Hyenas: Misunderstood Mammals of the Savanna
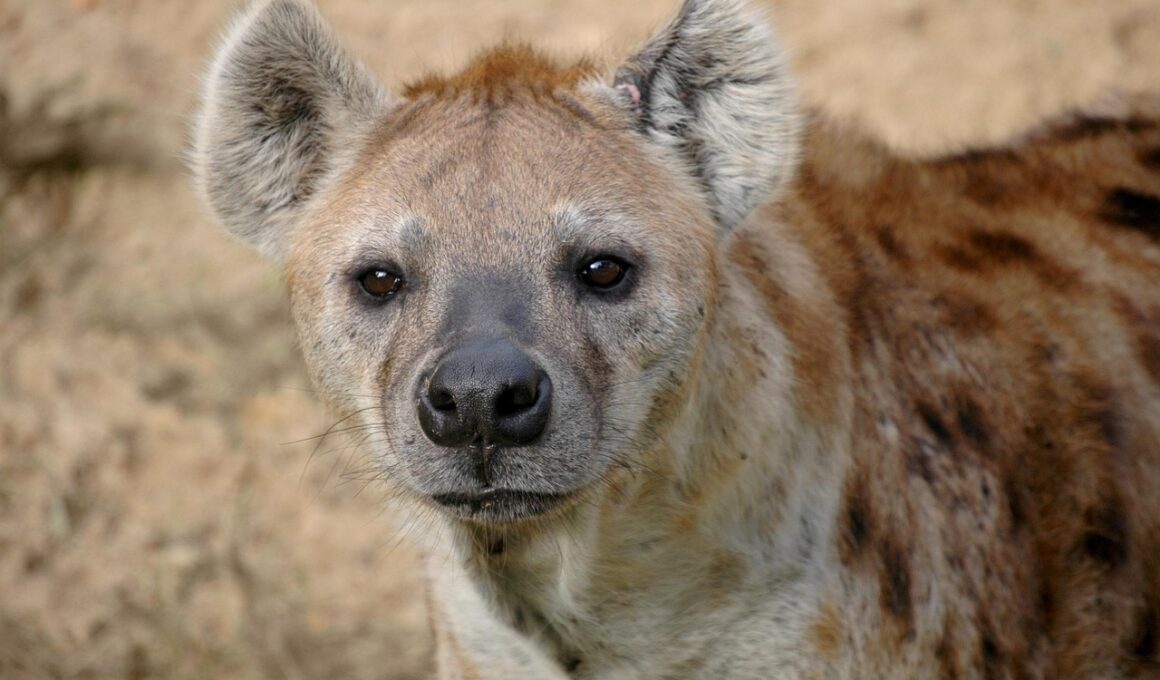
Hyenas are often portrayed negatively in popular culture, but these fascinating mammals play a crucial role in the savanna ecosystem. Known for their distinctive laughter-like vocalizations, hyenas are highly social animals. They live in groups called clans, which can consist of up to 80 individuals. Female hyenas typically dominate the social hierarchy, leading to some interesting dynamics within these clans. Intelligence is a hallmark of hyenas; they exhibit problem-solving skills and communication methods that are complex. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in various habitats across Africa, including grasslands and savannas. Despite common misconceptions, they rarely scavenge and often hunt for their food. With strong jaws and impressive stamina, hyenas can take down prey such as antelope and wildebeest. Their unique adaptations make them vital players in maintaining the ecological balance by controlling animal populations. Additionally, hyenas contribute to the health of their environment by helping to break down carrion and recycle nutrients. Understanding these remarkable mammals is essential for appreciating the biodiversity of the savanna.
To truly grasp the role of hyenas, it’s essential to examine their hunting strategies. Hyenas are skilled hunters, often collaborating within their clans to bring down larger prey. The social structure of a clan provides advantages when targeting animals that are more significant than an individual hyena could tackle alone. Unlike the solitary hunting nature of many predators, hyenas display remarkable teamwork. They employ various tactics, such as circling their prey or using their vocalizations to confuse and isolate them. Their keen sense of hearing contributes significantly to their hunting success. Hyenas can detect sounds from great distances, allowing them to locate potential meals quickly. This extraordinary sensory capability is complemented by their speed and stamina, enabling them to chase prey over considerable distances. They can run at speeds of up to 37 miles per hour, and their endurance allows them to outlast their prey during long chases. These factors ensure that hyenas are effective and efficient hunters, further proving their importance in the ecosystem.
Social Structure and Behavior
The social structure of hyena clans is incredibly complex, characterized by social hierarchies and intricate relationships. Female hyenas are dominant, and this matriarchal system allows them to establish leadership roles within the group. This dominance is evident in their physical size and aggressive behavior during conflicts. Males often leave their birth clans upon reaching maturity, seeking positions in other clans, which helps prevent inbreeding and fosters genetic diversity. Clan members communicate through various vocalizations and social behaviors, which further strengthen bonds within the group. Body language plays a significant role, particularly in social interactions and displays of dominance or submission. Hyenas also engage in playful behaviors, especially among younger members. Play is crucial for developing important skills such as hunting and social interactions. These playful encounters allow young hyenas to learn from older, experienced clan members. Their social behaviors indicate a high level of intelligence, showcasing their emotional connections and cooperative living. Hyenas exemplify that alliance-building and social structures can contribute to success in the wild.
Moreover, hyenas exhibit fascinating communication skills that play a pivotal role in their clan dynamics. They possess a rich vocal repertoire that encompasses various sounds, including laughs, whoops, and growls. Each vocalization conveys specific meanings, facilitating coordination during hunts or warnings about potential threats. The famous ‘laugh’ of the hyena, often mistaken as a sign of aggression, actually serves to express excitement or to inform clan members of their presence. Communication is not limited to sounds; physical posturing and scent marking also play significant roles in their interactions. Hyenas communicate through scent marking their territories with urine and droppings, which carries essential information about clan identity. Recognizing these signals fosters collaboration among members while deterring rival clans from encroaching on their territory. Over time, researchers have documented the complexity of hyena communications, revealing intricate social protocols and exchanges. This depth of communication suggests a cognitive complexity akin to that of primates, enhancing the perception of hyenas as intelligent and socially bonded creatures.
The Impact of Hyenas on Ecosystem Function
Hyenas serve not only as hunters but also as scavengers, contributing significantly to the health and balance of their ecosystems. Their scavenging habits help control the populations of large herbivores, preventing overgrazing and promoting vegetation growth, which is vital for maintaining the savanna’s health. By consuming carrion, hyenas play a crucial role in waste disposal, ensuring that decaying animals do not linger and spread disease. This recycling of nutrients supports the larger food web, positively impacting other species in the ecosystem. Competitors such as lions and leopards often scavenge from hyena kills, indicating their prowess in securing food sources. As a result, they contribute to the dynamics of predation and scavenging behaviors within the savanna. Furthermore, hyenas’ hunting practices help shape the behaviors of prey species, prompting them to adapt, flee, or find safer habitats. The overall biodiversity of the savanna ecosystem thrives because of the delicate balance that hyenas, as both predators and scavengers, help maintain.
Despite their important ecological roles, hyenas face numerous threats that can jeopardize their populations. Habitat destruction, primarily due to agriculture and urban expansion, diminishes their natural territories. Additionally, human-wildlife conflict arises as hyenas may prey on livestock, leading to retaliatory killings by farmers. Poaching, driven by demand for traditional medicine and bushmeat, also poses a risk to their survival. Climate change further exacerbates these challenges, altering habitats and affecting prey availability. Conservation is essential for protecting these remarkable animals and ensuring their continued presence in the savanna. Initiatives aimed at habitat preservation, as well as community engagement, can mitigate conflicts between humans and hyenas. By promoting coexistence, conservationists can foster a deeper understanding of hyenas’ ecological significance and the vital services they provide. Educating local populations about the ecological roles played by hyenas may help reduce misconceptions and negative perceptions. Collaborative efforts involving scientists, local communities, and governments can be instrumental in safeguarding hyena populations and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Conclusion: Embracing Hyenas as Essential Ecosystem Players
Hyenas should be embraced and recognized as essential players in the savanna’s ecosystems. Their complex social structures, communication methods, and hunting strategies demonstrate intelligence and adaptability. They contribute positively to the ecological balance by controlling prey populations and recycling nutrients through scavenging. Understanding these misunderstood mammals fosters greater appreciation for their roles in nature, highlighting the necessity of conservation efforts. Public awareness can help change negative stereotypes surrounding hyenas, promoting coexistence with local communities. By protecting their habitats and reducing conflicts with humans, we can ensure the survival of these remarkable mammals for future generations. The more we learn about hyenas, the clearer it becomes that these creatures are not merely villains but integral components of the savanna ecosystem. Their existence is vital to maintaining biodiversity and ecological health. A thriving population of hyenas indicates a balanced ecosystem, highlighting their importance. Embracing hyenas as ecologically significant mammals allows us to take informed actions for their conservation. Together, we can foster a future where hyenas continue to roam the savanna, enriching the tapestry of life in these vibrant ecosystems.