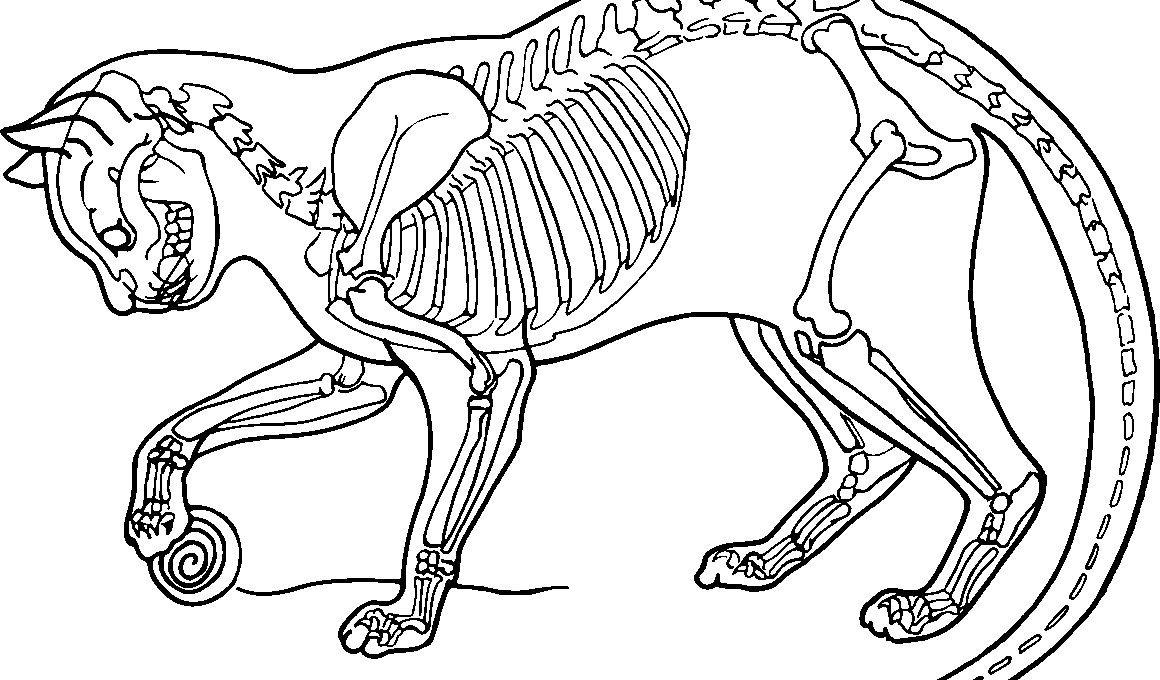
How Skeletal Structure Influences Animal Behavior
The skeletal system plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of animals. Different species exhibit a wide variety of skeletal structures, influenced by their environmental adaptations and evolutionary history. For instance, herbivorous animals possess flatter teeth and wider jaws, allowing them to graze efficiently. Conversely, carnivores have sharper teeth for slicing meat, demonstrating how skeletal adaptations are tied to dietary needs. The arrangement of bones also influences locomotion; for example, the elongated limbs of horses enable speed over long distances, while the compact body of a bear allows for strength and stability. Additionally, air sacs in bird skeletons reduce weight, facilitating flight. The presence of specialized bones or adaptations can also affect reproductive behaviors. Many species exhibit specific courtship rituals influenced by their skeletal structure. These adaptations are not merely for survival; they also impact social interactions and mating practices. Through various examples, we can observe this connection between skeletal anatomy and behavioral traits. In essence, the relationship between skeletal structure and behavior is a fascinating area of study, providing insight into evolutionary biology and the complexities of animal life.
Animals with diverse skeletal structures demonstrate distinct behavioral traits, which can be seen across various species. For instance, primates possess flexible limb structures that enhance their ability to swing through trees, significantly impacting their foraging and social behaviors. Such adaptations allow for a unique interaction with their environment, promoting behaviors such as grooming and complex social engagements within groups. Additionally, the skeletal structure of animals like dolphins and whales suggests evolutionary adaptations that enhance behavior in aquatic environments. These animals have streamlined bodies that improve swimming efficiency, thereby influencing how they hunt and communicate within their pods. Furthermore, certain skeletal features, such as the presence of tusks in elephants, play a crucial role in social behavior and hierarchy within herds. The way they utilize these structures for feeding and defense often dictates their interactions with other species. Conversely, certain terrestrial animals have developed robust skeletal systems that aid in territorial displays or combat, illustrating the diversity in behavioral expressions related to skeletal variations. Studying these relationships offers insights into the evolutionary pressures shaping behaviors based on anatomical differences within animal species.
Skeletal Variations and Behavioral Implications
Different skeletal variations can lead to unique behavioral implications among animal species, emphasizing the significance of anatomy in the evolutionary process. For example, the presence of specialized bones and structures directly correlates with various survival strategies. Take, for instance, animals like kangaroos, which exhibit elongated hind limbs adapted for powerful leaps. This adaptation not only affects their method of locomotion but also influences how they evade predators while foraging for food during their daily activities. Similarly, reptiles like chameleons possess unique skeletal structures that enable them to change color, crucial for communication and mating. Their skeletal triangulation allows for exceptional flexibility, enhancing behavioral responses in social situations. In contrast, animals with more rigid skeletal systems may engage in different forms of communication, relying on sound or scent. The interplay between these anatomical features and behavioral traits is vital for species survival. Observing these distinctions helps scientists and researchers understand how anatomy influences behavior in natural habitats. Moreover, unraveling these connections contributes to our broader knowledge of evolution and ecological interactions among diverse animal groups.
The behavioral adaptations influenced by skeletal structures extend beyond basic survival mechanisms. Social interactions among different species often hinge on these anatomical differences. For instance, the large antlers of male deer play a significant role in mating displays, shaping their behavior during the breeding season. These Structural characteristics dictate interactions, helping establish dominance and attract females. On the other hand, smaller males may rely on agility and stealth due to their lack of pronounced antlers. Moreover, pack animals like wolves utilize their robust skeletal structures in strategy and collaboration during hunts. Their physical prowess allows for coordinated behaviors driven by their skeletal adaptations. In comparison, seabirds have developed skeletal modifications for landing and take-off efficiency, influencing their flying behaviors. Some species show specific flight patterns that are heavily reliant on bone structure, allowing them to exploit feeding resources effectively. These relationships showcase the complexity behind how anatomical features shape animal behavior in social contexts. Studying these behavioral adaptations provides a deeper insight into animal ecology and the evolutionary significance of skeletal diversity.
The Role of Environment in Skeletal-Behavior Link
The relationship between skeletal structures and behavior is also profoundly influenced by environmental factors. Different habitats demand varying adaptations, impacting how animals evolve their skeletal systems over generations. For instance, species inhabiting dense forests have developed elongated limbs capable of navigating through thick undergrowth, influencing their foraging and social behaviors. Similarly, animals adapted to life in open savannas have developed longer strides to cover greater distances in search of food and water, shaping migratory behaviors. Marine animals face unique challenges that shape their skeletal adaptations and behaviors; adaptations related to buoyancy and hydrodynamics result in distinct swimming patterns and hunting strategies. Ice-dwelling animals, like polar bears, require sturdy skeletal structures to traverse snow, influencing their hunting behavior. On the opposite spectrum, desert animals exhibit compact bones that conserve energy and support their foraging habits. Environmental factors like these illustrate how skeletal features reflect adaptive responses, intertwining anatomy and behavior in diverse ecosystems. Understanding these dynamics enhances our comprehension of animal survival and ecological relationships in the face of environmental changes.
A fascinating aspect of this relationship is the idea of evolutionary pressure shaping behaviors through skeletal adaptations. Animals exhibit significant variations based on their adaptative needs, which evolve in response to changes in their environment. Take, for example, the evolution of birds; their lightweight skeletal structures are crucial for flight, influencing behaviors related to migration and nesting. In contrast, many ground-dwelling species have developed robust bones to support their weight and facilitate behaviors like digging or climbing. Their skeletal adaptations influence their ecological roles within their environments. Furthermore, the complexities of predatory versus prey behaviors illustrate how anatomical features drive survival strategies. For instance, prey animals may possess swift, agile body structures to evade predators. In contrast, predatory animals may have strong, muscular skeletal systems to pursue and capture prey. These dynamic relationships continuously evolve as environmental pressures change, creating an intricate web of adaptations that drive both skeletal structure and behavior. Exploring these evolutionary pathways reveals the remarkable resilience and adaptability of animal life.
Conclusions on Skeletal Influence on Behavior
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between skeletal structure and animal behavior presents a captivating study of evolutionary biology. A diverse range of structures informs behaviors, from basic survival strategies to complex social interactions. Animals adapt to their environments through specialized skeletal features, influencing how they forage, interact, and reproduce. For instance, amphibians, with their flexible skeletons, display a range of behaviors that enable them to thrive in diverse habitats. Likewise, terrestrial mammals, with robust structures, demonstrate aggressive and social behaviors crucial for their survival. This interplay underscores the adaptability of animals, showcasing how survival ultimately hinges on a delicate balance between anatomical features and behavioral adaptations. The study of these connections offers valuable insights into evolutionary history and species adaptation in various ecosystems. With ongoing research, we can further understand how skeletal structures continue to shape behavior, providing a broader perspective on animal evolution and diversity. Ultimately, this exploration enhances our appreciation of the complexity of life on Earth and the profound connections between anatomy and behavior in the animal kingdom.
As research progresses in the field of animal biology, the connections between skeletal structures and behavioral patterns promise to unveil even more surprises. The future holds the potential to further explore biometric technologies that could enhance our understanding of these relationships. Advanced imaging techniques may allow for clearer insights into how skeletal adaptations evolve over time in various species. With this knowledge, we can not only grasp the implications for individual species but also assess the wider ecological impacts. For instance, recognizing trends in skeletal adaptations could help in conservation efforts targeting specific habitats that are undergoing rapid changes due to climate factors. Understanding how these adaptations influence behaviors can also inform wildlife management strategies. This ongoing exploration drives home the importance of interdisciplinary studies in appreciating the connections between form and function. By integrating ethology, anatomy, and ecology, we can create a more comprehensive understanding of animal life. Such insights pave the way for effective conservation strategies and education programs to ensure the survival of intricate species. In essence, the study of skeletal structure and behavior is vital for fostering a deeper awareness of biodiversity and the preservation of our planet’s delicate ecosystems.