The Fascinating Life of Glaucous Gulls in the Arctic
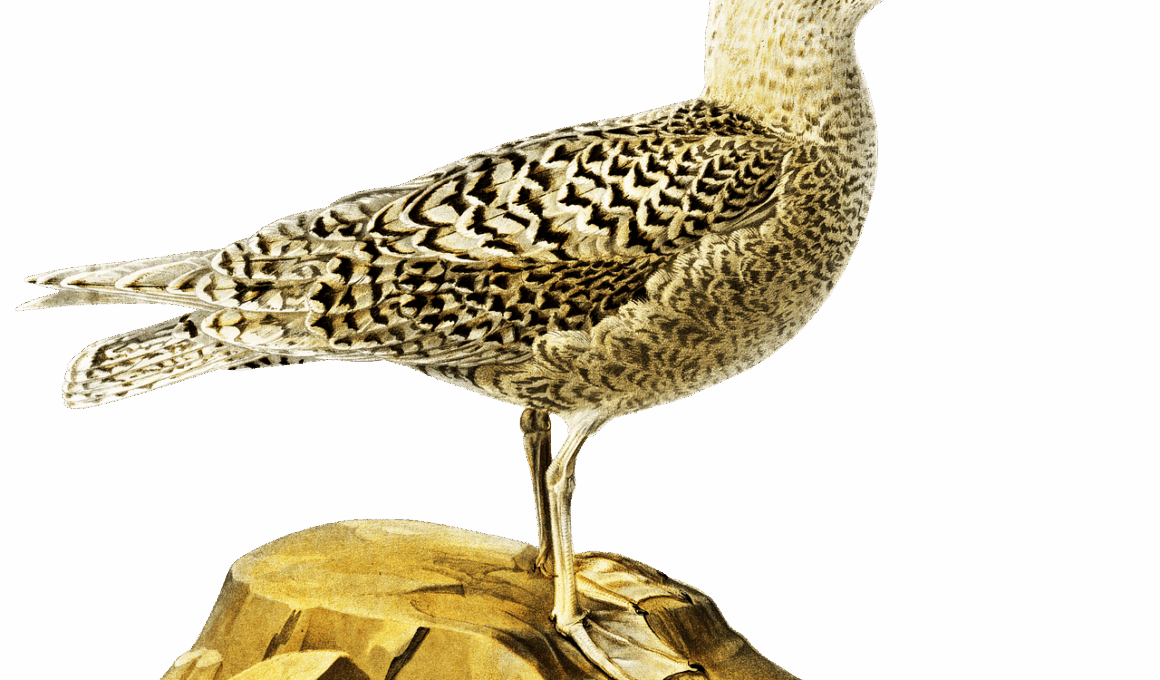
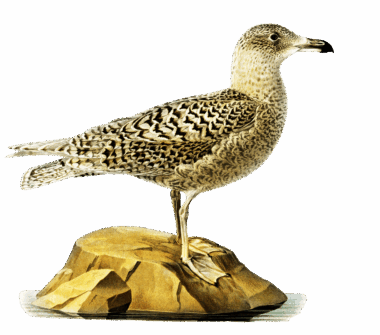
Glaucous gulls are remarkable birds inhabiting the Arctic regions. These large seabirds are known for their striking appearance and adaptive behaviors. Primarily found in areas along the northeastern and northwestern coasts of North America and Eurasia, they thrive in harsh conditions. An adult glaucous gull has distinctive pale plumage, which helps it camouflage against the icy landscapes. Their wingspan can reach up to six feet, making them one of the largest gull species. Glaucous gulls are opportunistic feeders, primarily consuming fish, carrion, and small birds, exhibiting fascinating scavenging behaviors. During the breeding season, they nest on rocky cliffs or tundra areas, where they lay clutches of typically two to three eggs. The parents are attentive, sharing duties to protect and feed their young. Glaucous gulls are also known to participate in aggressive behavior towards other birds, especially during feeding, ensuring they dominate the available food resources. Their adaptability and resilience make them captivating subjects for ornithologists and wildlife enthusiasts alike, as they are a stunning example of evolutionary success in extreme environments.
Glaucous gulls showcase remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in the challenging Arctic environment. Their thick body and powerful wings enable them to navigate the high winds and cold temperatures. The gulls have a unique diet pattern that changes with the seasons, allowing them to exploit available resources effectively. In summer, they primarily feed on fish and other marine life, while in winter, they rely more on scavenging, targeting carrion left by predators. This diet shift displays their versatility and crucial role in the ecosystem as scavengers. Their keen eyesight helps them spot food from significant distances, and their large webbed feet make it easier for them to land and take off from both ice and water. Glaucous gulls can also be quite social during the non-breeding season, often forming large flocks. They communicate with various vocalizations, including harsh cries or squawks when competing for food or protecting their territory. Additionally, their migratory patterns remain linked to the availability of food sources, demonstrating their ability to adapt to the Arctic’s dynamic conditions throughout the year.
The breeding behavior of glaucous gulls is a captivating process, marked by elaborate courtship displays and strong pair bonds. Males perform aerial displays to attract females, showcasing their strength and agility. Once paired, these gulls typically return to the same nesting sites year after year, reinforcing their monogamous relationships. Nesting occurs in colonies, which offers protection from potential predators. The nests are often built from stones, grass, and moss, and they blend well into the surrounding landscape. Females lay their eggs, usually two to three, and both parents share responsibility for incubation. The incubation lasts about 28 days, after which the chicks hatch and are cared for by both parents. The young gulls rely on their parents for food during the initial weeks after hatching. They quickly grow and develop feathers, preparing them for their first flights. Parental care is crucial, as it ensures high survival rates for the chicks. Social interactions among the fledglings also play a vital role, as they learn essential survival skills from their parents and gradually evolve into independent birds ready to face the Arctic’s challenges.
Interacting with the Ecosystem
Glaucous gulls play an essential role in their Arctic ecosystem. As scavengers, they contribute to the ecological balance by helping to dispose of carrion and waste. Their feeding habits prevent the spread of diseases, as they consume decaying remains and control the populations of other animal species. This scavenging behavior not only aids their survival but also sustains other species by providing them with food leftover from their foraging activities. Glaucous gulls often share feeding grounds with other seabirds, creating opportunities for collaborative interactions, which can lead to more successful foraging outcomes. Moreover, these gulls also serve as prey for larger predators, such as polar bears and Arctic foxes, illustrating another level of their ecological importance. Additionally, the presence of glaucous gulls may indicate the health of their habitat. A declining population could signal environmental issues, such as habitat loss or declines in food resources, making them indicators of ecological changes. Therefore, studying these birds contributes to a greater understanding of the Arctic ecosystem and the challenges it faces in a rapidly changing world.
The challenges faced by glaucous gulls in the Arctic have increased due to climate change and human activities. As the polar ice melts, their nesting habitats and hunting grounds are becoming more precarious, affecting their ability to thrive. The changes in sea temperatures also impact fish populations, reducing the availability of food for these gulls. Furthermore, increased shipping traffic and industrial activities in the Arctic pose additional threats, introducing pollution and habitat disturbance. Oil spills and plastic waste not only harm their environment but can also contaminate their food sources. These challenges compel glaucous gulls to adapt rapidly to shifting conditions. Ongoing research is crucial for understanding the implications of these changes on glaucous gull populations and their habitats. Conservation efforts may need to focus on regulating human activities and implementing measures to promote habitat protection. The survival of glaucous gulls is closely interconnected with the health of the Arctic ecosystem, underscoring the importance of addressing environmental issues. By educating the public and promoting awareness, we can help ensure a future for these remarkable birds and their unique Arctic habitat.
In conclusion, glaucous gulls are birds of extraordinary adaptability and ecological significance. Their fascinating lives in the Arctic showcase their resilience against harsh conditions and their essential role in maintaining ecological balance. As we continue to observe these captivating birds, we gain valuable insights into the health of the Arctic ecosystem. The exceptional behaviors, feeding habits, and breeding patterns of glaucous gulls demonstrate their place within a complex web of life. However, with increasing threats from climate change and human activities, their future remains uncertain. Conserving their habitat and understanding the dynamics of their environment is essential for their survival. Increasing public awareness can lead to more support for conservation initiatives that protect these remarkable gulls and their vulnerable ecosystem. The survival of glaucous gulls not only reflects the state of the Arctic but can also serve as a powerful symbol of the broader environmental challenges we face. Future generations must prioritize the preservation of these stunning birds and their natural habitats to ensure the continued existence of glaucous gulls in the Arctic.
Embracing the Future of Conservation
Protecting species like the glaucous gull requires a collaborative approach involving scientists, conservationists, and local communities. Initiatives focusing on habitat restoration, pollution management, and public engagement stand as vital components in preserving the Arctic ecosystem. Educating communities about the significance of glaucous gulls and their contribution to environmental health can foster a sense of responsibility towards these birds and their habitats. Engaging local stakeholders in conservation efforts ensures that the initiatives are practical and culturally sensitive. Participating in local conservation programs allows people to connect with their environment and empowers them to advocate for responsible practices that benefit wildlife. Additionally, supporting research focused on the effects of climate change on these gulls could yield crucial information guiding conservation strategies. Innovations in technology can also enhance monitoring efforts, allowing for more detailed understanding of their behavior and movements. Future conservation methods should emphasize adaptability, integrating knowledge among various disciplines to enhance the resilience of glaucous gull populations. By fostering collaboration and incorporating scientific understanding, we can embrace sustainable strategies for protecting these magnificent birds and preserving their Arctic habitats for generations to come.
The inspiring story of glaucous gulls highlights the intricate interconnection between wildlife and the environment. The challenges faced by these birds, driven by climate change and human influence, urge us to reassess our role in protecting these precious ecosystems. As stewards of nature, we have the responsibility to take proactive measures to ensure the survival of unique species like the glaucous gull. Emphasizing holistic approaches that recognize the delicate balance of Arctic ecosystems will be crucial for long-term conservation efforts. Encouraging responsible behaviors and supporting sustainable practices will make a significant difference. The future of glaucous gulls and their habitats relies on our collective actions today. Fostering a deep appreciation for wildlife and understanding their needs will empower individuals to advocate for effective conservation initiatives. It is vital that we celebrate these beautiful birds and the role they play in our world’s ecological fabric. Protecting glaucous gulls ensures not only their survival but also the health of the Arctic ecosystem. By engaging with local communities and embracing innovative solutions, we can work together to create a more sustainable future for glaucous gulls and the fragile environments they inhabit.