How Climate Change Shifts Affect Endangered Species’ Rights
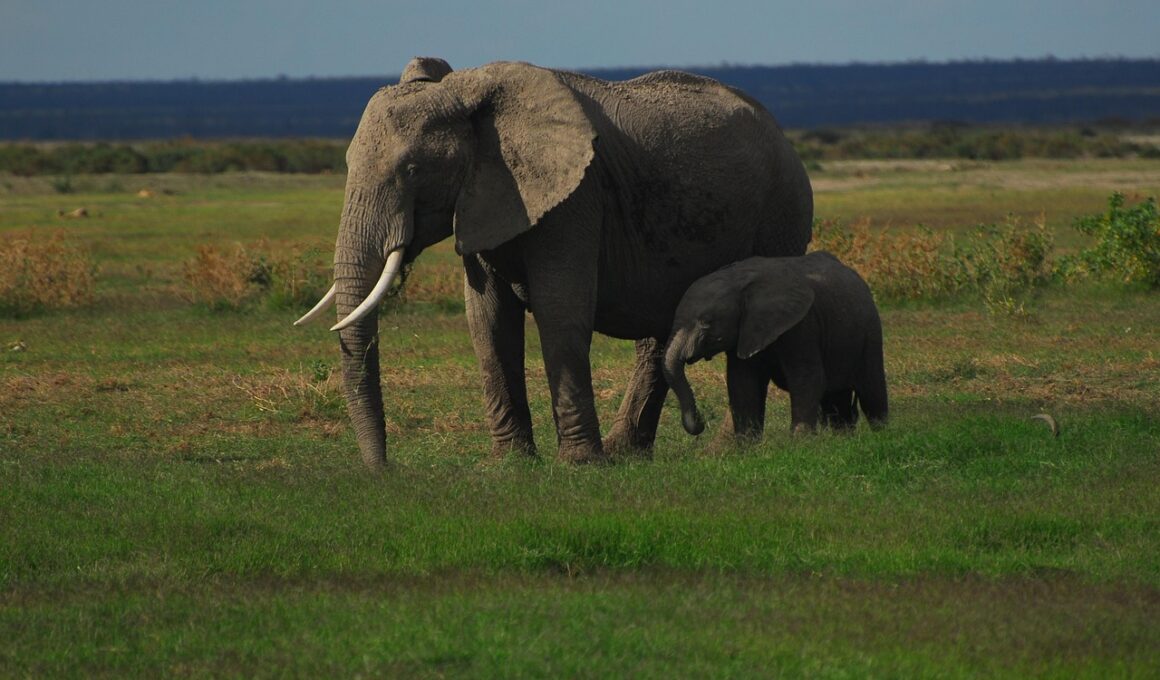
The ongoing impacts of climate change significantly alter the ecosystems in which endangered species thrive. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, many species face dire consequences. These changes force certain animals to relocate to more suitable habitats, impacting their survival rates. For instance, polar bears are losing their hunting grounds as ice caps melt. With diminishing sea ice, they struggle to find food, and this exacerbates their endangered status. The reallocation of resources necessary for various species creates an imbalance, as native habitats transform. Furthermore, climate change can lead to increased competition for dwindling resources among species, heightening stress levels. Additionally, many sites that used to be safe havens change drastically, diminishing the protected rights of these species. Governments and environmental organizations need to recognize the international implications of habitat loss and genetic diversity depletion. Proper enforcement of existing animal rights laws becomes crucial in such situations. The conversation on climate change is expanding beyond human welfare, pressing society to address the urgent needs of wildlife, including their rights, protection, and conservation efforts.
The Intersection of Climate Change and Biodiversity
Climate changes drive alterations in biodiversity, threatening various animal species more than ever. The relationship between climate and biodiversity is profoundly interconnected, as shifts in temperature and habitat directly influence species’ survival rates. Biodiversity loss occurs when specific species cannot adapt to new settings rapidly enough. For example, amphibians are particularly susceptible to environmental changes because of their sensitive skin and reproductive needs. Loss of biodiversity negatively affects ecosystems overall, disrupting food chains and other vital processes. This, in turn, further affects the rights of endangered species that depend on these ecosystems for survival. Additionally, climate change triggers extreme weather events, which can devastate habitats and leave species struggling to adapt. As a result, the rights of these vulnerable animals become secondary to human-centered developments. Laws and policies often overlook these changes, leaving gaps in protection for many species. Fostering an understanding of the interdependence between climate change and animal rights is crucial for future conservation efforts. Efforts must prioritize balancing human activities with wildlife needs to ensure the fundamental rights of all species are respected in the face of climate change.
Impact on Species Migration Patterns
Many animal species are already showing shifts in migration patterns due to climate change, which leads to increased vulnerability. Migration is essential for species to find food, breed, and sustain healthy populations. However, as temperatures rise, the natural cues that guide these migratory patterns become disrupted. Birds are a prime example, as many rely on specific climate conditions to signal their seasonal movements. Changes can lead to mismatches between the timing of food availability and migration, creating severe consequences for survival. Additionally, animals venturing into unfamiliar territories may encounter new predators and competitors, further jeopardizing their existence. Adaptation to new environments takes considerable time, and not every species has the luxury to adjust swiftly. Among those that fail to adapt, extinction becomes an ominous reality. To address these shifts, we need robust conservation strategies that account for changing patterns. Governments must consider these dynamic patterns when implementing policies related to endangered species and their habitats. A collaborative approach involving communities, researchers, and policymakers can help create inclusive strategies to mitigate climate change’s negative impacts on migration.
Pollinators like bees and butterflies illustrate how climate change threatens specific species crucial for our ecosystem balance. Their decline jeopardizes plant reproduction, which in turn affects the entire food web. As temperatures fluctuate, blooming times shift, disrupting the mutualistic relationships these pollinators share with plants. This disconnect can diminish food sources, leading to both plant and pollinator decline. Acknowledging the role of pollinator rights within the broader framework of animal rights is essential for preserving ecosystems. Furthermore, agricultural practices contribute significantly to pollinator decline, as pesticides and habitat destruction create barriers to their thriving. Protecting the rights of these critters can lead to more sustainable agricultural practices, benefiting both the environment and food production. Advocating for policy changes that prioritize pollinator preservation ensures that their inherent rights are acknowledged. Moreover, education around the importance of maintaining healthy pollinator populations can empower communities to take action. Supporting organic farming, rewilding efforts, and planting native flora offers direct avenues for restoration. The intertwining of animal rights with climate advocacy highlights the undeniable responsibility we hold in protecting those species struggling to adapt.
Legal Framework Surrounding Animal Rights
In many regions, existing legal frameworks surrounding animal rights fail to address the complexities surrounding climate change. Laws often don’t account for the heightened risks animals face due to environmental uncertainty. Current regulations may prioritize human interests over animal welfare. It’s essential to reevaluate these laws to include climate-related provisions that acknowledge the challenges species face. For example, the Endangered Species Act usually protects habitats, but how can it effectively adapt to changing environments? These challenges require innovative legal solutions that reflect modern ecological realities. Policymakers must strive to develop proactive measures that prioritize species resilience and recovery. Additionally, education around climate impacts on wildlife rights must enhance awareness among lawmakers and the public alike. Developing partnerships between conservation groups and governments can promote more effective legal responses to climate-driven threats. Integrating scientific research into lawmaking offers a pathway for informed decisions. Moving forward, we need a comprehensive approach that recognizes the interplay between animal rights and climatic shifts, ensuring that species have the support they need to thrive in a changing world.
The Role of Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts become increasingly vital as climate change brings challenges to endangered species. These efforts encompass a wide range of strategies aimed at protecting wildlife and their habitats. For instance, wildlife corridors are designed to enable species to migrate between fragmented habitats without jeopardizing their safety. Habitat restoration initiatives seek to revitalize areas significantly affected by changing climates, enhancing conditions for endangered species. Additionally, targeted breeding programs can help increase population numbers when natural reproduction rates decline. Organizations often focus on maintaining genetic diversity, which promotes resilience within species. Collaborating with local communities fosters a sense of ownership toward conservation initiatives, encouraging sustainable practices. Building awareness regarding the interconnectedness of climate change and species rights is crucial for garnering public support. Additionally, donations and volunteer efforts contribute significantly to these programs’ sustainability. Governments must allocate adequate funding to defense and recovery efforts as part of their commitments to international conservation agreements. Advocating for stronger wildlife protections ensures a brighter future for endangered species. Our collective responsibility to mitigate the impacts of climate change includes supporting effective conservation initiatives for the benefit of future generations.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Understanding the effects of climate change on endangered species leads to a critical conversation about animal rights in the face of uncertainty. Addressing their needs is not only an ethical responsibility but also essential for ecological balance. Striking a balance between human development and the rights of animals must be the priority moving forward. Further research on climate impacts will enable scientists to provide informed recommendations for policies that protect vulnerable species. Advocacy plays a crucial role in ensuring these rights are prioritized in discussions surrounding climate change. Public awareness campaigns can influence positive change by fostering empathy and urging communities to engage in sustainable practices. Continuous dialogue among stakeholders can promote collaborative approaches toward legally protecting endangered species as climate change affects their habitats. As we develop more robust frameworks to accommodate their growing vulnerabilities, maintaining transparent communication remains vital. Ultimately, the conversation about climate change must include the rights of those most affected. Prioritizing environmental justice and advocating for animal rights can create a future where all species coexist harmoniously, contributing to the greater ecological prosperity we all rely on.