The Chemical Defenses of Anura: Toxicity and Predation Avoidance
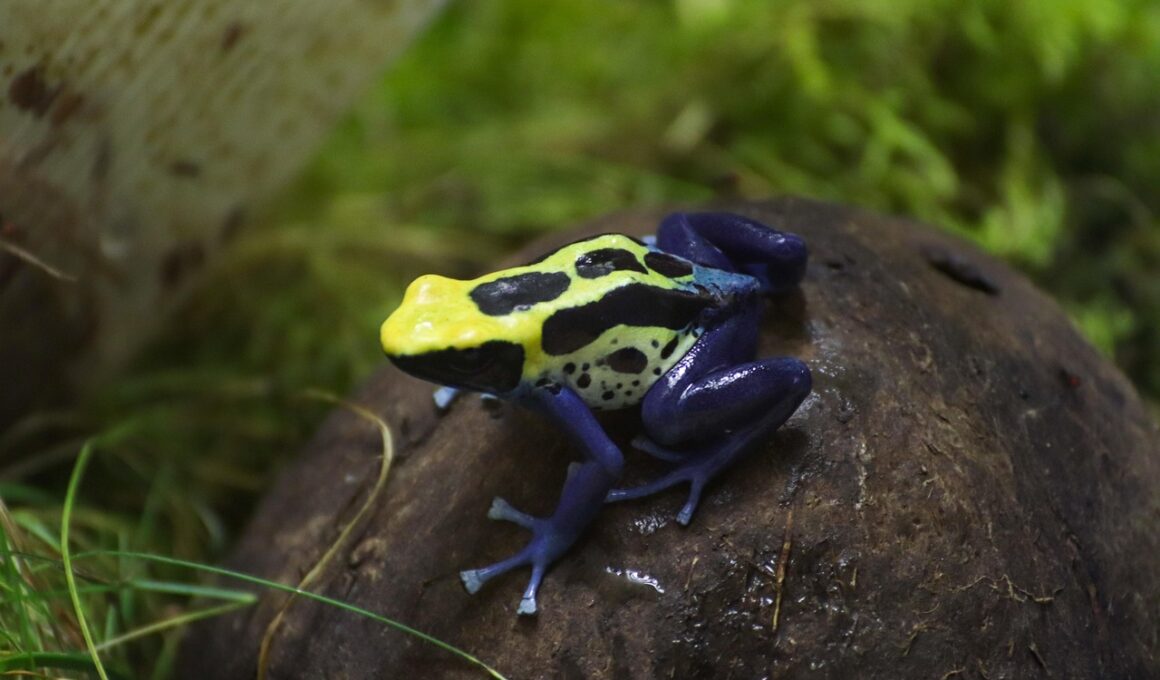
Order Anura, which comprises frogs and toads, demonstrates fascinating adaptations for survival, including chemical defenses. These organisms utilize a variety of toxic compounds primarily to deter predators. Various species, such as the poison dart frogs, are particularly noted for their vibrant colors and potent skin toxins. The bright coloration functions as an aposematic signal, warning potential predators of their toxicity. Moreover, the toxins can vary significantly among species, with some being more potent than others. The knowledge of these chemical defenses has implications for understanding ecological relationships within their environments. For instance, those predators that consume a toxic frog quickly learn to avoid them in the future. Additionally, these toxins may have bioactive properties that researchers find useful in medicine and pharmacology. Chemical defenses are essential for the survival of Anura, impacting prey selectivity and predator-prey dynamics. Given their ecological importance, it is vital to study these chemical adaptations in depth, contributing to the understanding of biodiversity and conservation. In particular, discovering new compounds could lead to groundbreaking medical advancements, offering insights into new treatments for various diseases.
In the diverse world of amphibians, Anura’s toxic defenses are vital for their survival. The primary chemical compounds responsible for their toxicity include alkaloids. These toxins affect the nervous system of predators, often leading to paralysis or even death. Notably, some species employ toxins obtained from their diet. For example, poison dart frogs accumulate toxic alkaloids from the insects they consume, thus enhancing their defenses. These adaptive strategies showcase the intricate relationships within ecosystems and highlight the reliance of Anura on environmental factors. Furthermore, the variations in toxicity and the evolution of chemical defenses among Anura underscore the dynamic processes of natural selection. Research indicates that different habitats impose unique selective pressures, influencing the chemical composition of toxins. For example, populations living in drier regions may develop different defensive traits compared to those in humid locations. These adaptations not only ensure their survival but also play a role in maintaining ecological balance. Anura’s evolutionary history is profoundly intertwined with their chemical defenses, showcasing resilience and adaptability in challenging environments. In understanding these mechanisms, conservation efforts can be better informed to protect these amphibians and their habitats.
Types of Toxins and Their Effects
The variety of toxins found in Anura species reflects their adaptability and ecological niches. Commonly known toxins include bufotenin and batrachotoxin, each varying in potency and effects. Batrachotoxin, found in the golden poison dart frog, is one of the most toxic substances known, causing severe neurological effects. In contrast, bufotenin is milder but still deterrent to various predators. The specific effects of these chemicals depend on the dosage and sensitivity of the consumer, establishing a complex interplay between prey and predator. Predators often possess physiological adaptations that allow them to tolerate some levels of specific toxins, illustrating a fascinating example of co-evolution. Anura species thus face the ongoing challenge of refining their chemical defenses as new predator adaptations emerge. This evolutionary arms race has resulted in a remarkable diversity of toxins across different species, enabling them to thrive in various habitats. Interestingly, some Anura utilize their toxins in mating displays, where the potency of their chemical defenses may signal fitness to potential mates. Such behaviors further elaborate on the multifaceted role of toxins, enhancing mate selection and population dynamics within these communities.
Predation avoidance in Anura is crucial for their survival, as predation is one of the primary causes of mortality in these animals. The evolution of chemical defenses has reduced predation rates, allowing for greater reproductive success. In particular, studies have shown that brightly colored, toxic species experience lower predation rates compared to non-toxic counterparts. Additionally, behavioral adaptations such as altered activity patterns and habitat selection further enhance their chances of survival. For example, some frogs may remain hidden during the day to avoid detection by hunting mammals or birds, emerging only at night when predation risks are lower. Furthermore, some species exhibit various strategies to enhance their chemical defenses in the presence of high predation pressure. Through these adaptive strategies, Anura continue to evolve, helping to maintain their populations despite ongoing environmental challenges. The effects of habitat destruction and climate change also pose significant threats to Anura populations, making their chemical defenses all the more critical for survival. Therefore, conserving their habitats is imperative to ensure these amphibians can continue to thrive, highlighting the importance of ecological preservation efforts in safeguarding their future.
Future Research and Conservation Implications
The ongoing study of Anura’s chemical defenses is increasingly vital for understanding ecological interactions and conservation needs. With habitat loss and climate change posing significant hazards, comprehensive research into their toxicity profiles can aid in developing effective conservation strategies. For instance, documenting the relationships between Anura and their toxic compounds may reveal connections to ecosystem health and biodiversity. Such insights emphasize the importance of preserving these amphibians, as their presence often indicates a balanced ecosystem. Furthermore, further investigation into the potential medicinal properties of Anura toxins could yield breakthroughs in pharmaceuticals. By studying these unique adaptations, scientists may enhance their understanding of evolutionary biology and develop strategies to support conservation efforts. Collaborations among researchers, conservationists, and policymakers are crucial in shaping effective frameworks for protecting Anura habitats. Educational programs aimed at raising awareness of these remarkable creatures and their role in ecosystems can foster public interest and support for conservation endeavors. Comprehensive approaches that emphasize the significance of Anura within their ecosystems could lead to more robust conservation policies that focus on habitat preservation. Collective efforts are necessary to ensure the continuity of these fascinating amphibians and their ecological roles.
Overall, Anura’s chemical defenses represent a remarkable evolutionary strategy to avoid predation and enhance survival rates. These adaptations symbolize the intricate connections in nature, emphasizing how species interact and evolve under environmental pressures. The vibrant colors of toxic frogs not only serve as a warning signal but also demonstrate the rich biodiversity within amphibians. By understanding these relationships, researchers can gauge the health of ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts. Additionally, the ongoing exploration of Anura toxins opens new avenues for medical research, potentially leading to novel treatments derived from their biochemical properties. Protecting these species and their habitats is crucial not only for their survival but also for maintaining rich biodiversity and ecological balance. As Anura continue to adapt to ever-changing environments, their contributions to ecosystems remain invaluable. Therefore, promoting awareness and education about Anura and their chemical defenses is essential. Implementing conservation programs aimed at safeguarding their populations is imperative. Future generations should have the opportunity to explore and learn about these fascinating amphibians, appreciating their role in our natural world while promoting sustainable practices to ensure their survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of chemical defenses in Anura reveals crucial insights into their adaptations and survival strategies. Their toxic compounds are not only fascinating from a biological perspective but also have significant ecological and medicinal implications. Recognizing the interplay between Anura’s chemical defenses and environmental factors will aid in effective conservation planning and ecological preservation. By learning more about these extraordinary amphibians, researchers can contribute to safeguarding biodiversity amid the ongoing challenges posed by climate change and habitat destruction. Anura’s unique adaptations illuminate the delicate balance of ecosystems, urging us to prioritize their protection. As we continue to learn about their toxins, we unlock potential medical advancements and deepen our understanding of nature’s complexity. It is essential to foster public awareness regarding the plight of Anura and the importance of protecting their habitats. Implementing conservation strategies will benefit these amphibians and facilitate broader environmental health. Thus, embracing these creatures and their remarkable adaptations is vital, ensuring future generations appreciate the beauty and diversity of Anura while supporting their ongoing survival efforts in changing habitats.