Adaptations of the Desert Hummingbird’s Story
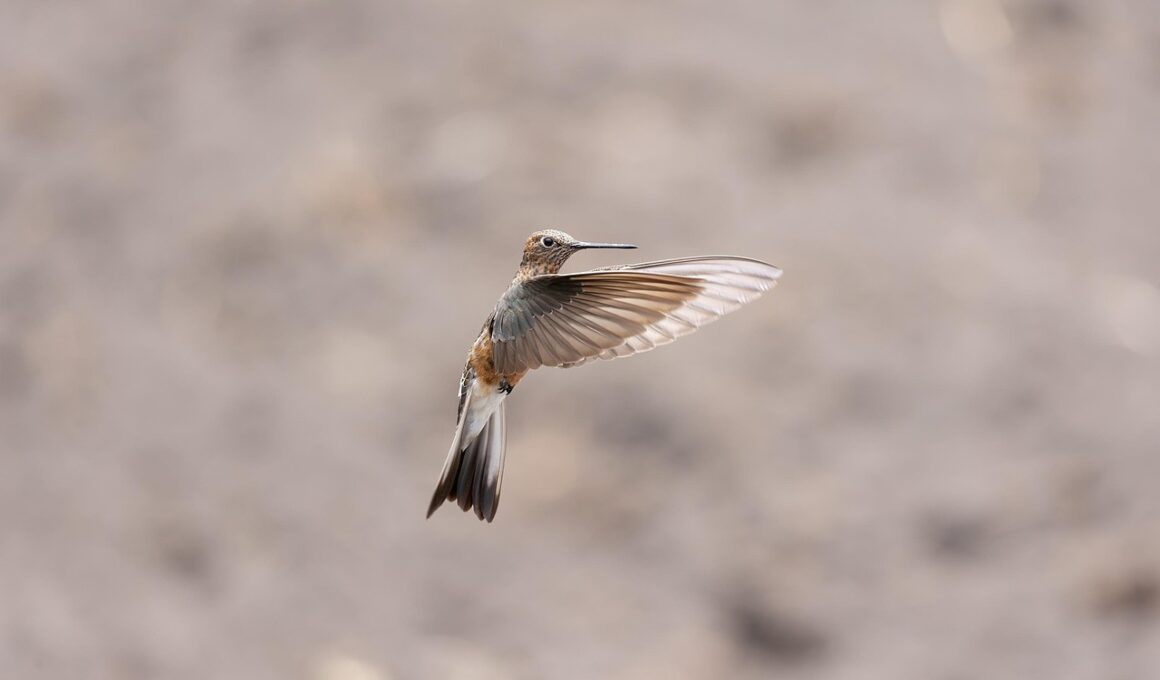
The desert hummingbird is a fascinating creature, known for its remarkable adaptations to survive in harsh desert environments. These birds are typically vibrant in color, and their iridescent feathers reflect sunlight, enabling them to blend into their surroundings. The desert sun can be brutally intense, and so they have developed an efficient way to regulate their body temperature. They do this by becoming more active during cooler parts of the day, such as early morning and late afternoon, while seeking shade at midday. Their lightweight bodies allow for agile flying, important for quickly finding food. One of their primary food sources is nectar, which they obtain from desert flowers. The birds possess long, specialized tongues that can extend deep into flowers to extract nectar. Their ability to hover in place while feeding is unmatched among birds, allowing them to explore difficult-to-reach flowers. Additionally, desert hummingbirds often travel significant distances to find food, demonstrating both their physical stamina and energetic foraging behavior. These adaptations showcase the hummingbird’s resilience and ingenuity in overcoming environmental challenges unique to deserts.
Another critical adaptation of the desert hummingbird is its ability to conserve energy. In the harsh desert environment, where resources are limited, energy management becomes essential. When food is scarce, these birds can enter a state of torpor, similar to hibernation. During torpor, their metabolic rate decreases significantly, allowing them to conserve energy until conditions improve. This ability can save them during times of extreme heat or drought. Furthermore, their wings provide them with incredible agility and maneuverability. The wings can flap at astonishing rates, often exceeding 50 beats per second, which is essential for hovering and rapid direction changes. Their flight is not only a survival mechanism for feeding but also for evading predators, such as larger birds and insects. Despite their small size, desert hummingbirds can display aggressive behavior when defending their feeding territories. They are fiercely territorial, ensuring that their feeding grounds remain exclusive. Often, male hummingbirds will engage in elaborate aerial displays to assert dominance over rivals. Understanding these behaviors paints a vivid picture of their life in the harsh desert ecosystem.
Feeding Habits of the Desert Hummingbird
The feeding habits of desert hummingbirds are closely tied to the timing and availability of floral resources. They primarily feed on nectar, but occasionally supplement this diet with insects and spiders, which provide essential proteins and nutrients. In the desert, flowers bloom seasonally, leading these birds to be highly adaptable in their feeding routines. They often migrate towards abundant flower patches during bloom times. As flowers may be spread out over vast areas, hummingbirds have incredible memory capabilities, remembering the locations of the best food sources. They visit these flowers repeatedly, ensuring a continuous supply of energy to sustain their high level of activity. Additionally, they have developed a symbiotic relationship with certain types of flora; while they feed on nectar, they inadvertently aid in pollination, helping these plants reproduce. This relationship highlights the interconnectedness of desert ecosystems, where every species plays a role. Observing these interactions not only illustrates the hummingbird’s importance in their habitat but also emphasizes the broader ecological dynamics at play in desert environments.
The breeding behavior of desert hummingbirds showcases their unique adaptations further. Males are known for their vibrant plumage and elaborate courtship displays, which they use to attract females. These displays often include aerial acrobatics, such as rapid dives and hovering maneuvers, intended to impress potential mates. After mating, females take on the sole responsibility of building nests and raising young, often with minimal help from males. The nests are typically constructed in hidden locations, using plant materials like leaves, spider silk, and feathers. This careful selection of materials is vital for ensuring the warmth and safety of the chicks. After laying eggs, the female will incubate them for about two weeks, during which time she continuously feeds to maintain her energy levels. Once hatched, her parental duties don’t cease; she tirelessly brings food back to the nest to nourish her growing chicks. This level of dedication demonstrates the hummingbird’s instincts and resourcefulness. Each breeding season reveals the intricate strategies these birds employ, ensuring the survival not only of themselves but also of future generations.
Challenges Faced by Desert Hummingbirds
Despite their extraordinary adaptations, desert hummingbirds face several challenges that threaten their survival. Climate change is one of the most pressing issues, altering bloom times and flower availability in their natural habitats. As temperatures rise or rainfall patterns shift, flowers may blossom earlier or later than usual, making it hard for hummingbirds to find food. Habitat destruction also poses a significant risk, as urbanization and agricultural expansion reduce the natural environments where these birds thrive. Additionally, increased competition for dwindling resources can lead to heightened stress levels within populations. Predators represent another challenge; with fewer plants for cover, hummingbirds may be more exposed to attacks. Furthermore, as humans introduce new methods of farming and landscaping with non-native plants, these birds may struggle to adapt. Conservation efforts must focus on preserving native plants and landscapes. Protecting the hummingbirds’ natural environment is crucial for maintaining their populations and supporting the intricate balance of the desert ecosystem. Awareness and proactive measures are essential to ensure these beautiful birds continue to inhabit our deserts for future generations to admire.
Another crucial aspect of their survival is understanding the role of water sources for desert hummingbirds. Unlike many other birds, they have a unique method of hydration; they can derive moisture directly from the nectar they consume. However, water availability can significantly impact their health and reproductive success. During particularly hot or dry spells, these birds may need to adapt their foraging strategies to include checking for water sources like puddles or dew on plants. By maximizing their access to hydration, they increase their chances of survival in the desert environment. Conservation efforts should also prioritize these critical water sources, ensuring that hummingbird-friendly habitats include accessible watering areas. Moreover, local landscaping can benefit these birds by incorporating plants that attract them and provide both food and hydration. Native plants require less water, thus promoting a more sustainable environment for desert hummingbirds. By fostering healthy ecosystems, we support the intricate interconnectedness of desert life, highlighting humanity’s role in preserving these vital habitats. This is an important step in securing the future of desert hummingbirds and the diverse life forms that coexist with them.
Conclusion on Desert Hummingbird Adaptations
In conclusion, the story of the desert hummingbird is one of remarkable adaptation and resilience. These birds are a testament to nature’s ingenuity, demonstrating how life can thrive even in the most challenging conditions. Their adaptations span behaviors, physical traits, and ecological relationships, ensuring their survival and well-being. From their hovering skills and remarkable memory to their intricate breeding practices and reliance on seasonal blooms, every element is a testament to their incredible evolution. As we face environmental changes impacting their habitats, it becomes crucial to advocate for their protection. Preserving the delicate balance of desert ecosystems is essential not just for the hummingbirds but for countless other species relying on these habitats as well. By understanding and respecting the adaptations of the desert hummingbird, we can inspire conservation efforts focused on protecting their life-sustaining environments. Engaging communities in awareness initiatives enhances appreciation for these enchanting birds. The desert hummingbird embodies the beauty of nature’s adaptability, urging us to value and protect our natural world fiercely. Through our efforts and commitment, we can secure their story and ensure they continue to astonish future generations.
Lastly, studying the ecological role of desert hummingbirds can reveal broader insights into desert ecosystems. As pollinators, they contribute crucially to maintaining plant biodiversity, which offers food and habitat for many other species. Their actions remind us of the interconnectedness of life within these environments, emphasizing that protecting one species can have ripple effects on the ecosystem. Their presence signifies a healthy habitat, where flora can thrive and sustain diverse forms of wildlife. Engaging scientists and conservationists to monitor hummingbird populations helps in assessing ecosystem health over time. Community involvement in conservation can foster respect for local wildlife while promoting interest in ecological studies. People can take steps by planting local flora, making their spaces hummingbird-friendly, thus providing refuge and food. Schools, communities, and organizations can collaborate toward conservation initiatives that benefit both plants and desert wildlife. Through educational programs, we can spread knowledge about the vital role of hummingbirds and teach future generations about ecology and their local environments. Addressing environmental challenges collectively can help mitigate threats facing them and improve overall desert biodiversity.