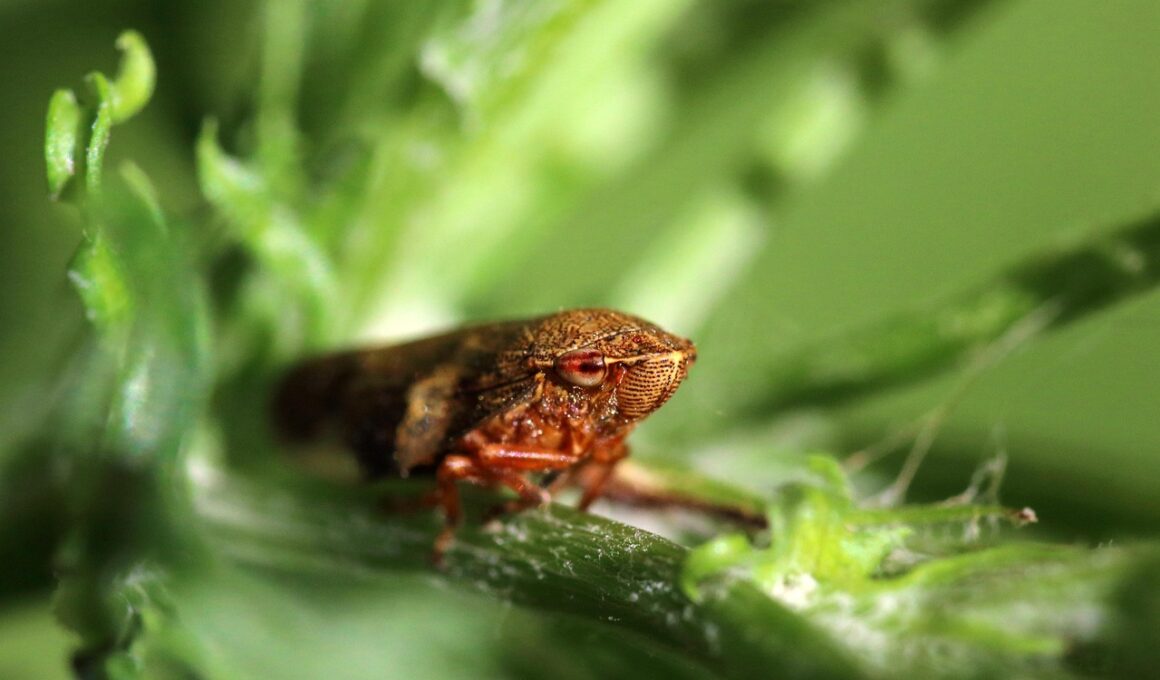
Spittlebugs and Their Unique Spittle Masses
Spittlebugs, classified under the family Cercopidae, are fascinating insects known for their intriguing behavior of excreting spittle-like substances. These small, sap-sucking insects undergo a unique life cycle that primarily revolves around the production of a protective foam, known as spittle mass, which serves multiple purposes. Spittle masses are often seen on the stems of grass and various plants, resembling small, frothy blobs. This form of protection is essential for the nymphs, which are the juvenile stages of spittlebugs. By covering themselves in this foam, they evade predators, staying safe from birds and other threats that may prey on them. Moreover, the spittle acts as a moisture reservoir, helping them survive varying environmental conditions. As they feed on plant sap, the production of this foam is critical not just for their safety but also for their overall development. Gardening enthusiasts may encounter these little creatures more frequently during warm, humid seasons, as this is when spittlebug populations thrive. Learning about the role of spittlebugs contributes to our understanding of biodiversity and ecosystems within insect wildlife.
There are various species of spittlebugs, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific environments. In North America, the Meadow Spittlebug, or Philaenus spumarius, is perhaps the most recognized due to its prevalence in grasslands and gardens. The nymphs create their spittle masses by mixing air, water, and their secretions, producing a frothy barrier that protects them as they feed on plant sap. Other species, such as the Clastoptera genus, also exhibit similar behavior, each adapted to their specific habitats. Spittlebugs are often overlooked due to their small size, but they play essential roles in their ecosystems. The spittle they generate can promote plant health by providing a unique microenvironment, contributing to the breakdown of organic matter. In addition to their ecological roles, some species serve as bioindicators of soil health, informing ecologists about the overall condition of an ecosystem. Furthermore, while they may be pests in larger populations, most spittlebugs tend to have minimal impact on plants compared to other insect species.
The spittlebugs’ intriguing behavior and life cycle have attracted the attention of researchers in entomology and ecology. Studying these insects provides insights into their adaptive strategies, which are vital in fluctuating environments. Their distinct spittle masses, which vary in size and appearance among different species, also serve as identification markers for researchers and enthusiasts alike. Creating a spittle mass is not merely for camouflage; it involves complex interactions between secretions and environmental factors. The foam must maintain its structure to prevent desiccation while being light enough to allow the nymphs to move freely. The chemistry behind spittle formation remains an area of active research, exploring how these substances interact with the environment. Additionally, understanding the life cycle of spittlebugs helps in developing sustainable pest management practices. For instance, engaging with local flora that minimizes harmful insects can reduce spittlebug populations. As such, recognizing and respecting the role of spittlebugs can promote biodiversity in gardens and agricultural settings, ultimately leading to healthier ecosystems and better food management with minimal pesticides.
The Role of Spittle Masses in Ecology
Spittle masses influence not only the surviving spittlebug population but also the overall health of the ecosystems where they reside. The foamy structures they create can aid in retaining moisture within the soil, thus supporting the growth of surrounding vegetation. In turn, healthy plant growth fosters larger populations of herbivorous insects like spittlebugs, creating an intricate food web that supports various animal species. As food sources for birds and other small predators, spittlebugs play a vital role in maintaining balanced ecosystems. Their feeding habits can also contribute to the natural pruning of plants, promoting new growth and maintaining ecological diversity. Furthermore, spittlebugs are part of the broader interconnected web of life, influencing the insect community in gardens and farms. They form part of the diet of numerous predators, including birds, spiders, and larger insects, which helps regulate their populations. By understanding their ecological niche, we can appreciate the importance of spittlebugs in sustaining biodiversity and the impact their spittle masses have on shaping healthy habitats.
While spittlebugs are often harmless, certain species can become pests, particularly in agricultural settings. Their feeding can cause stress on host plants, leading to reduced vitality and crop yields. In certain cases, large populations may result in stunted growth or even death of certain plants. However, naturally occurring predators often keep these populations in check. Awareness of the potential risks associated with spittlebug infestations is essential for gardeners and farmers alike. Integrated pest management strategies can mitigate the negative impacts of spittlebugs, including introducing natural predators or applying organic treatments that are less harmful to the environment. Keeping the garden balanced by planting diverse flowers can also attract beneficial insects. Additionally, recognizing the signs of spittlebugs, such as the foamy masses on plants, aids in timely intervention. Essential tools like magnifying lenses can help identify the pests effectively, allowing for early management. Encouraging natural predation within gardens can lead to a sustainable approach to keeping spittlebug numbers low without drastic chemical measures, thus ensuring a healthier ecosystem overall.
The future of spittlebug research promises exciting discoveries. As scientists explore their unique adaptations, there are potential applications in agricultural practices and pest management. Understanding the chemical composition of spittle could lead to developments in synthetic materials that mimic their protective qualities or even enhance soil health. The principles observed in the life cycle of spittlebugs could inform approaches aimed at increasing resilience within crops against pests and diseases. Awareness and appreciation of this insect family can foster greater collaboration between researchers and the agricultural community. By utilizing spittlebugs as natural pest control agents, it’s possible to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides, promoting ecological balance. Ongoing studies are essential for monitoring the impact of environmental changes on spittlebug populations and their associated ecosystems. Educational campaigns can help inform the public about the importance of all insects, including spittlebugs, in maintaining healthy environments. Efforts focused on preserving natural habitats may also enhance the resilience of spittlebugs and their spittle production, securing their role in local ecosystems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, spittlebugs and their unique spittle masses are not only scientifically intriguing but also ecologically significant. Their unique adaptations highlight the delicate balance between species within ecosystems and their role as essential players in biodiversity. By protecting habitats and embracing sustainable gardening practices, we ensure the survival of these mites, benefiting the broader ecosystem. Understanding the life cycle and ecological roles of spittlebugs equips both scientists and the public with knowledge crucial for fostering a harmonious environment. Their existence provides us with valuable lessons about resilience and adaptation in nature. Efforts aimed at research, education, and conservation can help emphasize their significance and promote awareness of insect biodiversity. As guardians of our gardens and natural spaces, spittlebugs remind us of nature’s complexity and interconnectedness. Taking steps to preserve spittlebug populations, like planting diverse vegetation and minimizing pesticide use, promotes sustainable ecosystems. Thus, through appreciation and respect for spittlebugs, we support the fragile balance of life and contribute to a more sustainable future both for our environment and the creatures that inhabit it.
In summary, spittlebugs, with their remarkable spittle masses, epitomize nature’s ingenuity. By learning about these insects, we not only safeguard their future but also enrich our understanding of ecological relationships. While small, their impact on biodiversity is profound, reminding us of the intricate tapestry of life surrounding us. In cultivating a world that respects all forms of life, we ensure the survival of spittlebugs and many more vital species.