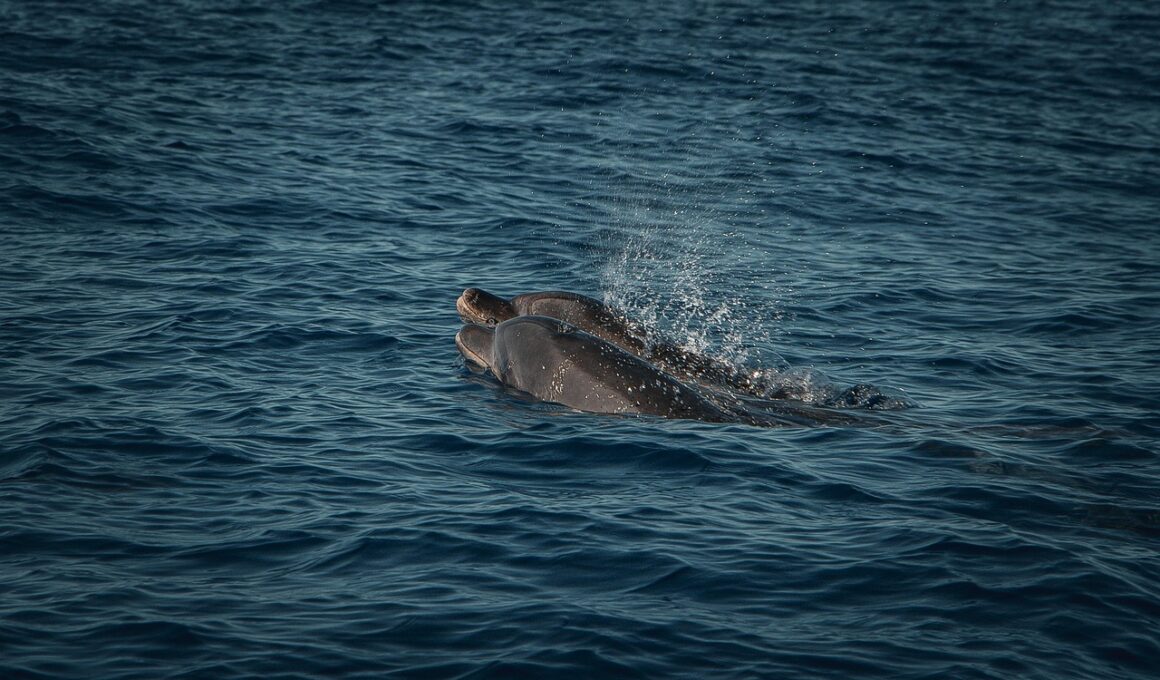
Diet and Feeding Habits of Porpoises
Porpoises are fascinating marine mammals belonging to the family Phocoenidae. As members of the cetacean order, they are often grouped with dolphins and whales. Both porpoises and dolphins share an oceanic habitat, yet their dietary preferences and feeding behaviors can differ significantly. Porpoises primarily feed on a variety of small fish and invertebrates, employing echolocation to detect their prey. Prey species include herring, mackerel, and various crustaceans. Due to their size, especially smaller species, porpoises have a higher metabolic rate compared to larger cetaceans, necessitating frequent feeding. They typically hunt alone or in small groups, often relying on teamwork to catch schools of fish. Their hunting strategies can include herding fish into tight formations, making them easier to capture. The feeding habits of porpoises can vary greatly depending on the region they inhabit as well as the time of year. Seasonal changes can lead to shifts in prey availability, forcing porpoises to adapt their diet accordingly. This adaptability is key to their survival in diverse marine environments, highlighting the intricate balance within marine ecosystems.
These positioning techniques not only facilitate successful hunting but also illustrate porpoises’ remarkable cognitive abilities. Similar to other cetaceans, porpoises display a variety of vocalizations, further allowing them to communicate while hunting. Their calls can help coordinate group efforts and locate prey effectively. In addition to social cues, environmental factors such as water temperature and salinity can impact the distribution of their prey. As a species, porpoises have shown a great adaptability towards changing ecosystems, which is crucial for their survival. Some species even venture into brackish waters, where they take advantage of local fish populations. This versatility indicates that porpoises can thrive in environments that many other marine animals would find less hospitable. Genetic studies have also uncovered the biological adaptability of these mammals, revealing their evolutionary traits over time. Regarding feeding, it’s noteworthy that porpoises exhibit variations in their foraging methods across different species. They may use strategies such as speed and agility to outmaneuver fast-swimming fish. Overall, understanding porpoise diets aids conservation efforts, as it underscores the ecological role they play in maintaining balance within marine environments.
Foraging Techniques of Porpoises
Foraging techniques employed by porpoises are both diverse and fascinating. When hunting, porpoises are often seen displaying behaviors such as diving and surfacing rapidly. They are known to use several hunting strategies that vary between individuals and species. One common technique is the use of speed and agility to chase down small fish. During these hunts, porpoises may pursue their prey to considerable depths, showcasing impressive skills for chasing fast-moving targets. Another interesting method includes the phenomenon of cooperative hunting, where two or more porpoises work together to capture larger schools of fish. This particular approach can significantly enhance their success rate. Porpoises also utilize echolocation, enabling them to detect prey in murky waters or when visibility is low. By emitting clicks and interpreting the returning sounds, they can locate food sources more efficiently. They can differentiate between various fish species based on their reflecting sounds, allowing them to target specific prey. The ability to adapt these techniques depending on environmental conditions showcases porpoises’ remarkable intelligence and dexterity, solidifying their status as skilled hunters in the marine ecosystem.
Porpoises exhibit different feeding habits depending on the specific environment they inhabit. For example, coastal porpoises may consume more benthic feeders, such as small crabs or shrimps, while their offshore counterparts tend to hunt pelagic fish. This feeding adaptability is paramount for porpoises, as prey availability can significantly fluctuate based on environmental changes and seasonal migrations. Hence, their diet is not only a reflection of their personal preferences but also a direct response to the local ecosystems they inhabit. As dedicated predators, porpoises have a variety of anatomical adaptations that assist in feeding. Their streamlined bodies allow for fast swimming, while their conical teeth are perfect for grasping slippery fish. Due to the varying sizes and shapes of prey, these physical adaptations enhance their hunting success. Additionally, porpoises may also engage in social learning, where younger individuals observe and mimic older porpoises during hunting expeditions. Hereby, the transfer of knowledge becomes essential for maintaining feeding proficiency across generations. These aspects highlight the intricate relationship between porpoises and their prey, emphasizing their role in sustaining the health of marine environments.
Impact of Environmental Changes on Diet
The diet of porpoises is intricately linked to their surrounding environment, making them susceptible to the impacts of climate change and human activities. Shifting water temperatures often affect fish migration patterns and availability, directly influencing porpoise feeding habits. As temperatures rise, some fish species may move to deeper waters, while others might follow the cooler waters, requiring porpoises to adapt their hunting grounds. Pollution and habitat degradation further compound these challenges, introducing toxins into marine ecosystems that can accumulate in prey species. Such bioaccumulation can lead to health issues for porpoises that rely on these contaminated fish as primary food sources. Changes to coastal habitats, including urban expansion and fishing practices, can adversely affect the distribution of prey species, making it harder for porpoises to find food. Conservation efforts must consider these factors when assessing porpoise populations and their dietary needs. Integrating ecological research with policy changes is crucial to protecting porpoises from continuing threats posed by environmental issues. Understanding how these animals adapt to shifting diets can guide effective management strategies that ensure their longevity in the wild.
Establishing protected areas and sustainable fishing practices can significantly benefit porpoise populations. By creating marine reserves, we can help maintain healthy prey stocks and safeguard essential habitats. Collaborative efforts between fisheries and conservation organizations can help mitigate the negative impacts of fishing on porpoise diets. Such partnerships are vital for balancing economic interests with the ecological needs of marine ecosystems. Promoting public awareness of porpoises’ dietary habits is equally important. Educating local communities about the role these mammals play in maintaining healthy oceans encourages support for conservation initiatives. Local stakeholders, including fishermen, can be allies in protecting porpoise habitats through responsible fishing practices. Moreover, engaging in citizen science projects allows individuals to contribute data on porpoise sightings and behaviors, enriching our understanding of these mammals. As more awareness spreads, a collective effort emerges, resulting in more robust conservation movements. Recognizing porpoises’ role as indicators of marine health can help prioritize their preservation amidst ecological challenges. Understanding the connection between their diet and environment enhances our appreciation for these remarkable creatures and underscores the importance of protecting their habitats for future generations.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Their Diet
In conclusion, comprehending the dietary and feeding habits of porpoises is essential for their conservation and overall ecological health. These marine mammals display extraordinary adaptations to ensure their survival in dynamic environments, showcasing their impressive hunting techniques and cognitive abilities. By learning about the variety of prey they depend on, we can gain insights into their ecological roles and the broader marine ecosystems they inhabit. The ongoing effects of climate change and human intervention pose significant challenges to their diets. Therefore, continuous research and adaptive management strategies are crucial to sustain porpoise populations. Conservation measures must not only focus on protecting these animals but also take into account their vital prey and habitats. Public education and awareness campaigns can galvanize support for conservation efforts, emphasizing the interconnectedness of marine species. Porpoises serve as key indicators of ocean health, making the understanding of their diets relevant for preserving marine biodiversity. Through deeper insights into their feeding habits, we can advocate for effective policies that protect their environments while promoting healthy oceans for generations to come.
As we strive to comprehend the intricacies of porpoise diets further, international cooperation becomes paramount. Collaborative initiatives among countries sharing oceanic resources can lead to more effective conservation strategies. Cross-border efforts allow for standardized fishing regulations that benefit both local fisheries and porpoise populations. By safeguarding marine habitats collectively, we ensure these delightful animals continue to thrive in their natural environments. Expanding research efforts into the dietary needs of various porpoise species is also crucial. Long-term studies can yield valuable insights into the effects of ecological changes on feeding behaviors and overall health. Gathering data over time also makes it easier to see trends in porpoise diets and how these correlate with environmental factors. Engaging scientists, conservationists, and communities in this research is vital for fostering a deeper connection to our oceans. The more we understand the dietary needs of porpoises, the better positioned we are to create impactful conservation measures. In conclusion, the continued protection of porpoises and their necessary habitats hinges on our commitment to understanding their diets. Together, we can make strides toward preserving these magnificent cetaceans for future generations.