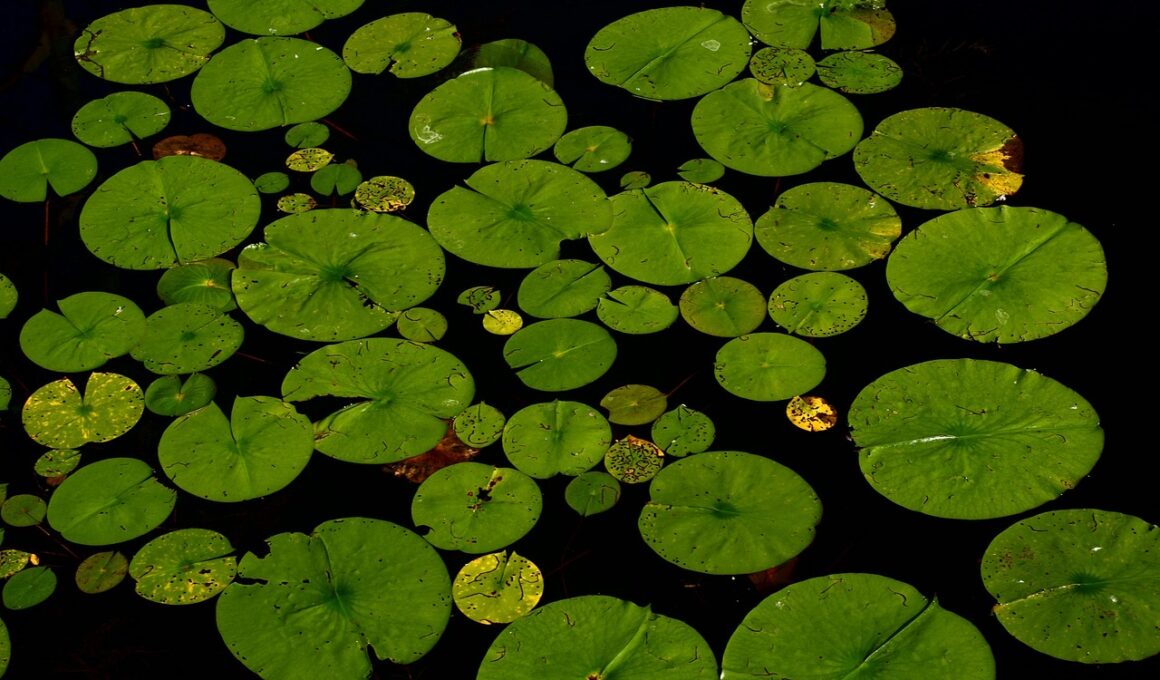
How Climate Change Affects Freshwater Plant Ecosystems
Climate change significantly impacts freshwater plant ecosystems, fundamentally altering the conditions in which these plants thrive. Rising temperatures can lead to a change in water temperature, affecting photosynthetic rates and overall plant health. Increased temperatures may cause metabolic rates to rise, prompting faster growth but also leading to greater susceptibility to diseases and pests. As ice melts and rainfall patterns shift, freshwater resources experience alterations that disrupt the delicate balance in which freshwater plants operate. Consequently, more invasive species may take hold, crowding out native species and reducing biodiversity. Alongside temperature changes, the frequency of extreme weather events can degrade freshwater environments. Floods and droughts, for instance, can lead to changes in sedimentation patterns and nutrient runoff, impacting the establishment of aquatic plant communities. Coupled with these stressors, increased carbon dioxide levels can promote some plant species’ growth but can create structural imbalances within ecosystems, affecting overall health. Scientifically, understanding these dynamics is crucial, as the loss of diversity has broader implications for ecosystem services. Prophetically, future strategies focusing on sustainability must address these multi-faceted challenges to protect freshwater plant life.
One of the significant consequences of climate change on freshwater plants is the alteration of nutrient cycles. Typically, nutrient cycles maintain a balance, ensuring flora receives sufficient sustenance. However, increased rainfall and melting glaciers can lead to higher nutrient runoff into freshwater systems. This alteration causes an influx of nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus, resulting in eutrophication. Eutrophication accelerates algae proliferation, which blocks sunlight needed by submerged plants. Then, oxygen depletion occurs due to algae decay, leading to hypoxic conditions detrimental for aquatic life. Some freshwater plant species can withstand these conditions, but many struggle to survive amid the changing environment. The result is a marked decrease in plant diversity, impacting the entire ecosystem. The relationship between various organisms becomes increasingly fickle due to the cascading effects caused by a loss of biodiversity. Furthermore, increased eutrophication can generate harmful algal blooms that pose risks to human health and local wildlife. Therefore, policymakers must understand these nutrient dynamics to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. The preservation of freshwater plant ecosystems consequently relies upon integrating ecological principles into environmental management to ensure sustainable practices.
The Role of Water Quality
Water quality is intricately linked with the health of freshwater plant ecosystems. Changes in climate can exacerbate water quality issues, impacting the survival and growth of native plant species. As temperatures climb, the concentration of pollutants and contaminants can rise, affecting plant health and reproduction. Moreover, fluctuating water levels, resulting from droughts or intense rainfall, can influence nutrient concentrations and sediment distribution. Sediment often carries pollutants and nutrients, which can either harm or benefit the plants. Ensuring the vitality of freshwater plants becomes complex as climate-induced changes alter the water’s chemical composition. Water temperature can significantly affect dissolved oxygen levels, which are crucial for the respiration of aquatic plant life. Low oxygen levels lead to stress in plants, stunting growth and making them more susceptible to disease. Additionally, poor water quality can cause shifts in species composition, favoring tolerant species while driving sensitive ones toward extinction. Protecting water quality thus becomes essential, requiring concerted efforts from communities, scientists, and policymakers to address pollution sources. Resultantly, maintaining high water quality is vital for safeguarding freshwater plant ecosystems amidst climate change.
Freshwater plants play a critical role in supporting biodiversity within their ecosystems, serving as habitat for numerous aquatic species. Climate change threatens this harmony as shifting environmental conditions lead to habitat loss and fragmentation. Species that rely on specific plants for food or shelter face increasing difficulty adapting to rapid changes. Altered hydrology, driven by climate patterns, affects the available habitat for aquatic plants and their associated fauna. As some plant species decline, the loss can unsettle the entire aquatic food web. Additionally, drought can severely limit plant growth, diminishing both habitat and genetic diversity. Research indicates that loss of native plant species can disproportionately affect smaller organisms, resulting in decreased fish populations and altered predator-prey relationships. The health of freshwater ecosystems hinges on maintaining diverse flora, as plants provide food, cover, and breeding grounds for various species. Furthermore, the ability of freshwater plants to adapt to climate change impacts varies among species. Understanding these trends and their connections to overall ecosystem functioning remains an essential area of investigation for ecologists. Thus, conserving plant diversity is pivotal in preserving the intricate balance within freshwater habitats.
Invasive Species Challenges
The threat of invasive species intensifies amid ongoing climate change, further complicating the survival of native freshwater plants. As temperatures rise and ecosystems change, invasive plants thrive, capitalizing on the distress of native species. These invaders often outperform local plants for resources, leading to shifts in community dynamics. Furthermore, invasive species tend to have different growth habits, making them more resilient to climate-induced stressors. This resilience can manifest in their rapid reproduction and adaptability to variable environmental conditions. As native plants struggle to cope with these newly introduced competitors, they often become endangered or extinct. The repercussions of such losses cascade through the ecosystem, leading to diminished habitat and resources for fish, insects, and birds reliant on traditional plant life. Managing invasives becomes increasingly urgent, prompting collaborative efforts from organizations and stakeholders. Education and public awareness campaigns are vital in preventing the spread of invasive species. Additionally, restoration projects focusing on re-establishing native plants can help rebuild habitats and combat invasives. Ultimately, addressing the challenges posed by invasives ensures the resilience of freshwater ecosystems amidst the pressures of a changing climate.
Adapting to climate change requires innovative approaches that prioritize the resilience of freshwater plant ecosystems. Recent studies indicate that fostering genetic diversity within populations may enhance species adaptability to shifting climate conditions. Diverse genetic pools allow for varying responses to environmental stressors, increasing the likelihood that certain individuals will possess the traits necessary for survival. Conservation efforts must focus on preserving a wide range of genetic variations among freshwater plants to safeguard their future. Moreover, restoring native plant communities can enhance ecosystem functionality and increase the capacity for natural resilience. Rehabilitation programs that consider ecological interactions and local climate projections are essential for long-term success. Engaging local communities in conservation initiatives promotes awareness and encourages sustainable practices. Additionally, integrating traditional knowledge with scientific research can lead to more comprehensive solutions. Future strategies must encompass habitat protection, invasive species management, and habitat restoration to mitigate the impacts of climate change. By prioritizing these adaptive measures, stakeholders can collaborate to conserve freshwater plant ecosystems for generations to come. Empowering communities and ensuring the resilience of freshwater ecosystems remains crucial in an ever-changing environment.
The Importance of Ecosystem Services
Freshwater plants provide vital ecosystem services that contribute substantially to human well-being and ecological balance. They play a critical role in maintaining water quality, as these plants filter pollutants and absorb excess nutrients, which is essential for healthy aquatic habitats. Moreover, freshwater plants contribute to carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change by capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Healthy aquatic plant populations are essential for controlling erosion, stabilizing shorelines, and maintaining the integrity of water channels. Various species of aquatic vegetation also provide habitat for fish and other wildlife, promoting biodiversity. As climate change threatens these plant communities, the loss of ecosystem services becomes increasingly evident. Declines in plant populations can lead to diminished water purification, reduced fish stocks, and increased flood risks. Furthermore, sustainable management practices are needed to ensure that these crucial services remain intact. Policymakers must recognize the interconnectedness of ecosystems and human societies, prioritizing conservation efforts to sustain the benefits provided by freshwater plants. Ultimately, acknowledging and protecting the roles of these plants fosters resilience in freshwater ecosystems amidst ongoing climate challenges.
In conclusion, addressing the effects of climate change on freshwater plant ecosystems is fundamental for securing healthy aquatic environments. Understanding the intricate relationships between climate factors, plant communities, and biodiversity is vital for mitigating adverse consequences. Collaborative efforts among policymakers, scientists, and local communities are necessary to create effective management strategies that safeguard these ecosystems. Protection measures should recognize the significance of maintaining water quality and promoting the resilience of native species. Furthermore, adaptive management approaches that consider potential climate impacts will be crucial in developing resilient freshwater systems. Engaging the public through education and advocacy can raise awareness about the importance of conserving freshwater ecosystems. Addressing challenges posed by invasive species, habitat loss, and changing water dynamics will be essential for preserving aquatic plant diversity. Restoration of degraded habitats must involve scientific research and community participation to ensure successful outcomes. By prioritizing the health of freshwater plants, ecosystems can continue providing vital services to both wildlife and humans. Future endeavors should emphasize sustainability, as this will equip ecosystems with the resilience needed to navigate the uncertainties and challenges posed by climate change. Protecting freshwater plant ecosystems must become a shared responsibility for a sustainable future.