The Importance of Savanna Mammals in Seed Dispersal
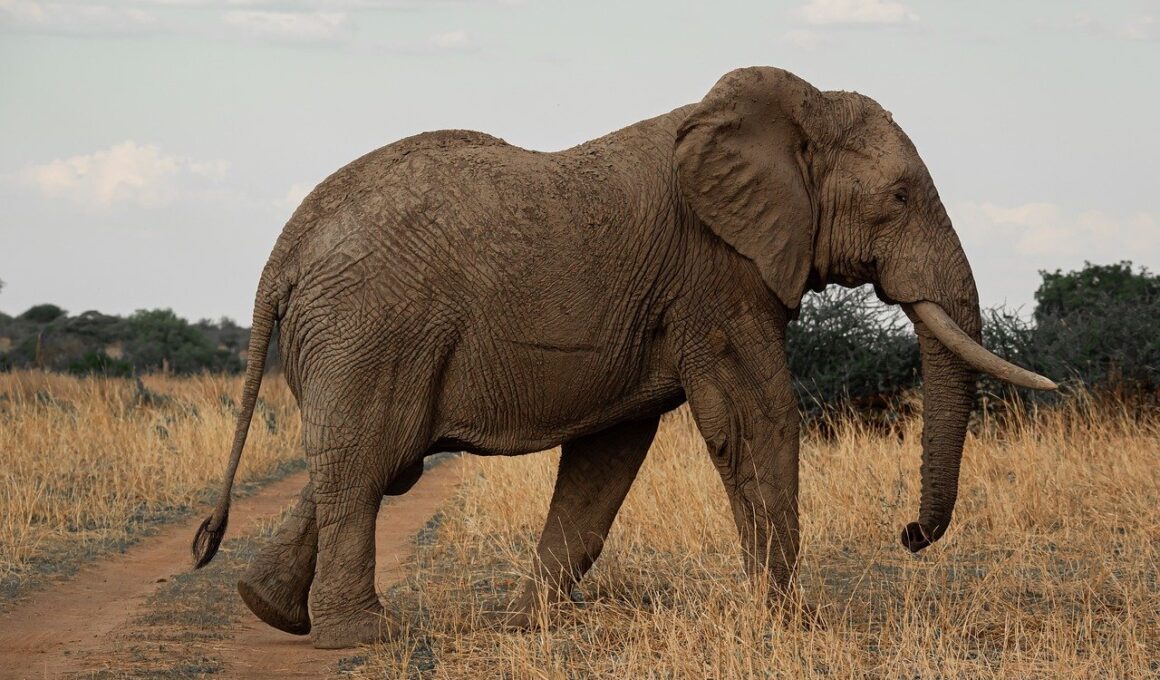
In the savanna ecosystem, mammals play an essential role in the process of seed dispersal, contributing significantly to the health and sustainability of this biome. Many savanna mammals, including elephants, giraffes, and various rodents, consume fruits and seeds as part of their normal diets, which is vital for the growth of new plants. By ingesting seeds and later excreting them in different locations, these mammals facilitate the spread of plant species across vast distances. The dispersal patterns also allow plants to colonize new areas, improving biodiversity within the savanna. Different species have unique mechanisms for dispersal; for instance, elephants can move substantial quantities of seeds due to their size. This further leads to increased plant variety, which also enhances the habitat of the savanna itself. Moreover, some seeds benefit from the digestive process, sprouting more effectively post-consumption. These interactions between savanna mammals and plants are a fundamental aspect of ecological balance, ensuring that forest and grassland ecosystems thrive. Therefore, protecting these mammals is critical, as their absence could lead to significant declines in plant diversity and overall savanna health.
Seed dispersal by mammals not only aids in plant reproduction but also supports various species within the ecosystem. The fruits consumed by mammals often provide essential nutrients and energy. This relationship promotes a cycle where healthy animals contribute to the regeneration of their habitat. As these mammals forage, they inadvertently manage plant populations, determining which species thrive and which decline. For instance, the seeds of some tree species remain dormant until they pass through a mammal’s digestive system, where they are prepared to germinate. Additionally, seed dispersal enhances resilience in ecosystems by allowing plant species to adapt to changing environmental conditions. Various factors, such as climate change, impact seed distribution and availability. Savanna ecosystems must maintain a robust network of interactions among species, creating a dynamic balance. Each mammal species contributes uniquely to this intricate web. Herbivores like zebras and antelopes also influence grass growth patterns, which indirectly helps in seed dispersal. The loss of these key mammals would lead to reduced vegetation and subsequently impact all levels of the food chain. Therefore, the protection of savanna mammals is paramount for sustaining the ecological integrity of these environments.
Moreover, the relationship between savanna mammals and plants is deeply intertwined with cultural significance; indigenous communities often rely on these animals for sustenance and traditional practices. This aspect highlights the importance of ethical conservation efforts, ensuring that mammals continue to thrive in their natural habitats. The interconnectedness of mammals and plants extends beyond ecological concerns; it encompasses economic, cultural, and spiritual dimensions of life. As these mammals disperse seeds, they also help shape the land and influence human livelihoods. Communities engage in agricultural practices that rely on the biodiversity facilitated by these animals. The decline of mammal populations due to habitat loss and poaching threatens not only the ecological balance but also cultural identities and practices. Continued education and awareness campaigns can build local engagement in conservation efforts, highlighting how vital these animals are within ecosystems. Additionally, establishing wildlife corridors can help connect fragmented habitats, enabling mammals to travel and access different resources, thus enhancing their role as seed dispersers. Active management and conservation strategies must consider both the ecological implications and the human dimensions for a holistic approach.
Challenges Facing Savanna Mammals
Despite their essential role in seed dispersal, savanna mammals face numerous challenges that threaten their populations and, consequently, the ecosystems they help sustain. Habitat destruction due to agriculture and urbanization poses a significant threat to these mammals’ survival. As their habitats shrink, mammals are forced into smaller areas, which hinders their ability to find food and reproduce effectively. Furthermore, poaching for ivory, bushmeat, and other wildlife products has led to significant declines in elephant and rhinoceros populations. Such declines disrupt the intricate ecological grip that these animals have on seed dispersal dynamics. Climate change is another major factor, impacting rainfall patterns and the overall temperature of savanna regions. This disruption can alter the seasonal growth patterns of plants that depend on mammals for reproduction. Moreover, invasive species can compete with native plants and disrupt traditional relationships between mammals and flora. The cumulative effects of these threats lead to reduced genetic diversity among both plant and animal species, jeopardizing the resilience of the entire savanna ecosystem. Conservation programs must now address these challenges to safeguard both mammals and the health of their ecological networks.
To combat these threats, innovative conservation strategies are crucial. Increasing awareness about the importance of mammal-driven seed dispersal can galvanize community support for conservation efforts. Engaging local populations ensures that they understand the benefits of preserving these mammals over exploitative practices. One effective strategy has been the promotion of ecotourism, which can provide revenue for communities while fostering appreciation for wildlife. By developing sustainable tourism initiatives, communities can rely on the healthy populations of savanna mammals to attract visitors, creating financial incentives to protect their habitats. Additionally, rehabilitation programs for injured or orphaned mammals can help rebuild populations and restore their roles within ecosystems. Monitoring animal populations using modern technology, such as GPS tracking, allows researchers and conservationists to gather critical data about their movements and habits. This information can feed into management plans, ensuring that the habitats meet the mammals’ needs. Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, and local communities can foster stronger protection policies, ultimately enhancing the resilience of savanna mammals against ongoing challenges through informed protection.
The Role of Education in Conservation
Education plays a pivotal role in the conservation of savanna mammals and their essential function in seed dispersal. By educating local communities about the ecological significance of these mammals, awareness grows regarding the intricate connections within ecosystems. Workshops, school programs, and community engagement can transform perceptions, encouraging respect for wildlife and a deeper understanding of their roles. Environmental education fosters stewardship, where individuals feel responsible for their local habitats. Schools can integrate lessons about local wildlife, including mammals, ecosystems, and biodiversity, helping students appreciate their biological heritage. This appreciation can translate into advocacy for conservation efforts. Additionally, partnering with civic organizations can lend resources and expertise to bolster educational initiatives. Collaborative projects that involve students and local communities in hands-on conservation efforts, like planting native species, create lasting connections. When communities understand the value of diversity in flora and fauna, they often become motivated to support environmental policies and initiatives actively. Education can create local champions for wildlife protection, enabling grassroots movements to flourish. By cultivating knowledge and respect, education ensures the ongoing survival of savanna mammals and promotes sustainable relationships with the land.
Ultimately, the intricate relationship between savanna mammals and seed dispersal illustrates the importance of biodiversity in maintaining healthy ecosystems. As connectors of nature, these mammals facilitate plant reproduction, which impacts countless species. The survival of various flora and fauna hinges on the presence of these mammals, marking their role as keystone species. The unexpected benefits of seed dispersal extend beyond immediate ecological networks; they influence the ability of savanna ecosystems to adapt and thrive in changing climates. Without the protection of these essential animals, the balance of the savanna could falter, leading to declines in overall ecological health. Each effort to preserve mammal populations is an integral step toward ensuring the longevity of savanna ecosystems. By fostering an understanding of these connections, conservationists and community members can work together to protect wildlife and their habitats. Strengthening the links between people and nature leads to a more sustainable future, emphasizing that the health of one depends on the health of the other. Therefore, protecting savanna mammals is not merely about saving a species but also about preserving the interconnected web of life within these dynamic ecosystems.
The journey of safeguarding the savanna and its mammals continues, urging collaborative action across various sectors. Scientists, policymakers, and local communities must integrate their efforts to confront the multitude of challenges these ecosystems face. Establishing protected areas and wildlife corridors will help ensure that these mammals can roam freely and continue their vital role in dispersing seeds across the savanna landscape. Additionally, sustainable land-use practices can help balance agricultural needs with wildlife conservation. It is vital to consider cultural factors, ensuring that conservation strategies respect the traditions and livelihoods of local people. Engaging with indigenous knowledge can reveal sustainable practices honed over generations that could benefit current conservation efforts. This multifaceted approach underscores the necessity of cooperative work to foster healthier ecosystems. The urgency of the issues affecting savanna mammals necessitates immediate and continued dedication to conserving the integrity of these ecosystems. Ultimately, through collaborative initiatives, we can ensure that savanna mammals thrive, maintaining their role in the tapestry of life that supports both nature and humanity.