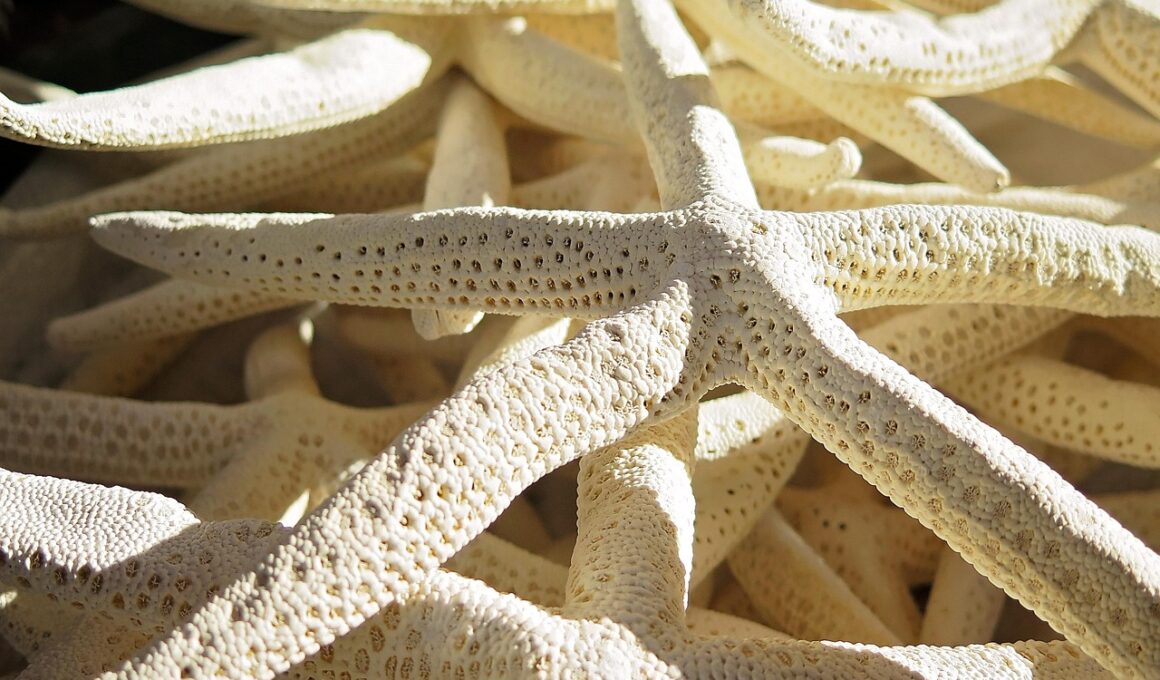
How Asteriidae Sea Stars Detect Their Environment
Asteriidae, commonly known as sea stars or starfish, exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to navigate and respond to their environment effectively. These echinoderms have a unique sensory system that involves various structures, enabling them to sense their surroundings in several ways. One of the most fascinating aspects of their anatomy is the presence of photoreceptor cells located on their arms, which allow them to detect light and dark effectively. This ability helps them understand their environment concerning light conditions, essential for survival and predation. Additionally, Asteriidae sea stars possess sensory cells, called tube feet, which can detect chemical signals in the water. This capability aids in locating food sources, identifying potential mates, and avoiding predators. Breathing and occupying different habitats also enhance their searching techniques, as these adaptations allow them to thrive in diverse marine environments. The uses of tactile sensory cells on their surface are crucial in recognizing textures and surfaces, which play a vital role in their interactions, feeding, and habitat choices. Therefore, the sensory adaptations of Asteriidae sea stars are vital for their survival in underwater ecosystems.
The sensory capabilities of Asteriidae sea stars extend beyond simple detection mechanisms. Each arm of a sea star is equipped with a series of sensory receptors that provide them with feedback from their environment. These receptors play a crucial role in their ability to perceive changes in water currents, temperature, and salinity. This information is vital for both migration and feeding strategies. Furthermore, their capacity to detect changes in water chemistry aids them in finding prey and avoiding dangerous locations. Sea stars can differentiate between various chemical structures in the water, which enhances their ability to find suitable habitats and food lead. Besides sensory receptors, their nervous system is decentralized, allowing them to process information from each arm independently. As a result, Asteriidae can react quickly to environmental changes without coordinating information from a central brain, which enhances their movement and responsiveness. The ability to gather and interpret information in this manner enables them to be highly adaptable to fluctuations in their habitats. Adaptation strategies are crucial for these remarkable invertebrates, allowing them to persist and thrive in the ocean.
Feeding Strategies of Asteriidae Sea Stars
The feeding strategies employed by Asteriidae sea stars are diverse, reflecting their specialized adaptations. These sea stars primarily feed on bivalves and other marine organisms, using their unique feeding mechanisms to access food. When prey is detected, Asteriidae sea stars will extend their tube feet and apply pressure to open the shells of their bivalve targets. This ability to manipulate their prey is a direct result of their keen sensory perception, allowing them to find prey relying on their chemical detection skills. Once the prey is accessible, sea stars can evert their stomachs through their mouths and into the shells of bivalves. This remarkable process allows Asteriidae to begin digestion before the food is fully consumed, making feeding an efficient process. Moreover, their capacity to detect the location of food through sensory input ensures they can locate patches of prey efficiently. Alongside their tube feet, their ability to quickly adapt to varying food sources guarantees their survival in fluctuating marine environments with competition for resources. Overall, these unique feeding strategies highlight the specialization of Asteriidae sea stars.
Another aspect of sensory detection in Asteriidae sea stars involves their ability to utilize tactile feedback. The surfaces of their bodies and tube feet are embedded with sensors that provide important information about texture and consistency. This information is crucial when navigating through rocky substrates and coral reefs, as these environments are often rich in crevices and hiding places. By relying on tactile cues, sea stars can more effectively locate hiding prey and navigate complex habitats. These sensory adaptations also facilitate communication with other sea stars, especially during mating seasons. The interactions among sea stars may include subtle tactile signals detected by their sensory modalities. Moreover, this ability to detect textures aids in habitat selection, ensuring that Asteriidae predominately reside in environments suitable for feeding or reproduction. The interplay between sensory feedback from their environment and behavior plays an essential role in their survival strategy. As such, the evolutionary developments in their sensory systems have greatly influenced their ecological niches and overall distribution within marine ecosystems.
Environmental Adaptability of Asteriidae
Asteriidae sea stars are known for their remarkable adaptability to various marine environments. Their ability to occupy different habitats results from their effective sensory detection mechanisms, which allow them to thrive in diverse ecosystems. From deep-sea floors to shallow tidal pools, Asteriidae can adjust to fluctuations in temperature, salinity, and light availability. This adaptability is crucial for their survival as it enables them to exploit available resources to ensure growth and reproduction. The ability to tolerate varying environmental conditions reflects their resilience as a species. Additionally, their sensory structures help them avoid extreme environmental hazards, such as potential predators or toxic conditions, ensuring their continued survival. Furthermore, the detection of environmental changes enables Asteriidae sea stars to migrate between habitats based on seasonal variations, enhancing their feeding strategies. Their overall adaptability enables them to respond dynamically to their surroundings in constant motion, showcasing their versatility as marine organisms. Incorporating strategies such as enhanced sensory perception ensures that Asteriidae can maintain stability in diverse ecosystems, allowing them to flourish where other marine species may struggle.
In research studies examining the behavior of Asteriidae sea stars, scientists have noticed intriguing patterns tied to their sensory perceptions. Enhanced sensory abilities facilitate greater efficiency in movement and environmental navigation, leading to observed strategies in grouping and dispersal. These behaviors can often be linked to changes in food availability, presence of competitors, or environmental shifts. As highly mobile organisms, Asteriidae may adjust their population density across different habitats, maximizing resource utilization while minimizing competition. It is essential to monitor their sensory adaptations closely as environmental pressures increase due to climate change. As changes occur in ocean temperatures, salinity, and chemistry, the resilience of sea stars can instance be tested. Their ability to respond to these changes depends on their sensory capabilities, playing a crucial role in their overall ecological health. Continued research into the interactions between Asteriidae and their environment is vital, as understanding these relationships can provide insight into the larger impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems. Therefore, the ongoing study of their sensory adaptations is vital to recognizing how these organisms can endure environmental challenges.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Sensory Detection
The sensory detection abilities of Asteriidae sea stars underscore their significance in the health of marine ecosystems. Their unique adaptations provide them with crucial capabilities, allowing them to navigate varied environments, locate food, and communicate effectively. As we continue to understand these adaptations in depth, it is essential to acknowledge the various roles sea stars play in maintaining balanced ecosystems. By controlling the populations of prey species and facilitating nutrient cycling through their feeding strategies, Asteriidae have a profound impact on marine biodiversity. Furthermore, the sensory adaptations that allow Asteriidae to endure and thrive provide vital information on their ecological roles as indicators of environmental health. Ultimately, the ongoing research into the sensory mechanisms of sea stars will contribute to our understanding of marine systems and the intricate relationships among organisms. Recognizing the importance of Asteriidae sea stars in the grand scheme of marine ecology will empower conservation efforts aimed at protecting these versatile organisms and their habitats. By prioritizing their well-being and understanding their role, we can ensure the preservation of the ecosystems they inhabit.
In maintaining the health of marine ecosystems, understanding the sensory adaptations of Asteriidae sea stars becomes increasingly important. These adaptations ensure their survival and highlight the interconnectedness of marine life, emphasizing the need for proactive measures in conservation. Additionally, preserving their habitats ensures not only the survival of Asteriidae but also the myriad of organisms they interact with. Their role as both predator and prey establishes them as key components within trophic levels, influencing the balance of marine environments. Conservation efforts focused on protecting Asteriidae populations can contribute to the stability of ecosystems, safeguarding the delicate relationships existing within marine biodiversity. The ongoing study of their sensory systems will shed light on how these organisms cope with changing environmental conditions, further illustrating their potential resilience. Education and awareness around Asteriidae and their sensory abilities can inspire efforts aimed at protecting their natural habitats. There is a critical need for focused research on marine ecosystems to develop strategies that ensure the long-term conservation of these extraordinary creatures. This collective effort is essential for maintaining the remarkable dynamics of marine life and preserving the natural beauty of our oceans.