Tracking Ungulate Movement Patterns in Relation to Water Sources
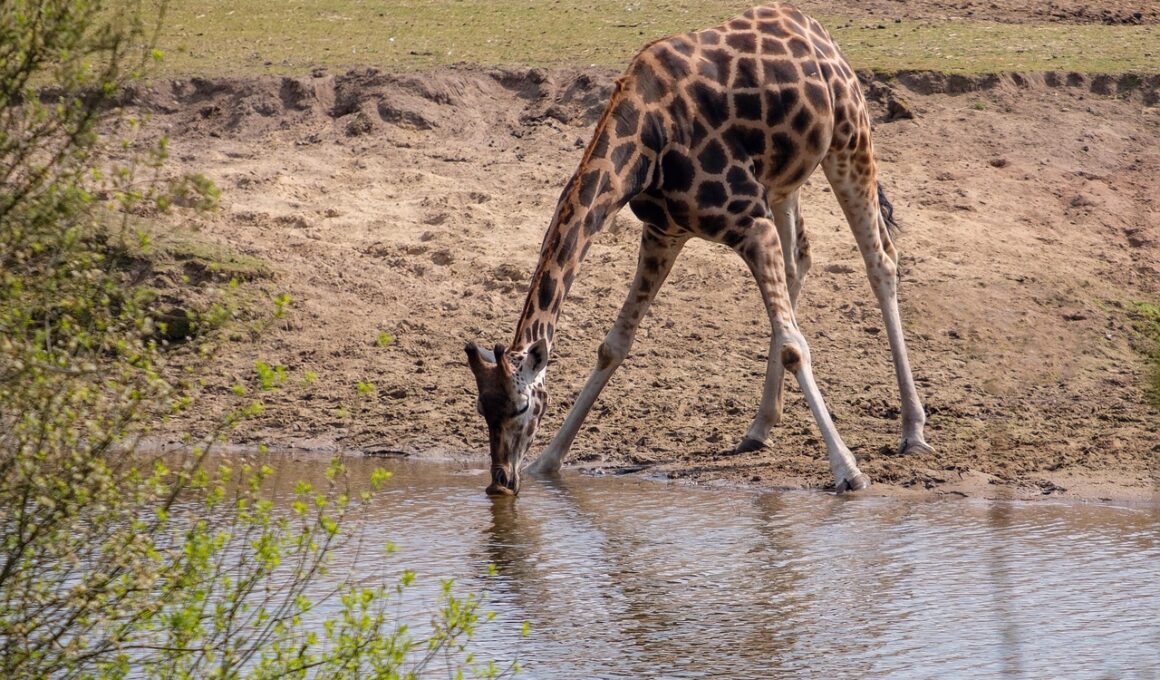
Ungulates, a diverse group of hoofed mammals, play a critical role in various ecosystems. Their movement patterns are closely tied to the availability of water sources, which are essential for their survival. Understanding how these animals navigate their environments in relation to water is crucial for conservation and management efforts. Observing the behavior of ungulates around water bodies offers insights into their migration routes and habitat preferences. Traditionally, these patterns were tracked using ground methods, but recent technological advancements have opened new avenues for research. GPS collars and satellite tracking have revolutionized the way scientists monitor ungulate movements. These technologies provide detailed data on the animals’ location, speed, and habitat use over time. With this information, researchers can analyze the relationship between water dependencies and various factors such as climate changes, seasonal variations, and human impacts. Additionally, this tracking can inform policy decisions regarding land use and water resource management. Protecting water sources is vital for ungulate populations and the entire ecosystem they inhabit.
Understanding Water Dependency in Ungulates
Water is a fundamental resource for ungulates, influencing their health, reproduction, and overall behavior. Each species has its unique strategies for locating and using water sources, which can greatly impact its survival. For example, some ungulates may migrate long distances to reach seasonal water sources. This behavior not only helps with hydration but also has significant implications for their social structures and interactions with other species. Ungulate populations often cluster around water, which can lead to increased competition and alter predator-prey dynamics. In arid regions, these water-dependent behaviors become even more pronounced as animals adapt to their harsh environments. Research indicates that when water availability decreases due to climate change or human activities, ungulates may change their movement patterns significantly. Some species could face grave risks if water sources are not managed sustainably. Monitoring these patterns enables conservationists to identify critical habitats and ensure adequate water supplies. By prioritizing water access in conservation plans, we can promote healthier ungulate populations and sustain biodiversity in their ecosystems.
One fascinating aspect of ungulate behavior is their acute sensitivity to changes in water availability. During droughts, ungulates frequently adjust their movements to find reliable sources of water. This behavior can be seen in various species, such as elephants and antelope, which actively seek out the closest waterholes. Tracking these movements not only provides clues about their adaptability but also highlights the importance of preserving water sources in their habitats. Scientists often employ a blend of observational studies and technological tools, like aerial surveys, to gather data on these behaviors. The findings suggest that ungulates adapt their routes based on the accessibility of water, which may also impact their foraging strategies. By understanding these shifting patterns, wildlife managers can better anticipate potential conflicts between ungulates and agriculture. Moreover, the knowledge gained helps in restoring degraded habitats by maintaining or rehabilitating water sources. Implementing effective management strategies is essential for ensuring the long-term survival of ungulate populations, particularly in regions experiencing ecological pressures.
The Role of Human Activity
Human activity poses significant challenges to ungulate water dependency patterns. Urbanization, agriculture, and industrialization can disrupt water habitats, leaving ungulates vulnerable. These changes often lead to reduced access to natural water sources, directly affecting the survival of populations reliant on them. Additionally, the construction of dams and water diversion projects may modify natural water flow and availability, further complicating ungulate movement. When water sources dry up or become contaminated, ungulates may face drastic shifts in their behavior. For instance, some species may migrate towards urban areas in search of water, leading to increased human-wildlife interactions. This poses risks for both parties, including accidents and the potential for conflict over resources. To mitigate these impacts, conservation strategies should incorporate sustainable land management practices that focus on maintaining natural water systems. Researchers advocate for initiatives that prioritize the restoration of natural water bodies and wetlands as crucial habitats for ungulates. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts can also have a profound effect on preserving these vital water sources for wildlife and ensuring biodiversity.
As we study ungulate movements, it becomes clear that there is a deeper interaction between species and their environment. Not only do ungulates depend on water, but they also influence the ecosystems around these sources. The presence of ungulates can impact vegetation dynamics, soil health, and water quality. For example, grazing patterns can help maintain grasslands, while their droppings can fertilize the soil, promoting a healthy ecosystem. However, overgrazing can lead to soil erosion and degradation, affecting water retention capacities in the long term. These complex interrelationships necessitate a multifaceted approach to ungulate conservation, focusing on both animal behavior and ecosystem health. Ecologists often utilize spatial modeling to understand these interactions better and predict future trends in ungulate populations based on environmental variables. Conservation efforts must foster understanding of habitat requirements and ecosystem functions. In doing so, we can create comprehensive management strategies that ensure both water sustainability and the health of ungulate populations. The ultimate goal is to develop ecosystems that thrive in balance, benefiting both ungulates and human needs alike.
Future Research Directions
Looking to the future, research on ungulate water dependency will need to evolve in response to changing environmental conditions. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns and water availability, tracking ungulate movements will become increasingly crucial. Future studies should consider the long-term effects of climate variability on ungulate behavior. By adopting innovative technologies, such as remote sensing and advanced data analytics, researchers can gather expansive data sets to analyze spatial patterns in movement and habitat selection. This approach will allow for more precise conservation initiatives that consider the unique needs of different ungulate species. Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations between ecologists, hydrologists, and climate scientists will enhance our understanding of the intersections between water availability and wildlife behavior. Such partnerships can lead to integrative management strategies that prioritize both ecological integrity and human activity. Public engagement in these research endeavors is also vital, as it fosters greater awareness of water conservation issues. Involvement of local communities will boost support for conservation measures that protect water sources and ultimately contribute to sustaining ungulate populations. The convergence of science and community action is key to successful conservation.
In conclusion, the examination of ungulate movement patterns concerning water sources is a rich field of study with far-reaching implications for conservation. Throughout this investigation, it is evident that water plays a pivotal role in the life cycles of ungulates, informing their migratory behavior and habitat selections. The integration of modern technologies has enhanced our ability to track species and understand their intricate needs. However, it is clear that human impacts significantly threaten the natural water habitats essential for these animals. Therefore, the collaboration of scientists, policy makers, and local communities is imperative to devise effective strategies for mitigating these threats. Sustainable management practices that consider both ecological balances and the needs of local populations will create better conditions for ungulates. Education and community involvement are equally significant in fostering a conservation mindset among the public. By prioritizing the protection and restoration of water sources, we can secure the future of ungulate populations, which in turn supports healthy ecosystems. The interdependent relationship between ungulates and their water environments ultimately underscores the importance of fostering a sustainable coexistence for wildlife and human communities.