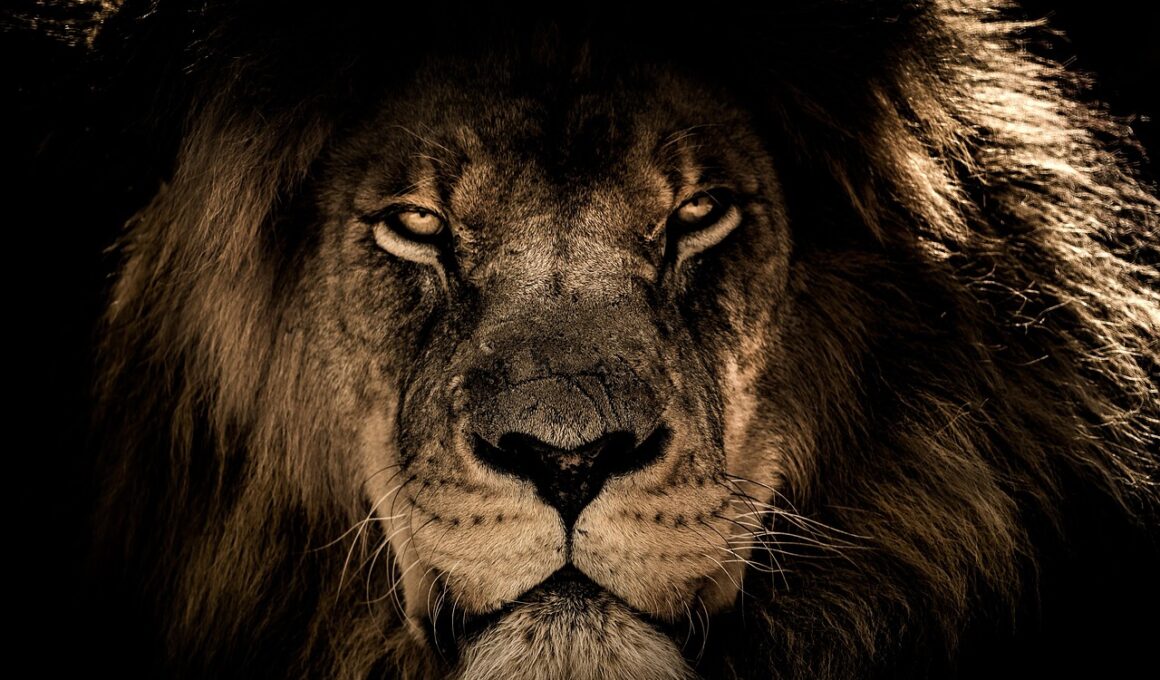
How Diurnal Carnivores Communicate During the Day
Diurnal carnivores, such as lions, tigers, and wolves, exhibit fascinating communication behaviors distinct from nocturnal species. These animals use various methods, including vocalizations, body language, and scent marking to convey social information. Understanding these communication techniques is crucial for conservation efforts and studying animal behavior in their natural habitats. Vocalization plays a significant role in how these creatures maintain group cohesion, allowing them to express emotions, warn of danger, or coordinate hunting efforts. Beyond vocal sounds, body language is equally essential, with postures and movements indicating aggression, submission, or readiness to mate. Furthermore, scent marking helps establish territory and communicate reproductive status. This multi-faceted communication approach ensures that these diurnal carnivores can effectively interact with both their peers and potential threats. In many cases, these communication methods evolve to suit their specific habitats and lifestyles, showcasing the adaptability of these animals. In the following paragraphs, we will delve deeper into specific communication forms, focusing on vocalizations, body language, and scent markings of various diurnal carnivores.
Vocal Communication Among Diurnal Carnivores
Vocal communication is a vital component of social interaction among diurnal carnivores. They employ various sounds to express their emotions, territorial claims, and warnings. For instance, lions communicate through roars, which can be heard several kilometers away, alerting other lions to their presence and maintaining pride cohesion. Wolves often howl to reinforce pack connections or signal their location during hunts. Such vocal expressions not only convey important information but also help strengthen social bonds within groups. The sounds made by these animals can vary significantly depending on the context and intention behind the call. For example, a soft growl or whimper may indicate submission or distress, while a bark can signal excitement or urgent alertness. Each species showcases its unique vocal repertoire, which has adapted over time to suit their ecological needs. Research suggests that vocalization patterns can vary between individuals, suggesting that personal experiences may shape individuals’ sounds. By studying these vocal patterns, researchers can gain insights into the social dynamics and behavioral ecology of diurnal carnivores in the wild.
Body language is another fundamental aspect of communication for diurnal carnivores, allowing them to convey messages without vocalizing. Through their postures, movements, and facial expressions, these animals can indicate their emotional states and intentions. For instance, a raised tail in canids may signal confidence and excitement, while lowered bodies or tucked tails can indicate submission or fear. Similarly, the stance of a lion on the prowl can indicate aggression or threat, especially when paired with intense eye contact. These non-verbal signals are crucial during interactions between members of the same species, as well as encounters with rival groups. Diurnal carnivores may also engage in grooming behaviors that serve both as bonding rituals and as calming signals. Understanding nuances within their body language can prove essential for wildlife enthusiasts and researchers alike. Observing these interactions in a natural setting allows us to appreciate the complexity of their social structures and hierarchies. Ultimately, body language acts as an invisible thread weaving social connections among diurnal carnivores, highlighting their adaptability in various environments.
Scent Marking as a Communication Tool
Scent marking is an essential component of communication among diurnal carnivores, providing a way to establish territory and convey mating readiness. Through urine, feces, and glandular secretions, these animals mark their presence in the environment, leaving behind information for others to decipher. For example, wolves regularly leave scent markings to communicate their location and pack boundaries to other canids. This olfactory communication, while often overlooked, plays a significant role in their social structures. Additionally, when female carnivores are in estrus, they emit specific scents that signal their reproductive status, attracting the attention of males. The ability to interpret these chemical signals is vital for breeding success, ensuring that only the fittest individuals mate. Scent marking can also help reduce conflict among rival groups by providing clear signals of territory ownership, thereby minimizing confrontations. As different species have unique chemical signatures, the diversity of scent marking strategies showcases their evolutionary adaptations. By studying scent marking, we can learn more about the social dynamics, territorial behaviors, and reproductive strategies of diurnal carnivores.
Environmental factors significantly influence the communication methods used by diurnal carnivores. These animals have adapted their vocalizations, body language, and scent markings to suit their surroundings and social environments. For instance, species inhabiting dense forests may rely more on subtle body language due to the limited range of their vocalizations. On the other hand, those in open savannahs often take advantage of their ability to project sound, using vocalizations to convey messages over long distances. Furthermore, seasons and time of day affect their communication patterns, as the presence of competing noises or changes in temperature can influence how and when these animals signal to each other. During mating seasons, vocalizations may increase in frequency to attract potential partners or repel rivals. Understanding these environmental influences allows researchers to develop insights into how diurnal carnivores adapt to changing circumstances. This observational data can be crucial for ensuring the conservation of habitats that support healthy communication among these animals. By identifying their needs and preferences, we can make informed decisions that promote ecological balance.
Impacts of Human Activity on Communication
The increased human activity in natural habitats poses significant challenges for diurnal carnivores, disrupting their communication methods. Noise pollution from urban development, road construction, and industrial operations can mask important vocalizations, making it harder for these animals to communicate effectively. This interference can lead to increased stress levels and social disruption within species. Additionally, habitat fragmentation as a result of land-use changes can isolate populations, making it difficult for carnivores to establish territories and find mates. The reduction of natural spaces forces these animals to adapt their communication strategies for survival, sometimes resulting in more aggressive encounters as they compete for reduced resources. Enhanced understanding of human impacts on their communication is vital for conservation efforts, as it informs strategies aimed at mitigating these effects. Implementing buffer zones around habitats can assist in reducing noise pollution and preserving the natural behaviors of diurnal carnivores. By prioritizing wildlife corridors and promoting awareness of their needs, we can create environments that support healthy communication among these fascinating species.
In conclusion, communication plays a pivotal role in the lives of diurnal carnivores, enabling them to interact with one another, establish territories, and attract mates. Through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking, these animals convey critical information essential for their survival and social structure. As we explore the dynamics of their communication methods, it becomes apparent that understanding these aspects is essential for effective conservation efforts. Furthermore, recognizing and addressing the impacts of human activity on their communication is crucial for protecting their habitats and upholding ecological balance. By fostering awareness and implementing conservation strategies, we can help ensure that diurnal carnivores thrive in their natural environments. Continued research into their communication behaviors will shed light on their social structures and ecological roles, providing fresh insights into maintaining healthy ecosystems. Observing and documenting these interactions allows us not only to appreciate the complexity of their behaviors but also to forge a deeper connection with wildlife conservation. Ultimately, as we unlock the mysteries surrounding diurnal carnivores, we enrich our understanding of the natural world.
Future Directions in Diurnal Carnivore Communication Studies
The future of studying communication in diurnal carnivores holds immense potential for new discoveries. Advances in technology, including acoustic monitoring and GPS tracking, enable researchers to collect rich data on animal behaviors and interactions. The integration of these technologies with field observations allows for precise assessments of how these animals communicate in various contexts. Moreover, interdisciplinary approaches that combine ecology, behavior, and technology will provide comprehensive insights into their communication adaptations. Researchers may harness machine learning to analyze vocalizations, expanding our understanding of species-specific signals and their nuances. The implications of such studies could lead to improved conservation strategies for diurnal carnivores and better habitat management. As researchers continue to uncover the intricacies of their communication, we can cultivate stronger connections with these species, fostering advocacy for their protection. Sustaining these efforts will contribute to our broader understanding of biodiversity and the importance of interspecies communication. The journey into the communication practices of diurnal carnivores is just beginning, and their fascinating world awaits further exploration.