Mangrove Forests and Their Role in Wild Animal Conservation
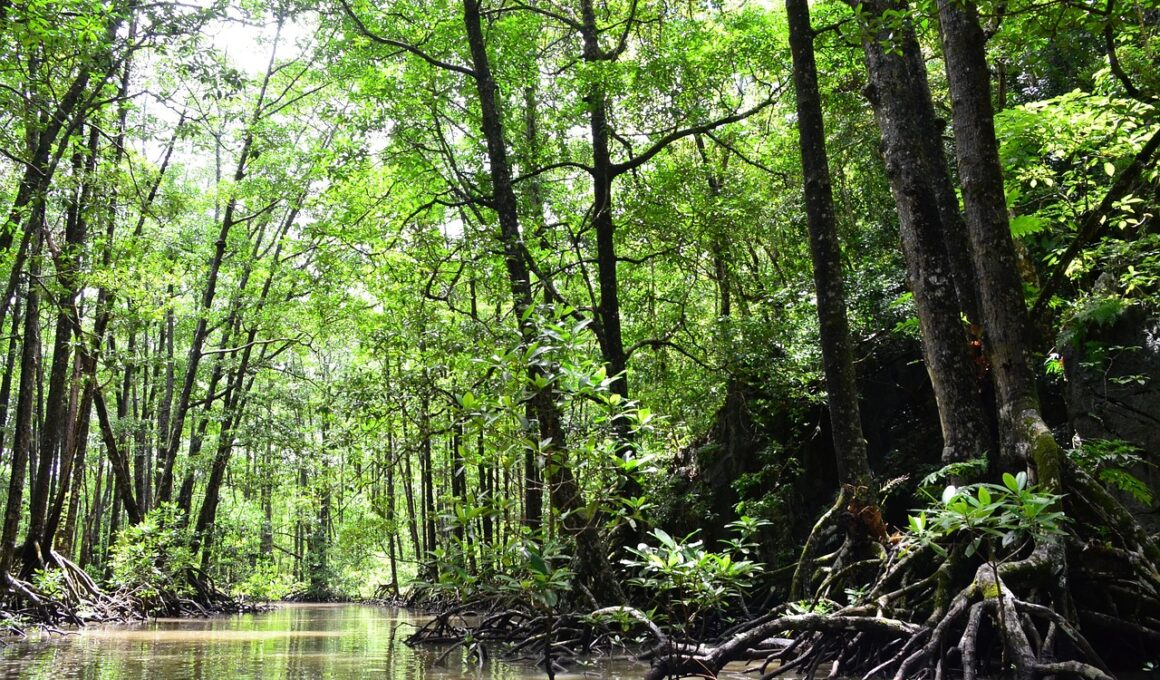
Mangrove forests are vital ecosystems found in tropical and subtropical areas, comprising salt-tolerant trees along coastal regions. These forests play a crucial role in conserving wild animals by providing an intricate habitat, which supports diverse species. The rooted trees create a complex environment for various marine life, including fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. Mangroves serve as spawning and nursery grounds for many fish species vital for the aquatic food chain. Additionally, these forests protect coastal areas from erosion and storm surges, acting as a buffer against environmental changes. As a home for numerous species, mangroves also support avian populations, including migratory birds which rely on these areas for sustenance and nesting. In many parts of the world, local communities depend on mangroves for resources such as fish and timber, promoting sustainable practices in animal habitats. Conservation efforts focused on protecting mangrove ecosystems are essential for maintaining biodiversity. Preserving these critical areas ensures that wildlife has the resources they need to thrive and adapt in a rapidly changing climate.
Mangrove forests are essential for numerous wild animal species, serving as critical habitats for many endangered animals. The diverse intertidal zones found in mangroves provide food resources and shelter from predators. Various reptiles, including saltwater crocodiles and sea turtles, utilize these forests during different life stages, highlighting their importance to survival. Wildlife conservationists recognize that protecting mangroves is incompatible with achieving broader conservation goals. By restoring and preserving these vital habitats, many species can recover from population declines caused by habitat loss and climate change. Specific conservation programs are implemented worldwide, often combining scientific research, local community engagement, and sustainable practices. Conservationists work to raise awareness of the ecological functions played by mangroves among communities reliant on these ecosystems. By enhancing local understanding and promoting stakeholder participation, these initiatives foster a culture of stewardship and responsibility toward mangrove conservation. Additionally, successful projects may include reforestation efforts to restore degraded areas, further assisting wildlife. Collaborative approaches to conservation help ensure that wildlife and local communities benefit from healthy mangrove ecosystems.
Mangrove forests are often referred to as the “lungs” of coastal ecosystems due to their significant role in carbon sequestration. They capture and store carbon dioxide, making them vital in combating climate change. By absorbing carbon, mangroves contribute to mitigating global warming, while providing habitats for various species that are crucial to the overall health of ecosystems. Protecting and restoring mangroves not only helps wild animals but also aids in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, these forests enhance water quality by filtering pollutants and improving ecological balance. The dense root systems of mangroves stabilize sediment, prevent coastal erosion, and protect shorelines from waves, benefiting various wildlife species. Various conservation organizations work tirelessly to ensure these ecosystems thrive despite challenges such as climate change and pollution. They conduct research to better understand the complexities of mangrove systems and the intricate relationships between animal species within them. Additionally, advocating for policies that protect coastal habitats is critical for future wildlife conservation efforts. Awareness campaigns and educational programs engage communities to appreciate and understand the vital functions of mangrove forests.
The Importance of Local Communities in Conservation
Engaging local communities in mangrove conservation initiatives is essential for effective wildlife protection. Communities living near mangroves rely on these ecosystems for their livelihoods, often engaging in fishing and tourism. By recognizing their dependence on healthy mangrove habitats, these community members become vital partners in conservation efforts. Local involvement contributes to sustainable practices that ensure the survival of not only marine life but also their economic benefits. Various organizations provide training and resources to help local communities engage in sustainable fishing practices that minimize habitat degradation. Furthermore, fostering a sense of ownership among locals encourages responsibility toward preserving mangrove ecosystems. Initiatives that promote ecotourism can provide alternative income sources for residents while raising awareness of the importance of conservation. Involving communities leads to the development of customized plans that meet both environmental and societal needs. Building cooperative relationships between environmental organizations and local stakeholders fosters trust and empowers communities to take action for mangrove conservation. By blending traditional knowledge with modern conservation strategies, successful outcomes are achieved, solidifying the partnership between people and nature.
Mangroves also serve as vital breeding grounds for numerous bird species, making them essential in the wildlife conservation ecosystem. The rich biodiversity within these habitats attracts various birds that depend on the subtropical environment for food and nesting materials. Many migratory birds use mangrove forests as stopover points when traveling long distances, proving their significance across geographic regions. The unique structure of mangroves provides shelter from harsh weather conditions and predators, promoting bird conservation. Certain bird species, including herons, egrets, and kingfishers, thrive in mangrove ecosystems, linking terrestrial and marine environments. By conserving mangroves, conservation efforts can simultaneously protect these avian populations, creating a unique intersection between land and water wildlife. Birdwatching and ecotourism opportunities based on mangrove forests foster community appreciation for the ecological role these habitats play. Preservation efforts led by conservation organizations focus on protecting both the forests and the species that utilize them. Further research into bird populations contributes valuable data to enhance conservation strategies targeting both mangroves and their inhabitants. Collaborative initiatives innovatively connect habitat protection and species conservation.
The complexities of mangrove ecosystems present a unique challenge for conservationists. Climate change, pollution, and unsustainable development threaten these delicate habitats, making it essential for global cooperation. The degradation of mangrove forests leads to significant loss of biodiversity, impacting wild animal populations dependent on these ecosystems. Programs focusing on the restoration of mangroves emphasize identifying local challenges and tailoring interventions accordingly. Collaborative research efforts help uncover the interactions within these ecosystems, informing effective conservation strategies. By sharing knowledge and experiences, stakeholders can develop integrated management approaches that include the participation of government, non-governmental organizations, and local communities. Furthermore, international cooperation is crucial in combating issues such as illegal logging and coastal development. Awareness campaigns to educate the public on the ecological importance of mangroves foster a culture of responsibility and stewardship. The momentum builds through collaboration and a shared vision for a bright future for mangrove forests, making notable advancements in conservation efforts. By prioritizing diverse approaches to address challenges and implementing specific restoration programs, wildlife populations benefiting from mangrove habitats can be sustained and thrive.
The Future of Mangrove Forests and Wildlife
Ensuring the future of mangrove forests and wildlife relies on broad partnerships and innovative approaches. Sustainable management practices are pivotal in balancing ecological health while allowing for responsible resource use. New technologies, such as remote sensing and data analysis, provide insights that enhance the understanding of mangrove ecosystems. Furthermore, investments in restoration projects can rejuvenate degraded mangrove areas, expanding animal habitats. Engaging youth through educational programs promotes awareness and encourages the next generation to take an interest in conservation efforts. Significant funding and resources are necessary for long-term conservation goals to be realized. Initiatives targeting mangroves will benefit from comprehensive policies that address climate change, pollution, and habitat loss. As communities work alongside marine scientists, effective monitoring systems can be established to track the health of mangrove ecosystems. Regular assessments help adapt management strategies to mitigate emerging threats. Lastly, collaboration with broader conservation organizations enables knowledge-sharing and enhances the effectiveness of local interventions. The dynamic interplay of these factors ensures a holistic approach toward preserving mangrove forests and the rich wildlife they support.
Mangrove forests epitomize the interconnectedness of ecosystems, providing significant benefits for wildlife conservation. As vital habitats and breeding grounds for a variety of species, they exemplify the need for focused conservation efforts. By prioritizing restoration, community involvement, and sustainable practices, future generations will continue to rely on the diverse wildlife that these ecosystems support. Protecting mangrove forests requires ongoing collaboration, innovative initiatives, and a strong commitment to conservation principles. A collective approach among stakeholders allows for more effective solutions to the challenges these unique environments face. Awareness campaigns, education, and research efforts must continue to spotlight the importance of mangroves in ensuring a sustainable future for wild animals and coastal health. Recognizing and advocating for the multifaceted roles that mangroves play highlights their irreplaceable value in global conservation efforts. As we navigate complex environmental issues, ensuring the protection of mangrove forests will be instrumental in preserving not only wildlife but also the health of our planet. In summary, mangrove ecosystems are crucial for supporting wild animals and require persistent commitment, effective strategies, and widespread engagement for their ongoing conservation.