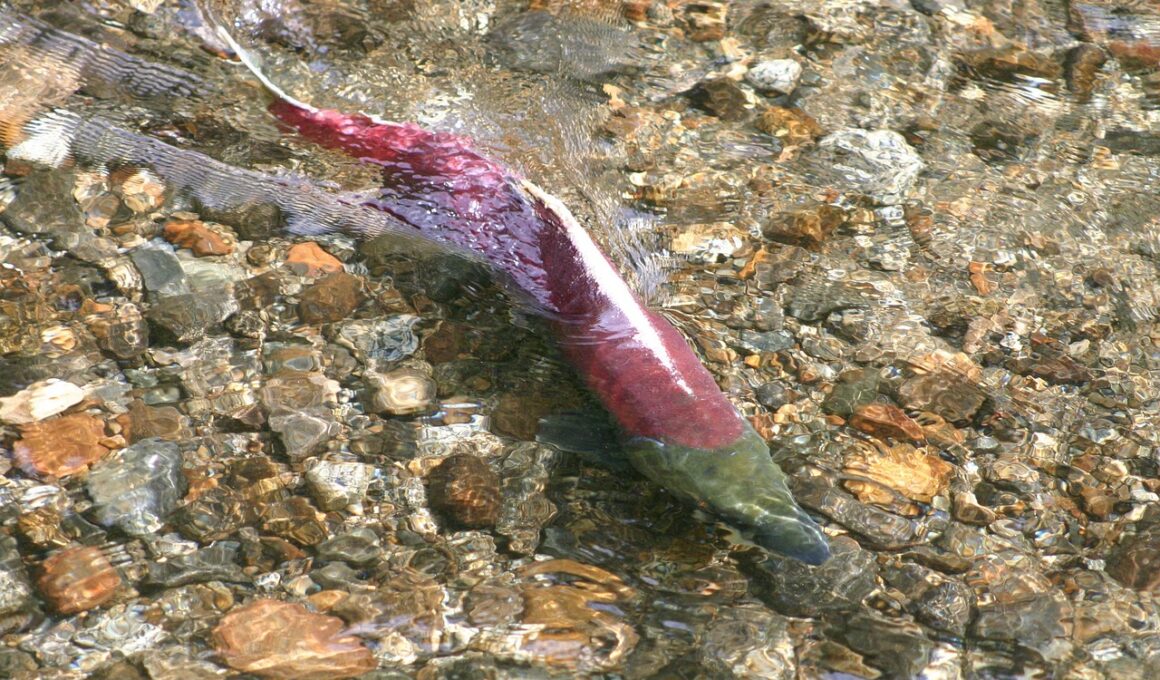
Diadromous Fish: Understanding Their Migration Habits
Diadromous fish are unique creatures known for their complex migration patterns, which are essential for their survival and reproduction. These fish are classified mainly into two categories: anadromous and catadromous. Anadromous species, such as salmon, are born in freshwater, migrate to the ocean to grow, and then return to freshwater to spawn. On the other hand, catadromous fish, like eels, begin their lives in saltwater, migrate to freshwater rivers to mature, and then return to the ocean to reproduce. Understanding these patterns is crucial for conservation efforts, as many species are threatened by habitat loss and climate change. The distinct migration routes taken by diadromous fish are influenced by various factors, including water temperature, salinity, and the availability of food resources. Their journey often spans vast distances, showcasing incredible endurance and navigation skills. Researchers utilize various techniques, such as tracking devices and environmental DNA sampling, to study these migrations. Such studies help us learn about the fish’s life cycles and the health of aquatic ecosystems, which are vital for biodiversity. Protecting these habitats ensures the future of diadromous species and the benefits they provide.
Migration cycles of diadromous fish are not just fascinating but also critical to the ecosystems they inhabit. Many species of diadromous fish play significant roles within their environments. They contribute to nutrient cycling when they migrate between freshwater and marine systems, transporting valuable nutrients. For example, salmon returns to rivers carries marine-derived nutrients that significantly enhance the productivity of river ecosystems. This nutrient transfer benefits various species, including plants, insects, and other fish. The decline in diadromous fish populations can lead to adverse consequences, such as reduced nutrient availability, which negatively impacts ecosystem health. Therefore, understanding and protecting the migration routes of these fish is crucial to maintaining the overall health of our aquatic environments. Conservation efforts should focus on mitigating threats faced by diadromous species, such as dams and pollution. Effective fish passage solutions must be implemented to allow safe migration routes for these species. Raising public awareness about the ecological importance of diadromous fish is key to garnering support for conservation initiatives. By educating communities and stakeholders, we can foster a better understanding of the necessity to protect these fish and their habitats for future generations.
Challenges Faced by Diadromous Fish
Diadromous fish encounter numerous challenges during their migration journeys, primarily due to human-induced changes in their habitats. One major threat is the construction of dams, which obstruct natural migration routes. Dams prevent fish from accessing spawning grounds, significantly impacting their reproductive cycles. Additionally, water quality degradation from pollution can make rivers and lakes inhospitable for young fish, further decreasing their survival rates. Overfishing is another critical challenge that directly affects diadromous populations by reducing their numbers and genetic diversity. As fish populations dwindle, their ability to recover from environmental stresses becomes increasingly compromised. Climate change also poses a significant risk, altering the temperature and flow of water systems that diadromous species rely on for migration. These changes can disrupt their migratory patterns, making it more challenging for fish to reach their spawning grounds. Lastly, habitat destruction due to urban development and agriculture reduces the available spawning and nursery habitats for these vulnerable fish. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive conservation strategies and collaborative efforts from governments, organizations, and local communities worldwide.
Efforts to conserve diadromous fish populations must employ a multifaceted approach that combines science, policy, and community engagement. Effective conservation strategies should incorporate habitat restoration, improving fish passage at barriers like dams, and implementing sustainable fishing regulations. Restoration projects often include replanting riparian vegetation, restoring flow regimes, and removing invasive species. Such efforts help rehabilitate ecosystems while providing essential habitats for young fish. Policymakers must work to establish protective regulations that ensure healthy fish populations and safeguard their critical migratory routes. This might include creating designated conservation areas and establishing fishing quotas to promote sustainability. Advocating for the incorporation of fish-friendly designs in infrastructure projects is vital to ensure that future developments are compatible with the needs of migrating fish. Local communities can also engage through citizen science programs, promoting awareness and education regarding the importance of diadromous fish. By participating in monitoring activities, individuals can contribute valuable data that support research efforts. Public outreach campaigns aimed at raising awareness can promote the intrinsic value of these fish and the ecosystems they inhabit. Together, individuals and organizations can play essential roles in the conservation of diadromous fish.
The Importance of Research in Fish Migration
Research plays an essential role in understanding the migration habits of diadromous fish, providing insights into their behavior, ecology, and population dynamics. Scientists utilize a variety of methods to study these fascinating fish, including telemetry, genetic analyses, and community monitoring. Telemetry involves using advanced technology to track fish movements in real-time, allowing researchers to gain a better understanding of their migration routes and behaviors. Genetic analyses can reveal the population structure and genetic diversity within diadromous species, informing conservation efforts. Furthermore, studying community interactions helps researchers understand how diadromous fish contribute to their ecosystems. Collaborative research initiatives that involve multiple stakeholders can enhance our understanding of fish migrations. Universities, government agencies, and non-profit organizations often work together on projects to develop comprehensive conservation strategies. Such collaborations ensure that various disciplines contribute to the advancement of knowledge around these species. Additionally, public involvement in research initiatives is crucial for data collection and raising awareness about the ecological significance of diadromous fish. Through the combination of scientific knowledge and community engagement, innovative solutions can be developed to address the challenges faced by migrating fish.
In conclusion, diadromous fish exhibit remarkable migration habits that play a crucial role in the health of both freshwater and marine ecosystems. Their complex life cycles and the challenges they face highlight the importance of understanding these species for effective conservation efforts. By recognizing the interdependence of diadromous fish and their habitats, we can promote sustainable practices that protect these vital resources. Conservation efforts must be collaborative, involving scientists, policymakers, and local communities to ensure successful outcomes. Public awareness is incredibly important; educating communities about the ecological significance of diadromous fish can foster a culture of stewardship. Additionally, innovative research methodologies enhance our understanding of these species, aiding in identifying the most effective conservation strategies. The future of diadromous fish lies in our hands, and the responsibility to protect their migrating routes and habitats must be embraced collectively. Advocating for fish-friendly policies, restoring essential habitats, and engaging communities will create a positive impact on diadromous fish conservation. By championing the cause of these unique fish, we are not only protecting a species but also ensuring the health of entire ecosystems for generations to come.
As we continue to learn more about diadromous fish, it is essential to integrate traditional knowledge from local communities. Indigenous practices, which have been handed down through generations, can offer valuable insights into fish migrations and their historical patterns. This knowledge provides a complementary perspective to contemporary scientific research, enriching our understanding of these intricate ecosystems. Involving local communities in conservation efforts fosters a sense of ownership and pride, ensuring the sustainability of initiatives aimed at protecting diadromous fish. Furthermore, recognizing the cultural significance of these fish in various communities underscores the need for conservation. It is essential to approach conservation holistically, respecting ecological, cultural, and economic dimensions. In recent years, collaborative programs that bridge science and indigenous knowledge have emerged, demonstrating the potential benefits of integrating diverse approaches. Such partnerships can empower communities to advocate for their fish populations while also providing scientists with valuable data derived from lived experiences. Ultimately, the quest to understand diadromous fish migrations requires an inclusive approach that welcomes contributions from all sectors of society. Through such unity, progress can be achieved in preserving our planet’s rich biodiversity and the species that depend on it.
In summary, the intricate migratory patterns of diadromous fish are crucial not just for their survival but also for the health of the ecosystems they inhabit. Their migration serves the dual purpose of ensuring their reproductive success while contributing to nutrient cycling within aquatic ecosystems. As stewards of the environment, we must prioritize the conservation of diadromous fish by addressing the challenges they face through innovative and collaborative strategies. Research is vital in understanding these species and providing a scientific basis for conservation measures. Additionally, community engagement and public outreach are essential to foster a deeper appreciation for these remarkable fish, thus promoting advocacy for their protection. Involving indigenous knowledge and practices can significantly enhance our approaches to conservation, ensuring that cultural aspects are respected and integrated into modern practices. The future prospects of diadromous fish are interwoven with the broader health of aquatic ecosystems, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to resource management. By championing these fish and their habitats, we safeguard biodiversity and contribute to ecological balance. Thus, sustainable practices must be our guiding principle to create a future where diadromous fish thrive alongside their surrounding environments.