Feeding Adaptations of Jungle Herbivores
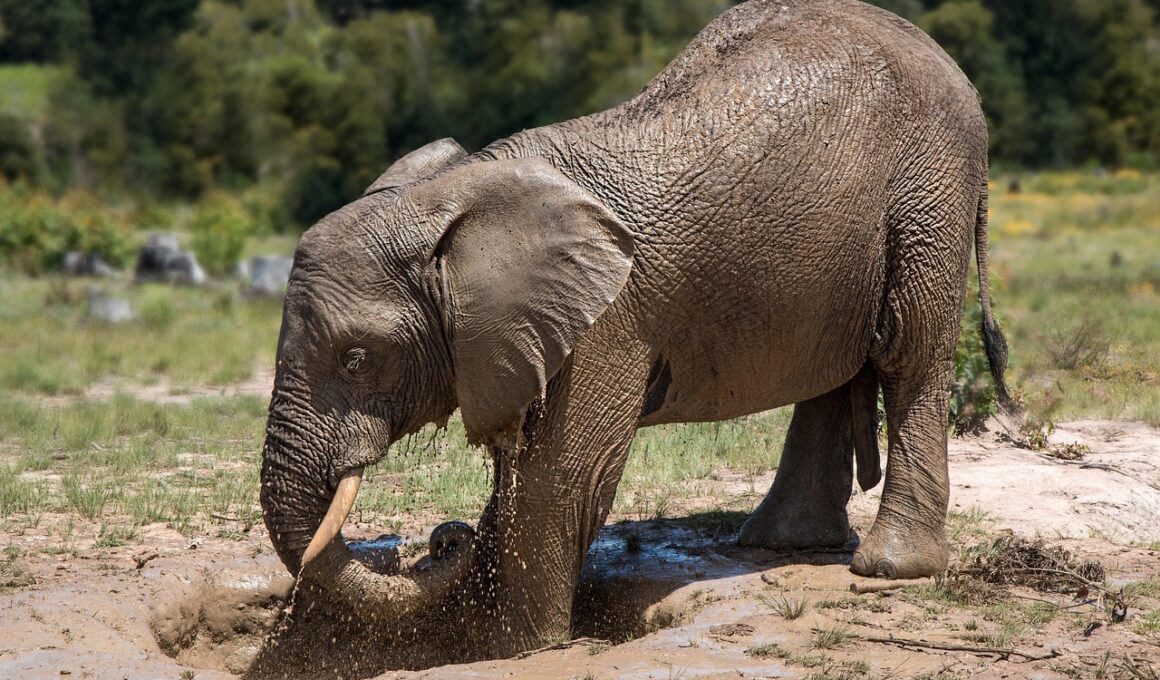
Jungle herbivores have evolved remarkable feeding adaptations to thrive in their lush, vibrant habitats. These adaptations are essential for their survival and involve various anatomical and behavioral traits. For instance, many of these animals possess specialized teeth that allow them to process tough plant material efficiently. Grazers like elephants have molars with broad surfaces designed for grinding, while browsers such as deer have sharper incisors for clipping leaves. Additionally, digestive adaptations are also prominent. Many jungle herbivores have developed complex stomachs to break down fibrous plant matter. Ruminants, like giraffes, utilize a multi-chambered stomach to ferment their food, maximizing nutrient absorption. Beyond these anatomical features, behaviors also contribute to their feeding success. Herbivores often exhibit foraging strategies that minimize competition and ensure access to diverse food sources. They may travel significant distances in search of their preferred foliage or fruits, adapting to seasonal changes in plant availability. Furthermore, jungle herbivores often have symbiotic relationships with other species, such as birds, that help them locate food. These intricate feeding habits are critical for maintaining the balance of their ecosystems.
Understanding the diverse diets of jungle herbivores reveals their intrinsic connection to their environments. Each species employs specific feeding strategies tailored to its niche. For instance, capybaras graze on grass and aquatic plants, using their webbed feet to navigate through wetlands, while iguanas primarily consume leaves, flowers, and fruits. These dietary preferences not only aid their survival but also influence the structure of plant communities in their habitats. By choosing specific plants to consume, herbivores impact plant growth and diversity. The foraging behavior of these animals often leads to the shaping of their ecosystems, as they create pathways and clearings within dense foliage. Furthermore, the dispersal of seeds through feces is significant, as many herbivores play a crucial role in plant regeneration. In turn, this mutual dependence highlights the importance of maintaining healthy populations of jungle herbivores. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting these species are paramount, given their influence on biodiversity. Ultimately, the diverse diets of jungle herbivores exemplify the intricate relationships that sustain their habitats and ensure their ongoing survival in a rapidly changing world.
Role of Competition in Feeding Habits
Competition among jungle herbivores significantly influences their feeding habits and dietary choices. Different species often share the same habitat, leading to a variety of strategies for resource acquisition. To reduce competition, herbivores have developed unique feeding niches, which involve differences in the types of vegetation they consume and when they feed. For instance, while some species may graze during the day, others become crepuscular, foraging at dawn or dusk to avoid overlap. Additionally, some animals opt for less competitive diets, consuming plants that are less palatable or harder to access. This niche differentiation helps maintain ecological balance and reduces direct competition for food resources. Furthermore, interactions between herbivores can lead to adaptive behaviors, as animals may adjust their feeding patterns based on the presence of competitors. Research has shown that large herbivores, like tapirs, can impact the feeding behavior of smaller species by altering the availability of food through selective foraging. Understanding these dynamics provides insight into the complex relationships that govern jungle ecosystems and the need for conservation measures to protect these unique interactions.
The seasonal availability of food sources also impacts the feeding habits of jungle herbivores. Throughout the year, different plants flower and bear fruit at varying times, leading to a dynamic change in diets. During the wet season, abundance in foliage may lead to increased competition among herbivores, requiring them to adapt their foraging behaviors. Some species, like the howler monkey, capitalize on the fruiting cycles of specific trees, resulting in changes in their social structures and behaviors during peak fruiting times. In contrast, during the dry season, food scarcity may force some species to adjust their diets more drastically, consuming bark or seeds that are less nutritious. Furthermore, herbivores may migrate to areas with more reliable food supplies, showing an adaptability that is essential for their survival. Conversely, these seasonal changes can influence predator-prey dynamics, as herbivores are often more vulnerable when foraging for scarce resources. Understanding these seasonal feeding habits provides a clearer picture of the challenges jungle herbivores face in their quest to survive amid highly variable environments.
Mutualism and Its Impact on Feeding
Mutualistic relationships play a vital role in the feeding strategies of jungle herbivores. Certain herbivores depend on specific plant species that provide not only nutrition but also protection. For example, the ants and acacia trees showcase this relationship well; the ants guard the tree from herbivores, while tangling leaves offer shelter. Additionally, many herbivores rely on fruits and flowers as a food source, aiding in pollination and seed dispersal, which enhances plant diversity. These relationships illustrate the interconnectedness of species within the jungle ecosystem. Furthermore, some birds serve as foragers for larger animals, helping them locate hidden food sources or warning them of potential predators. This type of symbiosis benefits both parties, as birds gain access to food while herbivores enjoy greater safety when foraging. By maintaining these mutualistic interactions, jungle ecosystems thrive, contributing to the resilience of various species. Recognizing the significance of these collaborative relationships is essential in conservation efforts to protect these species and their habitats. Ultimately, mutualism highlights the complex web of interdependencies that characterizes the rich biodiversity of the jungle.
Foraging efficiency is a crucial aspect of jungle herbivores’ success, focusing on maximizing nutrient intake while minimizing energy expenditure. Many species exhibit specialized foraging techniques, such as selective feeding, where they choose the most nutritious parts of plants. For instance, primates, like spider monkeys, are known for their dextrous grasp, allowing them to select the ripest fruits and leaves. Likewise, elephants demonstrate intelligence in their feeding behavior, utilizing their trunks to access leaves from tall trees or uproot shrubs. Such adaptability enhances their ability to process diverse diets effectively. Furthermore, herbivores may utilize social feeding strategies, where groups of animals work together to access food more efficiently. This cooperative behavior can reduce individual foraging time and enhance overall survival rates. Additionally, younger members often learn feeding techniques from older, more experienced individuals, showcasing the transfer of knowledge within species. Thus, the role of foraging efficiency underscores the adaptability and intelligence of jungle herbivores as they navigate their lush environments. This enables them to make the most of available resources in a highly competitive ecosystem.
Conclusion on Feeding Adaptations
In summary, the feeding adaptations of jungle herbivores are complex and multifaceted, reflecting the diversity of their environments. These adaptations highlight their resilience in meeting the challenges of foraging within rich ecosystems. From specialized teeth and digestive systems to sophisticated foraging behaviors, these animals have developed effective strategies for survival. The dynamic interplay of competition, seasonal factors, and mutualistic relationships further enriches our understanding of their feeding habits. The intricate web of interconnections between species exemplifies the need for ongoing conservation efforts to protect these vital ecosystems. Additionally, recognizing the importance of herbivores in maintaining ecological balance underscores the significance of each species in its habitats. By ensuring the health of jungle herbivores, we not only support their survival but also the diverse array of life that relies on these animals for sustenance and ecological integrity. As we continue to study these fascinating creatures, we foster a deeper appreciation for the complexity of jungle ecosystems and the vital roles that each species plays within these environments.
Understanding the feeding adaptations of jungle herbivores helps us appreciate their crucial role in ecosystem dynamics. These animals exemplify nature’s creativity and resilience as they adapt to survive in rich biodiversity. Educating ourselves and others about their importance can foster a greater sense of responsibility for conservation efforts worldwide. With increasing threats to their habitats due to human activities, protecting jungle herbivores and their environments is more pressing than ever. By preserving their ecosystems, we not only secure the future of these remarkable animals but also the myriad species that coexist alongside them.