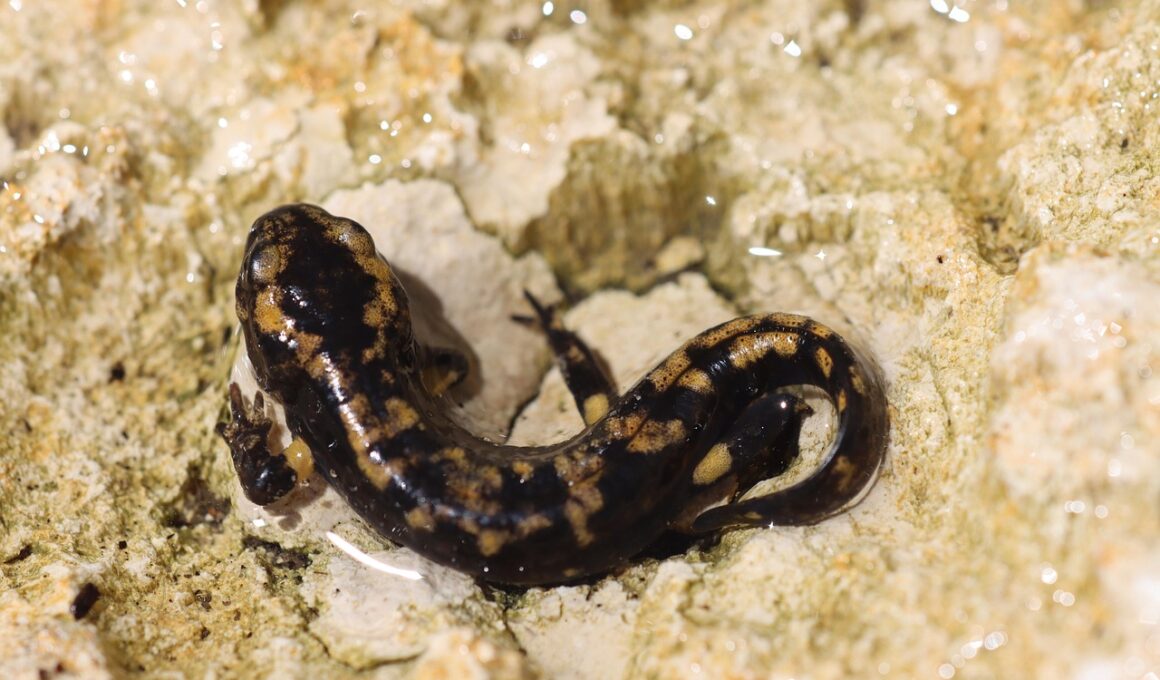
Rare Freshwater Amphibians in Their Natural Habitat
Freshwater amphibians are unique creatures that thrive in aquatic environments, blending characteristics of both fish and terrestrial reptiles. Their habitats include ponds, lakes, rivers, and streams, which are essential for their survival and breeding. Among the most fascinating are the critically endangered amphibians that face the threat of extinction due to habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Species such as the Japanese giant salamander and the North American hellbender exemplify the diversity found within freshwater ecosystems. These remarkable animals play vital roles in their ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey, contributing to the balance of life. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these species, highlighting the importance of preserving their natural habitats. This article delves into the world of rare freshwater amphibians, exploring their behaviors, lifestyles, and the current threats they face. By raising awareness about these intriguing creatures, we can better understand the significance of maintaining biodiversity in freshwater systems. Join us as we uncover the mysteries of these amphibians and the conservation challenges they endure in modern society.
Amphibians are often categorized into three main groups: frogs, salamanders, and caecilians. Each group displays distinct characteristics and habitats, contributing to the overall diversity of the amphibian class. Frogs are known for their jumping abilities and vocalizations, while salamanders often inhabit moist environments and showcase intricate skin patterns and colors. Caecilians, meanwhile, are less visible but play critical roles in soil ecology. All these groups are sensitive to environmental changes, which can significantly impact their population numbers. The interconnectedness of amphibians with their surroundings highlights the importance of monitoring their health as climate change alters freshwater habitats. Encroachment of human development poses additional threats, necessitating strict conservation measures. In response, various organizations have initiated programs fostering awareness and conservation, aimed at preserving these unique amphibians and their habitats. Community engagement through education and active participation is key to successful conservation efforts. Researchers and enthusiasts alike continue to study these fascinating creatures, gathering vital data that informs public policies. Understanding their ecological importance not only aids in their preservation but also enhances our appreciation of the delicate balance within freshwater ecosystems.
The Role of Wetlands in Amphibian Conservation
Wetlands serve as critical habitats for many freshwater amphibians, acting as breeding grounds and nurseries. These biodiverse ecosystems are uniquely adapted to support a wide range of plant and animal life, making them essential for biodiversity conservation. Wetlands help regulate water quality by filtering pollutants and providing flood protection, thereby maintaining the health of surrounding ecosystems. Unfortunately, wetlands are among the most threatened ecosystems globally due to urbanization and industrial development. As wetland areas shrink, amphibian populations face increased risks, necessitating urgent conservation action. Protecting existing wetlands and restoring those that have been degraded is vital for the survival of amphibian species. Collaborative efforts between governments, organizations, and local communities are crucial in implementing effective conservation strategies. Raising public awareness about the importance of wetlands can foster community involvement, encouraging participatory conservation initiatives. Educational programs and outreach campaigns highlight the connection between wetlands and amphibian health, promoting sustainable practices. By prioritizing wetland conservation, we are not only safeguarding amphibians but also supporting a healthy environment that benefits all living organisms thriving in or near freshwater habitats.
Research plays an essential role in understanding the intricate lives of freshwater amphibians and the unique challenges they face. Various scientific studies have highlighted the significance of genetic diversity within populations, underscoring its importance for adaptability and resilience against environmental stresses. Conservation biologists are working diligently to monitor amphibian populations, utilizing innovative technology such as genetic analysis and habitat modeling to collect valuable data. These insights inform conservation strategies aimed at maintaining biodiversity and preventing species extinction. By collaborating with local stakeholders and engaging communities, researchers can gather comprehensive information regarding habitat conditions and anthropogenic impacts. Additionally, the role of citizen science is increasing, allowing individuals to contribute to monitoring programs and increase the data pool available for analysis. This participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards local ecosystems. Public involvement is crucial not just for data collection but also for education and advocacy, empowering communities to support amphibian conservation efforts actively. Understanding how human activities influence these delicate ecosystems can lead to more sustainable practices that benefit both amphibians and the environment as a whole.
Education and Advocacy for Freshwater Amphibians
Education is key to fostering a greater understanding of freshwater ecosystems and the creatures inhabiting them. Awareness campaigns geared toward local communities can inspire engagement in conservation efforts. Schools and universities can incorporate amphibian studies into their curricula, emphasizing biological diversity and ecological balance. Educational initiatives can take various forms, from interactive workshops to field trips that allow students and participants to observe amphibians in their natural habitats. Engaging local citizens through awareness campaigns fosters a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards amphibians. Multimedia resources, such as documentaries and online videos, serve to raise awareness and inspire conservation efforts in a wider audience. Innovative storytelling can captivate emotions, prompting individuals to consider their role in safeguarding these vulnerable species. Collaboration among NGOs, educators, and researchers can produce comprehensive educational programs designed for all age groups. By providing accessible information and hands-on experiences, the public can become advocates for amphibians. As understanding grows, so does the potential for sustainable practices, ultimately leading to healthier ecosystems for both amphibians and humans alike.
Climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing threats facing freshwater amphibians today. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can drastically impact their habitats and behaviors. Many amphibian species are highly sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect their reproductive cycles and population health. Additionally, changes in water availability can disrupt breeding activities and food sources, putting more pressure on their survival. It is crucial to understand and quantify these impacts to develop effective conservation strategies tailored to specific species and environments. Researchers are actively studying the effects of climate change on amphibians through various modeling techniques and long-term monitoring projects. The findings from these studies can be instrumental in shaping policy decisions and conservation planning globally. Community resilience can also be enhanced by promoting adaptive practices that mitigate climate change impacts. By integrating traditional knowledge with scientific research, stakeholders can develop holistic approaches to conservation that benefit both species and communities. Continuous dialogue among researchers, policymakers, and local communities can pave the way for innovative solutions that ensure the survival of freshwater amphibians amid changing environmental conditions.
Concluding Thoughts on Freshwater Amphibian Conservation
In conclusion, the preservation of rare freshwater amphibians and their habitats is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity. These remarkable creatures provide vital services in freshwater ecosystems, acting as indicators of environmental health. Continued research, education, and public engagement are essential components in ensuring their survival amid increasing threats. Conservation strategies must be adaptive, utilizing the latest scientific findings and community insights to develop effective responses to emerging challenges. Collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and local communities is imperative in addressing the multifaceted issues affecting amphibians. Through education and advocacy, we can inspire individuals to appreciate the beauty and importance of freshwater amphibians as integral components of our ecosystems. Initiatives that promote habitat protection and restoration efforts will contribute significantly to their survival. By taking collective action, we can create a sustainable future for both humankind and the amphibians that enrich our planet. It is our responsibility to nurture the diversity of life found in freshwater habitats, safeguarding these extraordinary animals for generations to come. Together, we can foster a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of preserving its fragile ecosystems.