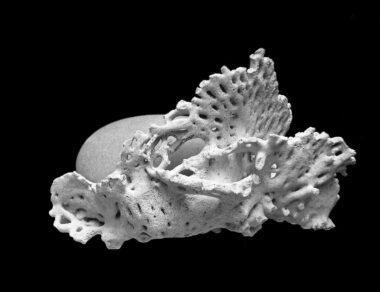
Fossilized Shells: What They Tell Us About Ancient Seas
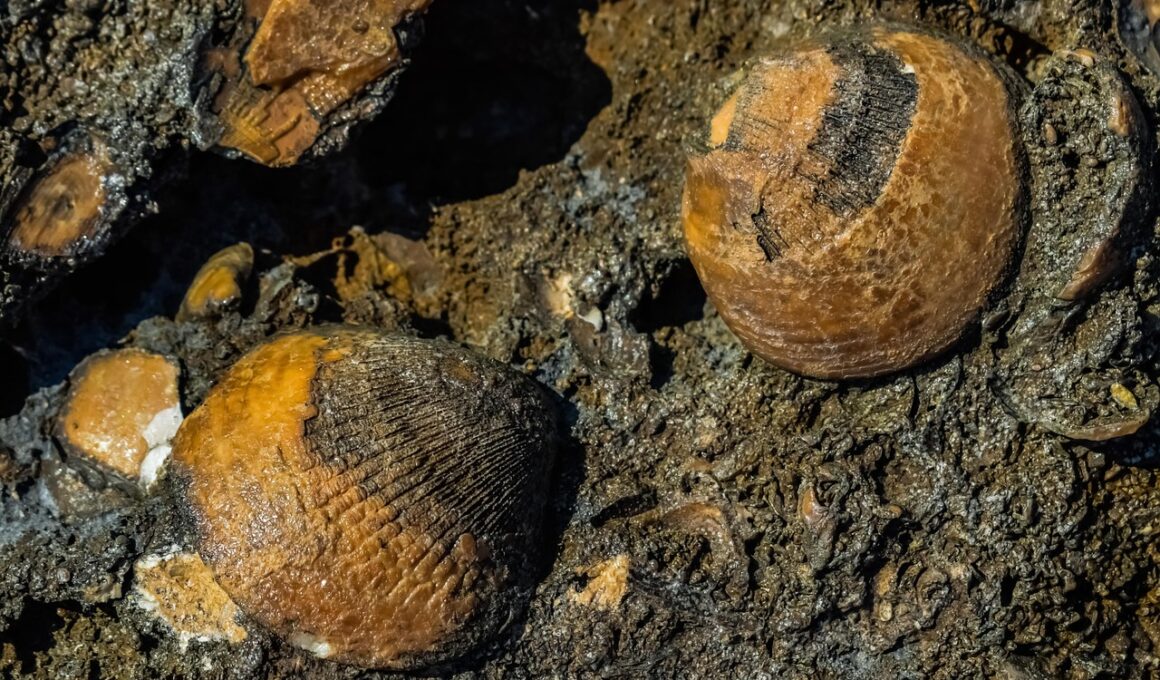
Fossilized shells are remarkable evidence of the ancient marine environment. These remnants provide insights into the diverse species that once inhabited our planet’s oceans. Each shell acts as a time capsule, preserving details about the marine ecosystem. The process of fossilization takes thousands of years, during which the organic material of the shell is replaced by minerals. This process reveals important information, such as the species’ age and environmental conditions. Furthermore, sediment layers where these fossils are found contribute to our understanding of geographical changes. By studying these fossils, scientists have been able to reconstruct ancient marine habitats, helping us visualize what these ecosystems might have looked like. In addition to species identification, fossilized shells can indicate past climate conditions. They reveal changes in sea levels and water temperatures through different geological eras. These findings allow researchers to trace the evolution of marine life and identify patterns of extinction and survival throughout history. The study of these shells serves as a bridge between the past and present, offering a glimpse into the evolutionary history of marine life on Earth.
One of the most fascinating aspects of fossilized shells is their ability to inform us about the marine food web. Shells found in specific layers can indicate what types of organisms thrived during those times. For instance, mollusks, which include snails and clams, were major players in marine ecosystems throughout history. By analyzing the isotopes contained in these shells, scientists can infer what these animals were eating. The evidence can also show changes in food availability over time. Many fossilized shells are found in areas that were once ocean beds, further connecting us to the ancient seas. The types of shells found can vary greatly, from those of very small organisms to massive, ancient species. This diversity showcases the complexity of past marine ecosystems. Additionally, through comparative analysis of modern and ancient shell structures, scientists can gain insights into how species adapted to their environments. These adaptations often tie back to how organisms interacted with their surroundings. Understanding these relationships provides a fuller picture of ecological dynamics throughout geological periods. Marine fossils thus serve not just as relics but as vital records for understanding life’s evolutionary trajectory.
The Role of Marine Fossils in Paleoclimatology
Marine fossils, particularly shell fragments, serve a critical role in paleoclimatology, the study of ancient climates. They provide evidence of past temperature fluctuations and ecological shifts. For example, the presence of certain shell types can indicate warmer or cooler ocean conditions. Certain species thrive under specific temperature ranges, making their fossilized remains excellent indicators of historical climate trends. By analyzing the compositions of these shells, researchers can reconstruct past sea surface temperatures and other environmental factors. Fossils contribute to a timeline of Earth’s climatic changes, revealing how climates have shifted in correlation with geological events such as volcanic eruptions and meteor impacts. In addition, analyzing fossil layers helps identify patterns of extinction and survival that occurred during significant climate events. This information is invaluable for understanding how modern marine ecosystems may respond to current climate change. The knowledge gained from marine fossils aids in predicting future scenarios by extrapolating past data. Thus, fossilized shells do not merely serve as historical artifacts; they are essential in informing our current understanding of climate change dynamics by providing context and continuity through deep-time observations.
The study of fossilized shells is not only beneficial for scientific understanding but also for conservation efforts towards current marine life. By grasping how ancient species responded to environmental changes, we can better understand the vulnerabilities of today’s marine ecosystems. Present-day marine animals are facing unprecedented stressors such as climate change, pollution, and habitat destruction. Insights gained from examining past shell fossils inform how current species might adapt or become extinct under similar pressures. Additionally, the data collected from these fossils can guide marine management and conservation strategies. For instance, knowing which species were resilient during past climatic changes can help prioritize conservation efforts today. Scientists urge that protecting marine biodiversity is crucial in sustaining healthy ecosystems. Fossil evidence highlights the intricate interconnections between species and their environment. Disruptions to these relationships can lead to unforeseen consequences. As we face a biodiversity crisis, understanding the past through fossil records helps us clarify the importance of ecosystem conservation. By learning from history, we can take proactive steps to preserve today’s marine treasures. The preservation of these ancient records ultimately aids in safeguarding our oceans for future generations.
Modern Technology in Fossil Analysis
Modern technology has revolutionized the analysis of fossilized shells and enhanced our understanding of ancient marine environments. High-resolution imaging techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy, allow scientists to examine shell structures at a microscopic level. This detailed analysis reveals intricate features that provide clues about the organism’s life, including growth rates and environmental adaptations. Furthermore, advancements in isotopic analysis enable researchers to determine the chemical composition of fossils, offering insights into historical climate conditions. Molecular methods are also being employed to extract and analyze ancient DNA from fossil shells, providing new pathways into understanding evolutionary processes. These technologies bridge gaps that traditional methods could not address, revealing connections between fossilized remains and living organisms. Data collected from these approaches enhance the accuracy of ecological reconstructions, showcasing species interactions and environmental shifts over time. Moreover, digital modeling and simulation techniques allow for testing hypotheses related to evolutionary dynamics and adaption strategies. Such tools contribute to a comprehensive understanding of marine life’s resilience amid environmental changes. Overall, technological advancements enrich the field of paleontology, opening new avenues for research and expanding our knowledge of ancient oceans.
Preservation of fossilized shells is vital for both scientific research and educational purposes. Museums worldwide curate extensive collections of these fossils, often using them to educate the public about marine life evolution. Effective preservation techniques are crucial for maintaining the integrity of these specimens. Curators utilize various methods to protect fossils from environmental factors such as humidity and temperature changes. They often employ climate control systems and specialized displays to ensure optimal conditions. Public exhibitions featuring fossilized shells inspire interest and awareness concerning marine biodiversity. These educational programs engage younger audiences, encouraging future generations to explore marine sciences. Through educational outreach, museums foster a connection between the community and the history of life on Earth. Furthermore, the ongoing research surrounding these fossils contributes to scientific literature, shaping our understanding of past ecosystems. Collaborative projects between museums and universities help promote further discoveries in the field. In addition, citizen science initiatives enable the public to contribute to fossil studies, enhancing community involvement in scientific exploration. Educating society about fossilized shells not only inspires curiosity but also emphasizes the importance of marine conservation in a rapidly changing world.
Conclusion: The Importance of Fossils
In conclusion, fossilized shells are invaluable resources for understanding ancient marine ecosystems and climate change. They act as historical records, shedding light on the evolution of marine life and past environmental conditions. By combining fossil analysis with modern technologies, scientists can draw conclusions about how organisms have adapted over millions of years. Current conservation efforts also benefit from insights gained through these fossil records, illustrating the need to preserve both ancient and modern marine biodiversity. The significance of studying fossilized shells extends beyond academic interest; they offer lessons for addressing contemporary environmental challenges. Engaging the public, particularly young audiences, in marine sciences encourages a deeper appreciation for our oceans and the life they support. Knowledge of our planet’s history and evolution fosters a sense of responsibility towards conserving marine habitats. Through continued research, education, and conservation efforts, we can help protect the rich tapestry of life within our oceans. The future of marine biodiversity greatly depends on our understanding of past ecosystems, equipping us with tools to navigate the ongoing changes of the natural world. The legacy of fossilized shells is not just about the past; it’s integral to our future.
In conclusion, fossilized shells are invaluable resources for understanding ancient marine ecosystems and climate change. They act as historical records, shedding light on the evolution of marine life and past environmental conditions. By combining fossil analysis with modern technologies, scientists can draw conclusions about how organisms have adapted over millions of years. Current conservation efforts also benefit from insights gained through these fossil records, illustrating the need to preserve both ancient and modern marine biodiversity. The significance of studying fossilized shells extends beyond academic interest; they offer lessons for addressing contemporary environmental challenges. Engaging the public, particularly young audiences, in marine sciences encourages a deeper appreciation for our oceans and the life they support. Knowledge of our planet’s history and evolution fosters a sense of responsibility towards conserving marine habitats. Through continued research, education, and conservation efforts, we can help protect the rich tapestry of life within our oceans. The future of marine biodiversity greatly depends on our understanding of past ecosystems, equipping us with tools to navigate the ongoing changes of the natural world. The legacy of fossilized shells is not just about the past; it’s integral to our future.