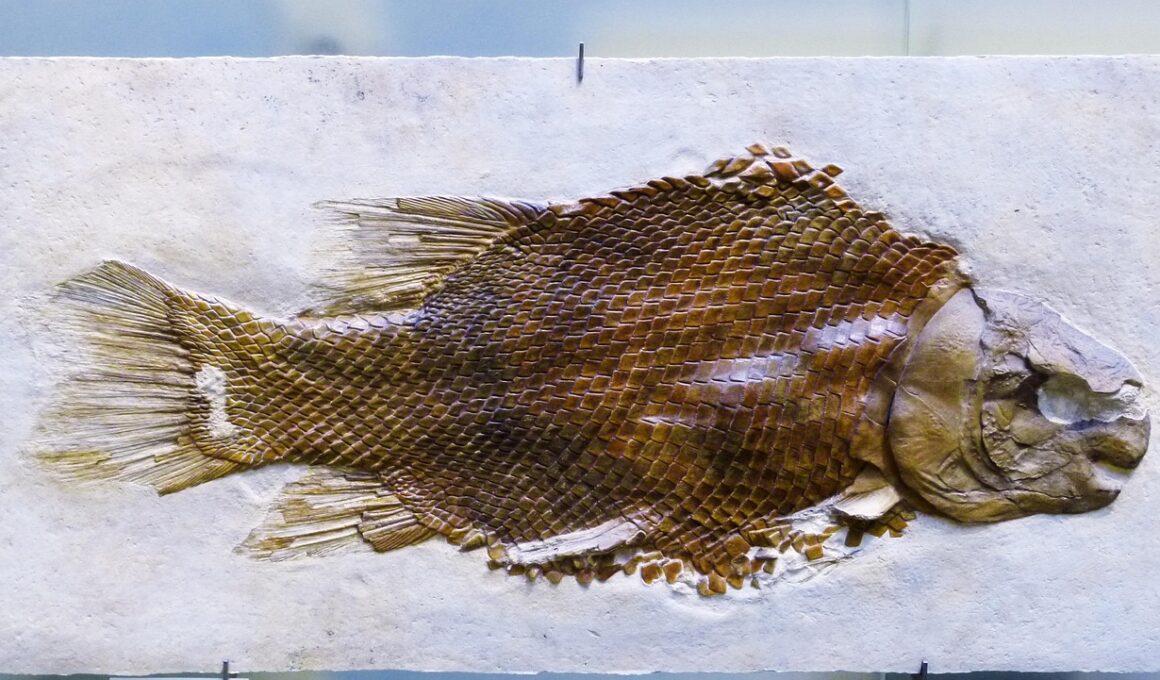
Jurassic Fish Fossils: What We Know So Far
The Jurassic Period was a remarkable epoch in Earth’s history, stretching from 201 to 145 million years ago. It was during this time that the oceans flourished with an incredible diversity of fish species. These fish, which include both bony and cartilaginous varieties, demonstrate various adaptations that allowed them to thrive in ancient marine ecosystems. Fossils from this period are crucial for understanding the evolutionary changes that took place and offer significant insights into the biodiversity of the time. For paleontologists, studying these fossils provides a window into the past, revealing not only the characteristics of these ancient creatures but also the environmental conditions in which they lived. Fossil discoveries often include preserved body structures, scales, and even evidence of feeding habits, offering a detailed glimpse into the ecological roles these fish played. Notably, some Jurassic fish had unique features that differ significantly from modern relatives. Through meticulous excavation and analysis, researchers aim to uncover more about their life cycles, habitats, and interactions with other marine organisms.
Fossil evidence indicates a rich variety of fish that existed during the Jurassic Period. Some of the most notable fish from this time include members of the Actinopterygii, or bony fish, along with Chondrichthyes, which includes sharks and rays. These categories represent a significant evolutionary step and introduced various forms, intricacies, and adaptations. Among the bony fish, Leptolepis is particularly noteworthy for its significance as one of the earliest known bony fish, while species like Diplomoceras highlight the adaptations of marine reptiles. Interestingly, fossils also indicate that fish behavior and feeding strategies were diverse, with some exhibiting complex predatory behaviors. Additionally, trace fossils, such as bite marks and feeding patterns on other fossils, reveal interactions between various species, illustrating the ecological dynamics of Jurassic marine ecosystems. As researchers continue to unearth and study these remnants, they uncover critical evidence supporting theories about the evolution of fish and the drastic changes in marine environments and climates during this significant period.
The Role of Fossilization in Understanding Jurassic Fish
Fossilization processes during the Jurassic Period were vital in preserving remnants of ancient life, particularly regarding fish. Various factors influence fossilization, including sedimentation rates, mineral content in the water, and environmental stability. In marine environments, rapid burial under layers of sediment significantly increased the chances of fish being fossilized. Conditions such as anoxic environments, where oxygen levels were low, contributed to the exceptional preservation seen in some Jurassic fish fossils. Researchers who study these fossils often rely on techniques such as radiographic imaging and isotopic analysis to interpret and classify the specimens accurately. Such technologies have revealed unique anatomical features that may have evolved to adapt to specific living conditions within the Jurassic seas. In addition, understanding fossilization helps scientists connect these species to their modern counterparts, providing clues about evolutionary paths taken by fish throughout history. The insights gained through fossilized remains inform current knowledge about biodiversity, species adaptations, and environmental changes over geological time scales.
Fieldwork plays a crucial role in fossil discovery and study. Paleontologists traverse various geological formations and sedimentary deposits to locate fossil-rich sites from the Jurassic Period. One famous fossil site is the Solnhofen Limestone in Germany, renowned for its exceptional preservation of soft-bodied organisms, including fish. Such locations provide valuable context for understanding fish diversity and evolution during this crucial period. Unique fossils discovered in this region, such as the beautifully preserved Aspidorhynchus, reveal intricate details of ancient marine life. Beyond Germany, regions like the Codorus Formation in the United States and various locations in England have produced significant Jurassic fish finds. Each discovery contributes a piece to the larger puzzle of understanding the ecosystem, evolutionary lineage, and adaptation strategies of these ancient animals. Researchers meticulously document each find, often leading to collaborative studies that expand knowledge. As new technologies and methods emerge, paleontology continues to evolve, providing clearer images of Jurassic fish and their habitats.
Notable Discoveries of Jurassic Fish Fossils
Several significant discoveries of Jurassic fish fossils have enriched our understanding of ancient marine environments. One important find is the fossilized remains of a small predatory fish called Noturus, which provides a view into the predation patterns of the time. Its delicate structure helps experts analyze feeding mechanics and practices among Jurassic fish. Additionally, fossils from the genus Osmerus reveal adaptations in body shape and fin structure that are relevant for understanding locomotion and survival strategies. Another intriguing group was the ray-finned fish, which saw diversification that set the foundation for modern fish. Their fossils indicate unique skeletal structures, suggesting evolutionary strategies for thriving in competitive marine environments. Each fossil discovery triggers further investigative efforts, prompting scientists to ask new questions about interactions within aquatic ecosystems. Not only do these findings illuminate the evolutionary history, but they also inform us about past climate conditions. Continuing excavations promise to uncover more secrets of Jurassic fish as researchers delve deeper into unexplored territories.
The study of Jurassic fish fossils also raises questions about the ecological roles these creatures played during this era. Many fish species interact complexly with their environments and other organisms, influencing and shaping ancient marine ecosystems. Predatory species like Liassicthys provide insights into food webs, illustrating the hunting strategies prevalent in these ancient waters. Furthermore, the presence of herbivorous fish indicates diverse feeding behaviors that may have had significant impacts on plant life in marine habitats. Analyzing isotopic compositions of these fossils can illuminate dietary preferences and adaptations to available resources in their surroundings. Such information not only enhances our understanding of specific species but also illustrates broader ecological trends during the Jurassic Period. The relationships between fish and their ecosystems provide a framework for comprehending how ancient environments functioned. This approach allows scientists to glean information on resilience and adaptability in a time of changing climatic conditions and sea levels, shedding light on the long-term impacts on biodiversity.
The Future of Jurassic Fish Fossil Research
As new techniques and technologies emerge, the study of Jurassic fish fossils continues to advance. Emerging methods such as *computed tomography* (CT) scanning enable researchers to visualize internal structures without damaging the fossils. This innovation significantly enhances the ability to study the morphological features of these ancient animals in detail. Additionally, the application of molecular techniques may offer prospects for extracting ancient DNA from well-preserved fossils, opening doors to understanding genetic relationships among species. As research progresses, collaborations across institutions and geographies will likely enhance knowledge sharing and resource pooling, leading to more comprehensive studies. Furthermore, interdisciplinary approaches, combining paleontology with climate science, oceanography, and genetics, will enrich our understanding of the interplay between fish evolution and environmental changes. Continued efforts in paleontological fieldwork will undoubtedly lead to exciting new discoveries, deepening our comprehension of the myriad fish species that swam the oceans during the Jurassic Period. Given the essential role of these fossils in addressing current biodiversity concerns, ongoing research into Jurassic fish remains not just a historical pursuit but a pathway to understanding evolution and adaptation.
The journey of understanding Jurassic fish, from their significant evolutionary adaptations to their roles within the ecosystems of ancient oceans, reflects a critical area in paleontological research. The unearthing of well-preserved fossils sheds light on the complexities of marine life during the Jurassic Period, providing insights into biodiversity and environmental dynamics. Each fossil offers unique knowledge contributing to a broader narrative of life’s evolution on Earth, and the intersections of geological history and biological development play a pivotal role in many respects. As research ventures forward, the collaborative nature of paleontology, along with advancing technologies, will surely unveil even more about these intriguing creatures of the past. By piecing together paleoecological data, scientists will continue unraveling the relationships between Jurassic fish and their environments. This ongoing exploration not only satisfies human curiosity about prehistoric life but also serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that has evolved through eons. Thus, Jurassic fish fossils continue to forge connections between past and present, resonating with current discussions regarding biodiversity’s future.